More Info - Vivione Biosciences
advertisement

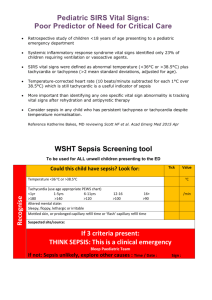
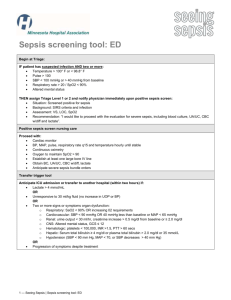
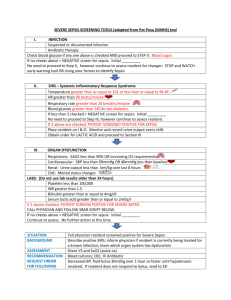
septiSTAT™ Overview septiSTAT™ is a rapid cell-based assay used to determine immune system hyperactivation associated with sepsis in critically ill patients. Sepsis represents a severe illness associated with bacterial infections of the blood. The disease has a very high mortality (30-50%) and is considered the most expensive hospital-associated pathology seen in modern medicine. There are approximately 750,000 cases of sepsis in the United States annually and the diagnostic component of the disease is estimated at $3-$5 Billion annually, and total expenditures, including therapeutics, is estimated at over $20 Billion. Current Methodologies for Diagnosing Sepsis Sepsis is currently defined as a state of body-wide inflammation with the addition of a positive blood culture. It is considered a difficult disease to diagnose, namely because systemic inflammation can be caused by non-infectious reasons, such as trauma, myocardial infarction, and cancer. Current diagnostic tests are acknowledged as having less than optimal sensitivity and specificity. These tests include serum lactate (a marker of organ dysfunction), C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation), and procalcitonin. Procalcitonin is a newly developed sepsis biomarker whose developer, Brahms Diagnostics, was sold to Thermo Fisher for $500 Million in 2008. Recent data has called into question the specificity of procalcitonin for diagnosing sepsis. septiSTAT The septiSTAT™ test is a cell-based assay being developed with help from the University of Rochester School of Medicine. septiSTAT™ represents the quantitative assessment of two biomarkers representing the two phases of sepsis. The first marker, VLA-3, has been determined by University of Rochester researchers to be over expressed on neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, in sepsis patients. This marker represents the hyper-stimulated immune system seen in the systemic inflammation phase of sepsis. The second marker, CTLA-4, is a marker related to the anti-inflammatory phase of sepsis called Compensatory Anti-inflammatory Response Syndrome (CARS). CARS often predicts a patient’s entry into Septic Shock and has a very high associated mortality rate. septiSTAT™ will be the first and only test on the market to inform clinicians regarding where there suspected sepsis patients are in the phases of sepsis, allowing better treatment decision and reduced mortality. The test will function in an automated fashion on the RAPID-B platform and when coupled with the bacSTAT™ test will offer a complete solution for monitoring critically ill patients for infections. Market Landscape The diagnosis of sepsis is a difficult clinical challenge. There is a lack of consensus regarding appropriate biomarker profiles for aiding the clinical diagnosis. The current offerings focus on serum-based markers such as C-reactive protein, lactate levels, and procalcitonin. Recent evidence supports the questionable sensitivity and specificity of these biomarkers. For this reason we are focusing on biomarkers directly involved with monitoring immune status because it is acknowledged that immune system hyper-stimulation is a component of all sepsis cases. Additionally it is coming to light that septic shock involves a compensatory anti-inflammatory immune response. The approach of assessing both phases of sepsis will be a first for the industry.