unsegmented worms - Mr. Lau's Biology 11 Page
advertisement

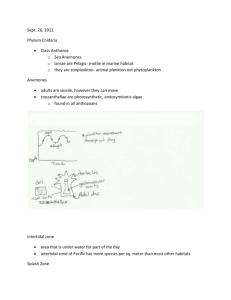
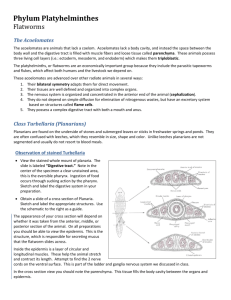
NAME: UNSEGMENTED WORMS DATE: PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES PHYLUM NEMATODA BLOCK: Why do we call Platyhelminthes and Nematoda UNSEGMENTED WORMS? PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES (FLATWORMS) - ‘Platy’ means _______________ and ‘helminthes’ refers to ___________________. - Flatworms are flattened ________________________ and are usually no more than a few millimeters thick. But flatworms can get extremely long – the record is set by a tapeworm found to be 39 meters long!!! - Flatworms have _________________ symmetry. - They also have an easily distinguishable __________________ and ________________ end. - Flatworms are found in ______________________ environments. - There are 3 Classes of flatworms: o Class _____________________ - planarians and marine flatworms o Class _____________________ - flukes PARASITIC o Class _____________________ - tapeworms Mr. Lau Page 1 of 7 Biology 11 FEEDING Please label this planarian: - Free-living planarians have a gastrovascular cavity with just _________ opening. At the end of this opening, there is a muscular tube called a ____________________ where the ____________ is. - The gastrovascular cavity branches off and forms ____________________. - Planarians are either _________________________ or scavengers. - Most flukes and tapeworms are parasitic so feeding is much simpler. These parasites may feed on _______________ or already digested food from the ____________________ of the host. These animals can attach themselves to a host with ________________ and/or ________________. These structures are found on the ______________ or head of a tapeworm. Draw the scolex of a Draw the scolex of a tapeworm: tapeworm: - Because of the parasitic lifestyle the digestive tract that is much ____________________. Mr. Lau Page 2 of 7 Biology 11 RESPIRATION, INTERNAL TRANSPORT, AND EXCRETION Why can flatworms rely on diffusion for respiration and waste removal? Planarians also have _____________________ that get rid of excess ____________________. There cells are precursors to the kidneys found in vertebrates. RESPONSE - We can easily identify the _____________ end of a planarian because of a process called _____________________ where a head is formed. This head contains a rather simple _______________. From this structure, a ladder-like network of _______________ run along the body - How is the environment detected by a flatworm (planarian)? - Parasitic cestodes and trematodes do not have much need for a nervous system since their lifestyle is very ___________________. SUPPORT SYSTEM AND MOVEMENT What 2 things do planarians use to move around? Mr. Lau Page 3 of 7 Biology 11 REPRODUCTION - Planarians are ________________________ and can produce both ___________________ and ____________________. Outline SEXUAL reproduction in planarians: Outline ASEXUAL reproduction in planarians: How do people become infested with parasitic flatworms? How do tapeworms reproduce? What structures are involved? Mr. Lau Page 4 of 7 Biology 11 PHYLUM NEMATODA (ROUNDWORMS) - Nematoda = thread-like - Roundworms are probably the most abundant of all multicellular animals – chances are, you make contact with a roundworm everyday! - There are both free-living and ______________________ species of roundworms living in all types of environments. - For the first time, we see the anatomical features of a tube within a tube body plan (a pseudocoelom). FEEDING What do roundworms eat? How is the digestive tract of a roundworm different from that of a flatworm? How are roundworms harmful to certain agricultural products? Mr. Lau Page 5 of 7 Biology 11 RESPIRATION, INTERNAL TRANSPORT, AND EXCRETION Once again, respiration (oxygen), waste excretion (ammonia and carbon dioxide), and internal transport (of nutrients) depend on diffusion to move through body walls or within the body. RESPONSE - Roundworms have several ____________________ which are groups or clusters of nerve cells. Nerves extending from these clusters run the length of the body and transmit sensory information and control of movement. SUPPORT SYSTEM AND MOVEMENT - The fluid-filled pseudocoelom acts as a ____________________________ skeleton. - Roundworms have strips of muscle down the length of their body. How does movement of a roundworm on land differ from movement of a roundworm in water? REPRODUCTION Roundworms generally have ______________________sexes and reproduce sexually. Thus, each sex has a different set of reproductive organs. Fertilization takes place ______________ the body of the female. Mr. Lau Page 6 of 7 Biology 11 Outline the stages of the life cycle of a common parasitic roundworm, the human ascarid (Ascaris lumbricoides): Stage What happens? Where does this happen? What parts of the human body are involved? 1 2 3 4 5 ROUNDWORMS AND US Identify and describe some diseases caused by roundworms. Mr. Lau Page 7 of 7 Biology 11