Fall-2011-Unit2
advertisement

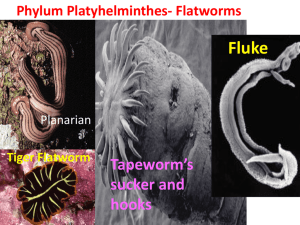
Sept. 26, 2011 Phylum Cnidaria Class Anthozoa o Sea Anemones o larvae are Pelagic- motile in marine habitat o they are zooplankton- animal plankton not phytoplankton Anemones adults are sessile, however they can move zoozanthellae are photosynthetic, endosymbiotic algae o found in all anthozoans Intertidal zone area that is under water for part of the day intertidal zone of Pacific has more species per sq. meter than most other habitats Splash Zone area directly above intertidal zone Benthic zone bottom of the ocean Symbiosis living together Parasitism one animal living in or on another animal at the expense of the host Commensalism free living, mutualistic relationship Charles Lyell Coral coral reef formation continental drift o there is a hotspot under Hawaii o fringing reefs form by growing on island's edges as the island subducts under the water surface the coral grows larger coral dies as it gets too far under water new coral builds on top of dead exoskeletons only about the top 1 meter is alive- sunlight reaches it Hawaii's Big Island is over a hot spot creating more island o tectonic plates are moving and old islands re subducted fringe reef results anthozoan that produces CaCO3 exoskeleton produces massive amounts of zooplankton, where they settle a new coral is formed Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms no coelom = Acoelomates Protonephridia- precursor to primitive kidneys o flame cells - maintain osmotic balance in flatworms o Marine flatworms are isosmotic with environment bilaterally symmetrical no circulatory system most don't have a complete digestive tract o no anus eye spots for detection of light o present in free living forms o parasitic forms lack them o pigment cells receive light and they can determine the direction it came from. Sept. 28, 2011 Platyhelminthes occur in marine, freshwater and terrestrial habitat some are parasitic o parasitic forms: in larval stages can detect light capable of regeneration o cellular differentiation Class Trematoda Digenetic = two separate parts to their life cycle Subclass Digenea o parasitic o 2 separate hosts for life cycle o a mollusc is the intermediate host for all intermediate host = used for increased amplification, a sexual reproduction, increased distribution through space Dicvocoelium dendriticum life cycle: definitive host is deer intermediate host is snail phoretic (carrier) host is ants Phototropic Positive = moves toward light Negative = moves away from the light Parasites use only 2 ATPs per 38 available o not a large amount of energy taken from host presence of parasites with complex life cycles are indicators of healthy ecosystems. Reference Parasites as Probes for Biodiversity written by Dr. Gardner E.O Wilson coined term "biodiversity" Flatworms hermaphroditic = both male and female reproductive systems are present o can self fertilize but usually cross o Protandrous = testes develop first in sequence of morphological growth o Protogynous = ovaries develop first in sequence of morphological growth Digenetic Trematode: Sept. 30, 2011 Trematodes Family Schistosomatidea means "split body" digenetic not hermaphroditic male and female never spilt from each other o female is attached to male important in humans o Schistosoma mansoni Schistosoma mansoni life cycle: Oct. 3, 2011 Flatworms Hymenolepis tualatinensis Gardner, 1981 tapeworm Family Hymenolepididae name means "membrane with filaments" "of the Tualatin River" Order Cyclophyllidea Hymenolepis spp. = many species of the genus Hymenolpeis o scolex is the head of a tapeworm o strobilization occurs at neck o has 3 testes in each segment o strobia = chain of segments Mature Segment: Gravid segment: beetle eats the gravid segment in feces cysticercoids emerge in beetle beetle gets eaten by rat develops into mature tapeworm in rat if a person eats the beetle with cysticercoids they will become infected o except H. dininuta Family Taeniidae Beef Tapeworm o Taenia saginata occurs in people (definitive host) Taenia solium Pork Tapeworm 25 other spp. spread by carnivory how did people get these tapeworms initially? Eric Hoberg: phylogeny of Taeniidae people shared lion or hyena kills contracted parasites from the uncooked meat host switch o parasite switched from hyenas and lions to humans Proximate Ecology how things are happening right now Historical Ecology looks at history of organisms and phylogenies