Study Guide
advertisement
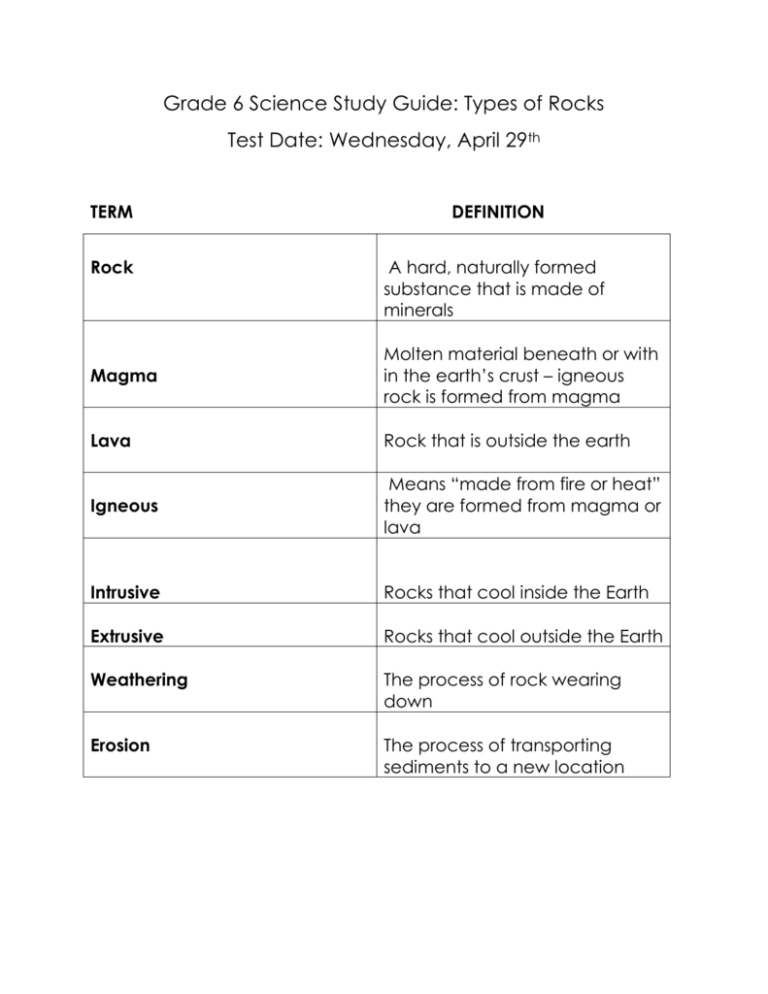
Grade 6 Science Study Guide: Types of Rocks Test Date: Wednesday, April 29th TERM DEFINITION Rock A hard, naturally formed substance that is made of minerals Magma Molten material beneath or with in the earth’s crust – igneous rock is formed from magma Lava Rock that is outside the earth Igneous Means “made from fire or heat” they are formed from magma or lava Intrusive Rocks that cool inside the Earth Extrusive Rocks that cool outside the Earth Weathering The process of rock wearing down Erosion The process of transporting sediments to a new location Metamorphic rock Is formed by heat and pressure. They are solid rocks that change when they are heated Sedimentary rock Are rocks that are formed from weathering, erosion, compaction, and cementation How are rocks formed? 3 types of rocks When minerals + fire or heat get together, rocks are formed 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Metamorphic Igneous rocks are formed.. When molten magma cools and solidifies with or with out crystallization Intrusive rocks examples Dunite, Granite Extrusive rocks examples Basalt, Obsidian By sediment that is deposited over time, usually as layers at the bottom of lakes and oceans. Sedimentary rocks form… Types of sedimentary rocks: Types of metamorphic rock 1. Well sorted 2. Poorly sorted 1. Foliated 2. Non- foliated Conglomerate rock is a sedimentary rock consisting of rounded fragments of a preexisting rocks How to identify IGNEOUS ROCKS - Large random crystals - Holes caused by air bubbles - Glassy appearance How to identify SEDIMENTARY ROCKS - Well sorted layers - Poorly sorted rock particles How to identify METAMORPHIC ROCKS - Wavy bands of crystals - Wavy texture







