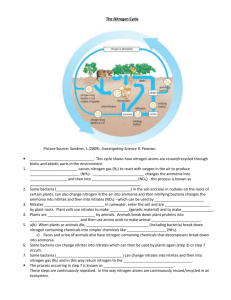
picture number definition vocabulary term type of nitrogen
advertisement

6 7 8 9 10 Definitions a.) excess water from rain and melting snow flows over the land releasing nitrogen containing compounds from rocks b.) process of converting nitrates and nitrites into nitrogen gas by certain types of bacteria in the soil c.) natural situation in which nitrogen gas makes up the majority (78%) of the Earth's atmosphere d.) fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter; organic compounds/biomolecules are converted to simpler molecules containing nitrogen (ammonia) e.) nitrogen oxides are produced along with carbon dioxide and water by chemical reactions as fossil fuels contaminated with nitrogen containing compounds are burned with oxygen to produce heat energy which is then used to make kinetic energy f.) process of assembling amino acids using information encoded in DNA to produce proteins g.) nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere combine with water to form acidic rain which decreases pH and dissolves limestone h.) heterotrophic organisms (usually carnivores) feed on other heterotrophic organisms to obtain energy and other nutrients i.) nitrogen is lost from the body as organisms remove nitrogen wastes and feces j.) process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia in the soil by certain types of bacteria 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 k.) heterotrophic organisms (usually herbivores) feed on autotrophic organisms to obtain energy and other nutrients l.) process of converting nitrogen gas into nitrates and nitrites in the air by lightning; the nitrates and nitrites then enter the soil m.) process of converting nitrogen gas into into nitrates and nitrites in nodules of roots of legumes by certain types of bacteria (mutualistic rhizobia) n.) process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia in factories using the Haber-Bosch process o.) an immediate increase in the amount of algae and other producers that results from a large input of a limiting nutrient (nitrogen containing compounds) p.) an increase in the amount of a limiting nutrient (nitrogen containing compounds) in the soil by humans q.) nitrates and nitrites dissolved in water is absorbed by plants and other autotrophs and are converted to more useful molecules/compounds r.) changes in ocean flow caused by wind or geographic features, where cold, nutrient-rich water rises to the surface, replacing warm, nutrient-depleted surface water s.) water-carried waste intended to be removed, includes nitrogenous wastes and feces t.) process of converting ammonia into nitrites then into nitrates by certain types of bacteria in the soil Vocabulary terms a.) acid rain formation b.) algal bloom c.) atmospheric nitrogen fixation d.) bacterial nitrogen fixation e.) combustion: transportation f.) decomposition g.) denitrification h.) excretion i.) fertilizer application j.) nitrification k.) l.) m.) n.) o.) p.) q.) r.) s.) t.) nitrogen in the atmosphere primary consumption protein synthesis secondary consumption sewage surface runoff, erosion symbiotic nitrogen fixation synthetic fertilizer manufacturing uptake by producers upwelling Types of nitrogen containing compounds involved a.) amino acids --> proteins b.) ammonia --> nitrates and nitrites c.) nitrates and nitrites --> amino acids d.) nitrates and nitrites --> nitrogen gas e.) nitrogen containing compounds f.) nitrogen containing compounds --> ammonia g.) nitrogen containing compounds --> nitrogen oxides h.) i.) j.) k.) l.) m.) n.) nitrogen gas nitrogen gas --> ammonia (use twice) nitrogen gas --> ammonia --> nitrates and nitrites nitrogen gas --> nitrates and nitrites nitrogen oxides --> nitric acid and nitrous acid nitrogenous wastes: ammonia + uric acid + urea (use 5x) proteins --> amino acids (use twice) j.) k.) l.) m.) n.) ocean floor --> ocean surface rivers + lakes + ocean soil soil --> atmosphere soil + rivers + lakes + ocean --> biomass Reservoirs involved a.) atmosphere b.) atmosphere --> biomass + soil c.) atmosphere --> land d.) atmosphere --> soil (use 3x) e.) biomass (use 3x) f.) biomass --> soil + rivers + lakes + ocean (use 3x) g.) land h.) land --> atmosphere i.) land --> soil reservoir type of nitrogen containing compound vocabulary term definition picture number reservoir type of nitrogen containing compound vocabulary term definition picture number reservoir type of nitrogen containing compound vocabulary term definition picture number reservoir type of nitrogen containing compound vocabulary term definition picture number 1 2 3 4 5