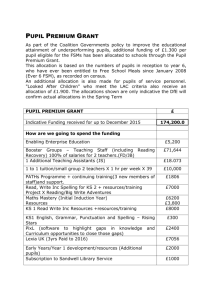
The Role of Class Teacher
advertisement

Glenflesk N.S., Glenflesk, Killarney, Co. Kerry. Tel: (064) 7754624 Fax: (064) 7754624 Email: Glenfleskns@gmail.com www.glenfleskns.com Provision for Pupils with Special Educational Needs (SEN) Introductory Statement: This policy was revised in January 2014. The policy was formulated by the Fiona Williams, Paul Favier and Deirdre O’ Donoghue. Rationale • This policy fulfills the Department of Education (DES) requirement for a unified policy covering provision for low incidence disabilities in the school. • The policy is available for inspection by parents in order to assist them in making an informed decision in relation to the enrolment of their child in our school. • Although the implementation of the EPSEN Act 2004 (Education for Persons with Special Educational Needs) has been stalled due to lack of funding in the Budget 2008, this policy is guided by the principles of EPSEN and provision and services will be delivered in accordance with resourcing. Relationship to the Ethos of the School Current Situation Based on our school numbers we have 2 classroom teachers which entitles us to access of 0.4 Teaching Posts under the GAM. This provision is to “cater for pupils with low achievement (i.e. functioning at or below the 10th/12th percentile on a standardised test of reading or maths) and higher incidence SEN (borderline mild general learning disability, mild general learning disability, mild attention difficulties and specific learning disability) DES 24th June 2004. As of January 2014 our school does not have any pupil who qualifies for low incidence hours Aims • To outline procedures and practices to be followed in relation to pupils with SEN • To outline our whole-school approach to teaching/learning in relation to pupils with SEN • To endeavour that educational outcomes for pupils with SEN are on a par with those of their typically developing peers. Staff Roles and Responsibilities The role of supporting learning is a collaborative responsibility shared by all: the Board of Management, Principal, Class teachers, LS/RT, Special Needs Assistants (SNAs), Parents and Children. The Role of the Board of Management (BOM) • Ensure adequate classroom accommodation and teaching resources are provided for the Special Education Teachers (SETs) • Budget for the purchase of materials for pupils with SEN and provide ongoing support for Professional Development of SETs • Provide a secure facility for storage for records relating to pupils with SEN The Role of the Principal “The principal teacher has overall responsibility for the school’s learning support programme and for the operation of services for children with SEN” (Learning Support Guidelines, p38) • Assume overall responsibility for the development and implementation of the school’s policies on SEN in cooperation with staff members • Monitor the implementation of the school plan on special needs teaching on an ongoing basis • Co-ordinate supplementary teaching services ie. monitoring the selection of pupils and organising caseloads/work schedules • Help teachers increase their knowledge and skills in the area of special needs education via relevant in-career development The Role of Class Teacher • Has primary responsibility for the progress of all pupils including those with SEN. • Support all pupils by using the following best practices: pair work, group work, adopting specific strategies, differentiation and liaising with parents. • Re pupils with SEN, the class teacher will modify presentation and questioning techniques to maximise inclusion, emphasise oral language and allow for differentiated responses to work (oral/drawing vs written) • Implement the school policies on screening and selecting pupils for supplementary teaching in English and Maths by administering and scoring appropriate screening measures every year • Contribute to the IPLPS of pupils with high incidence disabilities • Implement targets for pupils with SEN • Follow the staged approach (DES Continuum of Support 2008) for pupils experiencing difficulties – the class teacher being involved at Stages 1,2 and 3, with total responsibility at Stage 1 The Role of the Learning Support (LS) The activities of the LS/RT should include both teaching and non-teaching duties. According to the Learning Support Guidelines 2000 “the particular balance that the LS/RT achieves between supplementary teaching and consulting activities will depend on the specific circumstances of the school”. (p.32). Specific duties include: • Assisting in the implementation of a broad range of whole-school strategies designed to enhance early learning and prevent learning difficulties. • Co-ordinating the implementation of whole school procedures for the selection of pupils for supplementary teaching giving due consideration to: The selection criteria specified in the Special Needs Policy Teacher’s professional observation Input of parents • Providing advice to the class teacher (if requested) about pupils who are experiencing learning difficulties in areas such as; Individual pupil assessment Curriculum differentiation Teaching methodologies • Contributing at school level to decision-making regarding the purchase of learning resources, books, games and ICT for use