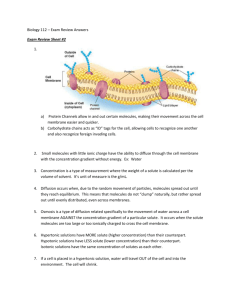
Name: Date: : ______ CELLS PRACTICE QUIZ 1. Which of the
advertisement

Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ______________Block: ______ CELLS PRACTICE QUIZ 1. Which of the following do NOT have a cell wall? A. plant cells B. bacterial cells C. Fungi D. animal cells 2. The plasma membrane is composed of… A. a single layer of proteins B. a phospholipid bi-layer C. a carbohydrate bi-layer D. a single layer of lipids 3. This organelle stores the DNA in a eukaryotic cell. A. Nucleus B. Ribosome C. Vacuole D. Cytoplasm 4. Which of the following is the energy supplier in eukaryotic cells; this organelle contains its own DNA A. Lysosome D. endoplasmic reticulum B. Mitochondria E. ribosome C. Golgi apparatus 5. This organelle is found in animal cells and is used in cell division; the spindle fibers attach to it. A. vacuole D. ribosome B. chloroplast E. centriole C. nucleus 6. Which of the following is an enzyme filled organelle for breaking down waste in the cell? A. Lysosome C. Mitochondria B. Chloroplast D. Golgi body 7. The major job of the ribosome is to A. make fats B. make proteins C. break down proteins D. make sugars 8. What is a semi-permeable membrane? A. A membrane that allows all molecules to pass through. B. A membrane that is different on each side. C. A membrane that allows some molecules to pass through but not others. D. A membrane that doesn't allow any molecules to pass through. 9. The STRUCTURE of the plasma membrane is best described as A. a single lipid layer C. a rigid, strong layer protecting the cell B. an impenetrable barrier. D. a lipid bi-layer. 10. The plasma membrane is referred to as a “fluid mosaic” because it is made up of A. phospholipids and cellulose C. phospholipids and proteins B. nucleic acids and proteins D. proteins and cellulose 11. Plasma membranes are “selectively permeable”. This statement means that A. No substances can enter or exit the cell through the plasma membrane. B. The plasma membrane allows some substances to enter or exit a cell more easily than others. C. All substances are able to enter or exit the cell through the plasma membrane. D. It is random chance whether a molecule can or cannot enter or exit the cell through the plasma membrane. 12. Which of the following will pass through a cell membrane most easily? A. small polar molecules D. large non-polar molecules B. small non-polar molecules E. large neutral molecules C. large polar molecules 13. Simple diffusion is defined as the movement of… A. molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. B. molecules from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration. C. water molecules across a membrane. D. gas molecules across a membrane. E. gas or water molecules across a membrane. 14. The rate of diffusion is affected by which of the following? A. Temperature B. Size of molecules C. Steepness of the concentration gradient D. A, B and C 15. When the process of diffusion reaches an equilibrium state: A. the movement of molecules stops completely B. molecules continue to move but in equal parts C. a hypertonic solution is formed D. none of the above 16. Which of the following statements regarding simple diffusion is TRUE? A. Simple diffusion uses ATP as an energy source. B. Simple diffusion can move a solute against its concentration gradient. C. Simple diffusion is driven by the potential energy represented by a concentration gradient. D. None of the above 17. Which of the following statements regarding active transport is TRUE? A. Active transport uses ATP as an energy source. B. Active transport can move a solute against its concentration gradient. C. Active transport requires the cell to expend energy. D. All of the above 18. Which of the following statements regarding diffusion is FALSE? A. Diffusion is a result of the thermal energy of atoms and molecules. B. Diffusion requires no input of energy into the system. C. Diffusion occurs when particles spread from areas where they are less concentrated to areas where they are more concentrated. D. Diffusion occurs even after equilibrium is reached and no net change is apparent. 19. The only DIFFERENCE between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion is A. facilitated diffusion requires energy B. facilitated diffusion uses protein channels to move substances in or out of the cell C. simple diffusion requires energy D. facilitated diffusion moves substances from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. 20. Facilitated diffusion occurs A. into the cell only. B. out of the cell only. C. in either direction depending on the temperature. D. in either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule. E. in either direction depending on the size of the molecule. 21. Exocytosis is a process by which cells A. release substances from the cell through pores in the cell membrane. B. release substances from the cell via vesicles. C. release substances from the cell via carrier proteins. D. bring in substances from the outside via vesicles. 22. Certain white blood cells engulf microorganisms and bring them in to digest them. This process is A. Pinocytosis. D. Phagocytosis. B. Osmosis. E. Diffusion. C. Receptor-mediated exocytosis. 23. Cells occasionally need to take in or “drink” large amounts of water, which term best describe the process by which cells “DRINK” or take in vesicles of water? A. Pinocytosis. C. Phagocytosis. B. Receptor-mediated endocytosis. D. Diffusion. 24. When a cell needs to get rid of waste products and push them OUT OF THE CELL, which term best describe the process by which cells release substances from the cell? A. Pinocytosis B. Endocytosis C. Phagocytosis D. Exocytosis 25. Which method of transport moves substances in or out of the cell that REQUIRES ENERGY? A. Diffusion C. Facilitated diffusion B. Osmosis D. Active transport 27. Facilitated diffusion is used to transport A. H2O and O2 B. O2 and CO2 C. CO2 and H2O D. Ions and H2O 28. Osmosis is best defined as the movement of A. solute molecules across a membrane from an area of high solute concentration to an area of lower solute concentration B. solute molecules across a membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration C. water molecules across a membrane from an area of low water concentration to an area of higher water concentration D. water molecules across a membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of lower water concentration 29. A solution in which the solute concentration outside a cell is LOWER cell than the solute concentration inside the cell is called a A. hypotonic solution C. isotonic solution B. hypertonic solution D. cytotonic solution 30. A solution in which the solute concentration outside the cell is HIGHER than the solute concentration inside the cell is called A. an isotonic solution C. a hypotonic solution B. a hypertonic solution D. a cytotonic solution 31. A cell in a hypertonic solution A. loses water and shrinks B. gains water and expands C. gains and loses the same amount of water, staying the same shape D. none of the above 32. A red blood cell placed in an isotonic medium will A. Expand. B. Burst. C. Shrink. D. Not change. 33. A cell in a hypotonic solution A. loses water and shrinks B. gains water and expands C. gains and loses the same amount of water, staying the same shape D. none of the above 34. After eating a salty snack like potato chips, the cells in your mouth become saturated with salt. What happens to the cells in your mouth as they react to the ELEVATED salt environment? A. water moves into the cells causing them to burst B. salt moves into the cells causing them to burst C. salt moves out of the cells causing them to shrink D. water moves out of the cells causing them to shrink. 35. When a plant cell is placed in a salt water solution, the cell is affected and changes size. What part of the cell will be UNAFFECTED? A. The cytoplasm C. The cell wall B. The cell membrane D. The vacuole 36. What is the total magnification of a microscope if you are using the 10x objective lens? A. 10x B. 20x C. 100x D. 200x OPEN ENDED: A frog egg is taken from a freshwater pond and placed into a saltwater pond. Draw the two scenarios. Be sure to include the salt concentrations in each (numbers can be made up where necessary). The frog cell membrane is not permeable to salt. Freshwater Pond Saltwater Pond a. Describe the movement of water. In Freshwater Pond (1 point): In Saltwater Pond (1 point): b. Describe the two types of solutions (tonicity) and what happens to an animal cell in each. In Freshwater Pond (2 points): In Saltwater Pond (2 points):