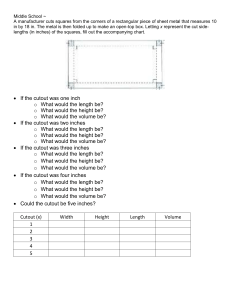
An Elevated View Topographic Maps Purpose: To be able to
advertisement

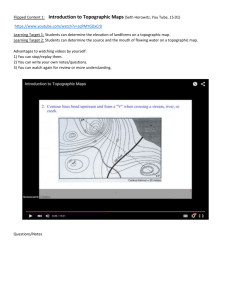
An Elevated View Topographic Maps Purpose: To be able to interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering. Engage 1. Take your fist with your nonwriting hand, hold it eye level, fingers and thumb away from the body. a. Pretend you are a tiny ant crawling across a fist. From the ant’s point of view, what landform does the ridge of your knuckles look like? b. How are your knuckles and a mountain range similar? 2. Take a piece of plastic wrap horizontally across your knuckles and hold onto the overhanging pieces with your fingers. 3. Take a sharpie marker and on all four knuckles mark a line around the base of each knuckle, a line around the middle of each knuckle and a line around the top of each knuckle. a. Is this a three-dimensional or a two-dimensional model? b. How many peaks does your mountain range model have? c. How does this type of map help determine height? d. If I asked you to make a similar map of the top of your desk, how would that map compare to the map you made during the activity? e. What are the limitations to this model? 4. Tape the plastic wrap to the paper. Explore – Topographic Map-on-a-Stick 1. Follow the Topographic Map-on-a-Stick – Part A instructions on your table. a. What type of landform does this model represent? Justify your answer. b. Observe your model from an aerial (above) view. How is this model similar to the model you made on the plastic wrap? c. How is this model different from the model you made using the plastic wrap? d. How many peaks are represented on this model? e. Observe your model from a side view, placing the Es to the right and the Ws to the left. What do the Es represent? What do the Ws represent? f. Use a metric ruler to measure the distance from E1 to E4 and the distance from W1 to W4. Which distance is greater and why? g. Pretend you are the tiny ant again and you are going to climb up the peak. Would it be easier to crawl up the east side or the west side and why? Part B 2. Follow the Topographic Map-on-a-Stick – Part B instructions on your table. Topographic Map a. What does each layer represent? b. Elevation is the height above or below sea level. Where would you go to see sea level? c. Is sea level always the same? d. Which layer of your map represents the highest elevation? e. Which layer represents the lowest elevation? 3. Compare all the models from your activities (knuckles, plastic wrap, skewer and map). a. Which models are three-dimensional? b. Which models are two-dimensional? 4. Each model has lines drawn called contour lines. Each line represents the layers in the model that have the same elevation above sea level. a. What do we call the place on your map where the water and the land meet? b. If you are the ant again and you are standing on the line that represents sea level, what would be your elevation? 5. Locate the steepest side of the landform on the skewer and the topographic map. a. How is the steepest side shown on the topographic map? 6. Locate the gradual slope on the west side of the landform. a. How is this represented on the topographic map of our model? b. How is the top of our model mountain represented on the topographic map? 7. Observe the indentation on the northeast side of your skewer. a. What do you think may have caused this area? b. How is the indentation, which may have been caused by a river, represented on the topographic map? c. How do we know that the river doesn’t flow in the direction the Vs are pointing? Drawings go here: Topographic Map-on-a-Stick – Part A 1. Cut out the four pieces of cardstock along the solid lines. (This may already be done) 2. Insert the toothpick through the black dot on Cutout 1 (place the cutout on the table and then skewer into the table, not into your hand). The piece should be face up on the toothpick. Slide Cutout 1 down o the middle of the toothpick. 3. Insert the toothpick through the black dot on Cutout 2. Slide the piece down the toothpick, face up, so that it is 2 cm above Cutout 1. 4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for Cutouts 3 and 4, placing each piece 2 cm above the previous layer. 5. Arrange the pieces on the toothpick so that the eats (E) sides are aligned on the right and the west (W) sides are aligned on the left. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Topographic Map-on-a-Stick – Part A 6. Cut out the four pieces of cardstock along the solid lines. (This may already be done) 7. Insert the toothpick through the black dot on Cutout 1 (place the cutout on the table and then skewer into the table, not into your hand). The piece should be face up on the toothpick. Slide Cutout 1 down o the middle of the toothpick. 8. Insert the toothpick through the black dot on Cutout 2. Slide the piece down the toothpick, face up, so that it is 2 cm above Cutout 1. 9. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for Cutouts 3 and 4, placing each piece 2 cm above the previous layer. 10. Arrange the pieces on the toothpick so that the eats (E) sides are aligned on the right and the west (W) sides are aligned on the left. Topographic Map-on-a-Stick – Part B 1. Remove all of the pieces from the toothpick. 2. Place Cutout 1 on the sheet labeled “From Model to Map,” making sure that E is at the east side of the paper and W is at the west side. 3. Trace around the outside of Cutout 1 and make a small dot through the toothpick hole. 4. Pick up Cutout 1 and place it back on the skewer stick. 5. Continue steps 2-4 for Cutouts 2, 3, and 4. Each time, align the east and west ends of you pieces as well as the location of the toothpick hole. 6. Color the area around the drawing blue to represent water. 7. Make a compass to represent North, East, South and west. 8. Place the 4 Cutouts back on the toothpick. 9. Make a key for your map using the following information: 1cm=500m Blue area- less than 0m a. Cutout 1- 500 to 750m b. Cutout 2- 750 to 1250m c. Cutout 3- 1250 to 2000m d. Cutout 4- 2000 to 3500m 10. Trace the model laying on its side and color to match aerial model. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Topographic Map-on-a-Stick – Part B 1. Remove all of the pieces from the toothpick. 2. Place Cutout 1 on the sheet labeled “From Model to Map,” making sure that E is at the east side of the paper and W is at the west side. 3. Trace around the outside of Cutout 1 and make a small dot through the toothpick hole. 4. Pick up Cutout 1 and place it back on the skewer stick. 5. Continue steps 2-4 for Cutouts 2, 3, and 4. Each time, align the east and west ends of you pieces as well as the location of the toothpick hole. 6. Color the area around the drawing blue to represent water. 7. Make a compass to represent North, East, South and west. 8. Place the 4 Cutouts back on the toothpick. 9. Make a key for your map using the following information: 1cm=500m Blue area- less than 0m a. Cutout 1- 500 to 750m b. Cutout 2- 750 to 1250m c. Cutout 3- 1250 to 2000m d. Cutout 4- 2000 to 3500m 10. Trace the model laying on its side and color to match aerial model.