with children with SEN. • Liaising with external agencies (NEPS Psychologist, Speech and Language Therapist, Child and Adolescent Services, Special Education Needs Organiser (SENO) • Collaborating with the principal to discuss issues relating to the development and implementation of the school plan on SEN • Co-ordinating the administration by class teachers of the Nfer Nelson Non Verbal Reasoning Assessment to pupils aged 7 and older every second year • Consulting with class teachers on the identification of pupils who may need diagnostic assessment. • Carrying out diagnostic assessment of each pupil who has been identified as experiencing low achievement and/or learning difficulties and in consultation with class teacher and parents, identifying the type and level of support that is needed • Monitoring and reviewing the on-going progress of each pupil in receipt of supplementary teaching • Developing an Individual Education Plan (IEP) for each pupil with a low incidence disability • Developing an Individual Profile and Learning Programme (IPLP) for each pupil who is selected for supplementary teaching • Delivering early intervention programmes and providing supplementary teaching in English and or Maths to pupils in accordance with the school’s selection criteria • Delivering support, as appropriate to the needs of the individual child, on a withdrawal or in-class basis (co-teaching/team-teaching) The Role of Parents “Parents through their unique knowledge of their own child have much to contribute to their child’s learning programme” (Learning Support Guidelines, p 52). Specifically, parents contribute through: • Fostering positive attitudes about school and learning in the child. • Creating a home environment where there are opportunities to participate together in language, literacy and maths activities. • Support the work of the school by participating with their child in such activities as writing, shared reading, counting and measuring. The Role of the Pupil “The involvement of pupils in the development, implementation and review of their own learning programmes is an important principle, underlining effective supplementary teaching” (Learning Support Guidelines, p 54). • Pupils selected for supplementary teaching will complete the Pupil Profile. • Pupils will make some choices regarding specifics in their learning in order to promote commitment and responsibility, eg. draw up a work contract. • Pupils will be encouraged to set mini targets for themselves, eg. self-assessment, checklists. • Pupils will be encouraged to develop intrinsic motivation through regular motivational assessments by class and resource teachers. Enrolment of Children with Special Needs On enrolment of children with special needs the Board of Management will request a copy of the child’s medical and/or psychological report or where such a report is not available, will request that the child be assessed immediately. The purpose of the assessment report is to assist the school in establishing the educational and training needs of the child relevant to his/her disability or special needs and to profile the support services required. Following receipt of the report, the Board will assess how the school can meet the needs specified in the report. Where the Board deems that further resources are required, it will request the Special Education Needs Organiser (NCSE see Circular 01/05) to provide the resources required to meet the needs of the child as outlined in the psychological and/or medical report. These resources may include, for example, access to or the provision of any or a combination of the following: visiting teacher service, resource teacher for special needs, special needs assistant, specialised equipment or furniture, transport services or other. The school will meet with the parents/guardians of the child and with the SENO to discuss the child’s needs and the school’s suitability or capability in meeting those needs. Where necessary, a full case conference involving all parties will be held, which may include parents, principal, class teacher, learning support teacher, special class teacher, resource teacher for special needs, Special Educational Needs Organiser or psychologist, as appropriate. It may, in exceptional circumstances, be necessary for the Board of Management to defer admission, attendance, commencement date of a child pending the completion of an assessment report and/or provision of the necessary resources by the Department of Education and Science. Prevention Strategies • The development and implementation of agreed whole school approaches to language development eg. phonological awareness training. • Ensure continuity from class to class in both English and Maths by specifically developing agreed approaches to both subjects in the school plan. (see Plean Scoile English and Maths) • Promotion of parental understanding and involvement through holding an Induction Meeting for the parents of incoming Junior Infants, the provision of a Tips for Parents booklet, the arrangement of formal and informal Parent/Teacher meetings. • Provision of priority support in language development, early literacy and maths skills to pupils from Juniors to Second class. • Implementation of Forward Together Programme, with Senior Infants when deemed