Air Pressure and Wind Notes: Meteorology Basics
advertisement

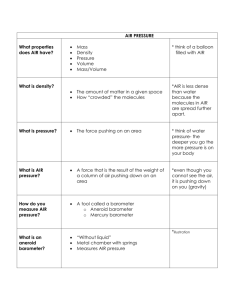
Air Pressure and Wind Notes Air Pressure is the weight of the gases in the atmosphere pushing on the surface of the Earth. - At sea level, standard air pressure is 14.7 lb/in2 or 1013.2 mb or 29.92 in Hg. How does air pressure change with altitude? The pressure of the atmosphere decreases as altitude increases. - The greatest change in air pressure occurs in the lower atmosphere (troposphere). Air pressure is measured with a Barometer. Aneroid Mercury Why Does Air Pressure Change? Air pressure can be analyzed on a weather map using Isobars- lines that connect points of equal air pressure. - Each line differs in pressure by 4 millibars. - Isobars on a map are used to determine the location of pressure system and act as a way to forecast weather. So far we know the air pressure decreases with altitude because there are less air molecules pushing down from above. - It also changes with temperature & humidity. Characteristics of High and Low Pressure Systems (Draw in arrows & pressures) High Pressure Low Pressure Cool temperatures Rising barometer Fair weather Air moves out from center - clockwise Warm temperatures Falling barometer Poor weather Air moves toward centercounterclockwise A Pressure Gradient is change in pressure between two places. This creates a force that makes wind move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. What causes Wind & Pressure Differences? Differences in the heating of land and water creates different pressure systems. - Land heats up and cools faster than water. - On a local level, this difference in heating creates Breezes. Sea Breeze Land Breeze