Vascular shunt mechanism
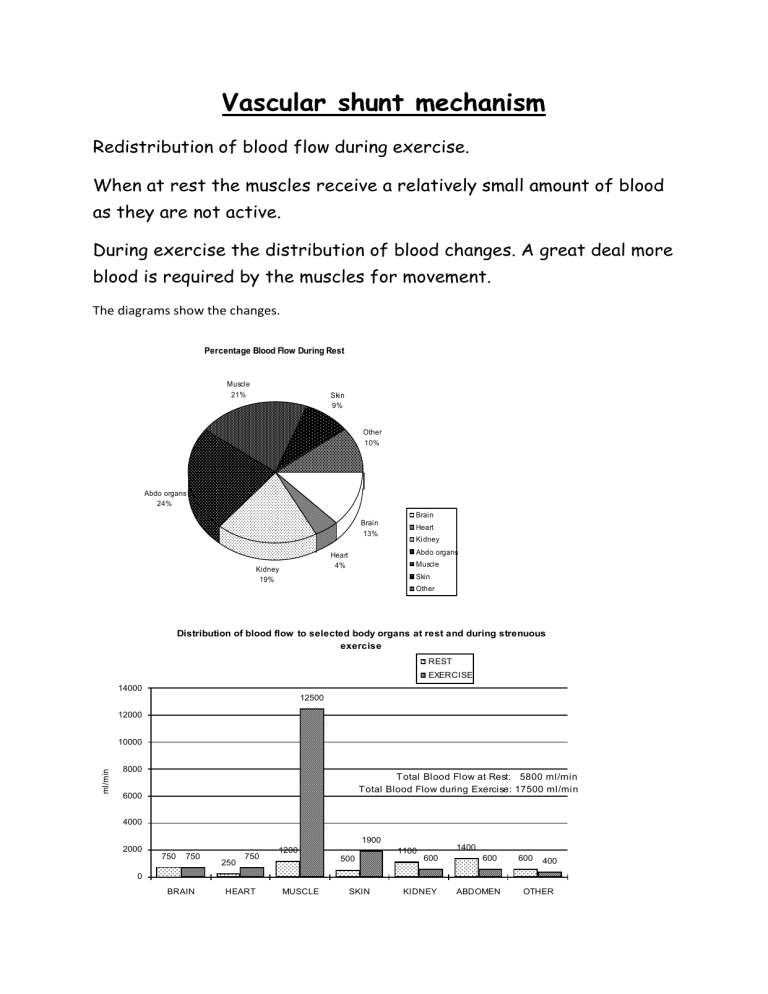
Vascular shunt mechanism
Redistribution of blood flow during exercise.
When at rest the muscles receive a relatively small amount of blood as they are not active.
During exercise the distribution of blood changes. A great deal more blood is required by the muscles for movement.
The diagrams show the changes.
Percentage Blood Flow During Rest
Muscle
21% Skin
9%
Other
10%
Abdo organs
24%
Kidney
19%
Heart
4%
Brain
13%
Brain
Heart
Kidney
Abdo organs
Muscle
Skin
Other
14000
Distribution of blood flow to selected body organs at rest and during strenuous exercise
REST
EXERCISE
12500
12000
10000
8000
Total Blood Flow at Rest: 5800 ml/min
Total Blood Flow during Exercise: 17500 ml/min
6000
4000
2000
750 750
0
BRAIN
250
750
1200
HEART MUSCLE
500
1900
1100
600
1400
600 600
400
SKIN KIDNEY ABDOMEN OTHER
This process of increasing the blood flow to the muscles during exercise is called the Vascular shunt mechanism.
There are three key words to learn:
Vasodilation
– arterioles widen, increasing diameter and blood flow.
Vasoconstriction
- arterioles narrow, decreasing diameter and blood flow.
Pre-capillary sphincter
– these are ring- like muscles situated between the arterioles and capillaries acting like doors that can open and close, increasing or decreasing blood flow
The process is outlined below:
Chemoreceptors
– pick up chemical changes –O2/CO2/pH in aorta/carotid artery/muscles
Baroreceptors
– pick up changes in systolic blood pressure in the aorta/carotid artery
These send this information to the brain, Specifically:
Medulla oblongata (Vascular Control Centre –VCC)
Arterioles have a middle layer of muscle which is connected to the
VCC (sympathetic nerve) this causes vasoconstriction by increasing nervous stimulation – decreasing blood flow. By decreasing the stimulation, the arteriole can vasodilate – increasing blood flow. This nervous control also dictates whether the pre-capillary sphincter opens or closes.
When at rest the arterioles to the organs vasodilate with the pre- capillery sphincter open.
Meanwhile the arterioles to the muscles vasoconstrict and the pre – capillary sphincters close.
The process reverses during exercise.
The arterioles to the organs vasoconstrict with the pre- capillary sphincters closing.
Meanwhile the arterioles to the muscles vasdilate with the pre- capillary sphincters opening.