necessary. • Ongoing observation and assessment of pupils by Class Teacher. • Operation of a Reading Buddies system between infant and senior classes. • Adoption of Shared Reading approach from Juniors to First. • Operation of a lending system from the class library for each class from second up. Intervention Programmes • Early Intervention is a vital part of the Learning Support Provision in this school. The class teacher or LST may provide it. • Early Intervention will involve small group teaching or one-to–one teaching where group teaching has not been effective. • The school year will be divided into two instructional terms- September to Christmas and January to June. • Classes will be intensive in terms of frequency. • English lessons will include oral language work, development of phonemic awareness, word identification skills, supervised oral and silent reading, development of comprehension strategies and writing. • Maths lessons will include language development and development of mathematical procedure and concepts through the use of concrete materials where possible. Selection of Pupils for Learning Support The staged approach to meeting the needs of pupils with SEN as outlined in Circular 02/05 is implemented in the school. The principle of Early Intervention applies, ie. Pupils from Senior Infants to Second Class are given priority in the allocation of Learning Support. • In Junior Infants pupils are screened using teacher and LST observation. BIAP is administered in Junior Infants in May each year. • From Senior Infants upwards, all pupils are screened annually, using appropriate standardised tests. Current provision includes: • Screening of Senior Infants using the Middle Infant Screening Test (MIST) after they have completed 5 terms at school. • First Class upwards are screened for English using the DPRT test in May/June each year. • First Class upwards are screened for Maths using the DPMT test in October each year. • Class teachers administer and correct screening tests. • The LST will discuss the recorded results with the staff and carry out further screening tests and/or diagnostic assessment. • If a pupil is receiving support in English/Maths under Resource provision, s/he will not normally be provided with supplementary teaching from the LS teacher as well. • If a pupil is receiving support under Resource provision to address other needs eg. behavioural problems, sensory difficulty, it may be appropriate for the LS teacher to deliver supplementary teaching as well. The following is the priority order of pupils to receive supplementary teaching: • Children performing below the 10th percentile in standardised tests of achievement in English. • Senior Infants/First Class early intervention programmes for low achievers in English, based on class teacher observations and test results. • Children performing below the 12th percentile in standardised tests of achievement in Maths. • Senior Infants/First Class early intervention programmes for low achievers in Maths based on class teacher observations and test results. • Pupils performing at or below the 24th percentile in standardised tests of achievement in English. • Pupils performing at or below the 24th percentile in standardised tests of achievement in Maths. Written parental permission is not required for children to attend Learning Support Continuing and Discontinuing Supplementary Teaching Pupils with low incidence disabilities continue to receive resource support throughout the primary school until a psychological report or the SENO advises against it. The following applies to pupils who are receiving support under the weighted system of general allocation. In general, children should not stay for more than 2 years on supplementary teaching, unless they are still at or below the 12th percentile. (DES Learning Support Guidelines) The first instructional term runs from September to Christmas with the second being from February to June. Following the end of each Instructional term, a decision is made to continue/discontinue the provision of supplementary teaching. The decision making process involves consultation between the Class Teacher, the LS teacher and the pupil’s parents. An account is also taken of the overall Learning Support demands in the school. The criteria on which the decision to discontinue supplementary teaching will be made include: Consideration as to whether the pupil has achieved some/all the learning targets set . Consideration as to whether the pupil will be able to cope independently/semi-independently in the classroom. Review of the pupil’s IPLP Monitoring Progress Monitoring the academic progress of the pupils in this school will be accomplished by: Ongoing structured observation and assessment of the language, literacy and numeracy of the pupils in the Infant classes to facilitate early identification of possible learning difficulties by the class teacher. Formal and informal testing and observation of work by class teacher. Standardised and Diagnostic testing. Record keeping. Children with SEN have a file in a secure filing cabinet where records and test results are kept. Individual pupil profiles are kept by the class teacher. Non-academic progress of pupils is reviewed informally eg. improvement in pupil’s selfesteem, school attendance, attitude to learning, attitude to school and general behaviour. Communication Strategies Parents Parents of pupils with low incidence disabilities will be invited to attend IEP/IPLP meetings and reviews. Additional meetings may be held to monitor progress as necessary. A daily home-school journal may be used in situations where pupils cannot carry information and news or in order to track an intensive intervention. When pupils are selected for supplementary teaching (Stage 2) by the LS teacher, it is necessary to advise parents of this: To clarify the child’s learning needs. To clarify the role of the parent in relation to these needs To obtain consent to supplementary teaching This communication may take the form of a meeting. At a suitable stage during the year the LS teacher will meet the parents to discuss progress and outline ways to support their child’s learning. Class Teacher: A time slot is created for collaboration with the class teachers during the first fortnight in September. Issues to be discussed should include: discussion of pupil’s progress/lack of progress, setting of targets for IEPs and IPLPs, carrying out error analysis (eg. running record in Reading) to pinpoint specific areas of difficulty, establishment of prevention/intervention systems e.g. shared reading or reading buddies. Outside Agencies If Stage 3 of the Curriculum of Provision is reached, the LS/RT and principal co-ordinate with parents and appropriate outside agencies for the relevant assessments. The class teacher completes the necessary referral form in consultation with the appropriate school personnel. Where concern arises regarding the supply of assessment reports, this matter is pursued by the principal with the agency concerned. LST will be involved in meetings with NEPS psychologists, SENO, speech and language therapists, Occupational therapists and other HSE ‘key workers’. IEP Meetings Parents, class teacher, LST and principal will be invited to attend all IEP meetings. Outside professionals such as Psychologist, Speech and Language Therapists, Occupational Therapists, Social Workers and Key Workers will be invited as appropriate. It has been the experience that outside professionals are frequently unavailable to attend on a given day and that the pragmatic approach is to have separate meetings where necessary or to get the input of these professionals by way of their written Reports or phone conversations. Timetabling • The LS/RT in consultation with class teachers draws up the timetable at the beginning of the school year. • The provision of learning support is in addition to the regular class teaching in English and Maths. • The provision of Learning Support/Resource Support may include withdrawal of pupils from their classrooms and/or in-class support. • In-class support, if appropriate, will be jointly designed and monitored by the Class teacher and LS/RT. • Every effort is made to ensure that pupils do not miss out on the same curricular are each time they are withdrawn for Support. • Where pupils have exemptions from Irish, every effort is made to provide support during this time. • PE. Every effort is made not to withdraw pupils during favoured subjects such as Art or • Changes have to be accommodated every term due to swimming, football, rugby, outings, etc. • Consultation/collaboration time is included in the timetable. Transition from Primary to Secondary School Our focus for transition to Secondary School will be to prepare the child for change before he/she enters post-primary education by following the three phase approach as suggested in the Guidelines. (Introduction pp. 5-6) Communication • Our school will invite visits from the local Secondary schools, who will in turn invite all students to their Open Nights. • We make contact with the school of choice. The SENO and the NEPS are also contacted so that updated assessments and recommendations can be made. Consultation • The Principal, in consultation with the parents, SENO and NEPS will forward all reports to the new school so that all supports, resource time and personnel eg. Special Needs Assistant, can be applied for and put in place prior to the student starting. • Resource Teachers from both schools will meet, together with the parents, to discuss the NEPS recommendations and the current IEP, along with levels of achievement reached to enable onward planning. • Support Services and health personnel will be informed so that any equipment which may be needed can be put in place. Also, mobility issues can be discussed for those with physical or sensory disabilities. Consolidation • Communication between school staff, parents, NEPS and the SENO and all other personnel will continue in the months leading up to the transition of the student so that all possible help and support can be given to meet the needs of the student prior to his/her arrival in the school. POLICY APPROVAL/RATIFICATION Provision for Pupils with Special Educational Needs (SEN) This policy was ratified by the Board of Management of Glenflesk National School on: Signed: _______________________________________ Fr. Bill Radley Chairperson of Glenflesk N.S. Date:_____________________



![afl_mat[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005387843_1-8371eaaba182de7da429cb4369cd28fc-300x300.png)