4-7 Protein Denaturation-Renaturation
advertisement

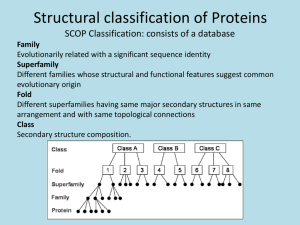
4-7 PROTEIN DENATURATION, RENATURATION AND FOLDING Denaturation Denaturation of proteins is caused by _______________ changes or _______________ treatments that disrupt the __________ conformation. o This also causes the protein to lose its _______________ activity. o Some denature and _______________ completely, while others may retain considerable _______________ structure. Proteins commonly denature upon _______________, resulting in the loss of secondary and tertiary structure. o The destabilization of just a few __________ interactions leads to almost complete loss of native conformation. Proteins can also be denatured by … o _______________: Chemicals like urea and guanidinium chloride allow water molecules to disrupt the hydrophobic interactions in the interior of proteins. o _______________: Hydrophobic tails of these (like SDS) denature proteins by penetrating the protein interior and disrupting hydrophobic interactions. The presence of _______________ bonds makes the protein less susceptible to unfolding. o Thiol reagents like _______________ can be added to a denaturing medium in order to reduce disulfide bonds. Renaturation Christian B. Anfinsen and his coworkers studied the renaturation pathway of ribonuclease A. o Added 8 M urea and 2-mercaptoethanol to ribonuclease A and caused the complete loss of _______________ structure and _______________ activity. o When the 2-mercaptoethanol is removed, the –SH groups re-formed the four disulfide bonds _______________, in 105 different possible combinations, but… o When both urea and 2-mercaptoethanol are removed simultaneously and the protein is exposed to air, ribonuclease A spontaneously regains its _______________ conformation, its _______________ set of disulfide bonds, and full _______________ activity! Denaturation and renaturation of ribonuclease A: Some proteins fold incorrectly and form incorrect disulfide bonds. Anfinsen discovered an _______________ that can catalyze the reduction of these incorrect bonds and allow the misfolded protein to refold into the intended native conformation! Anfinsen won the 1972 __________ _________ in Chemistry for his work on the refolding of proteins. Protein Folding Polypeptides are synthesized in the cell by a translation complex within ribosomes. As the polypeptide emerges from the ribosome, it __________ into its __________ conformation. This conformation has the __________ possible energy, making it the most __________ conformation possible. Proteins fold through ____________________ of folding – where the formation of one part of a structure leads to the formation of the remaining parts of the structure. Folding is extremely __________ - taking less than a second. o The polypeptide collapses upon itself due to the hydrophobic effect, causing elements of _______________ structure to form. o Subsequent steps involve the rearrangement of the backbone chain to form characteristic __________, and finally, the native conformation. o The _______________ of protein folding is one of the most challenging problems in biochemistry. No actual protein-folding pathway has yet been described in detail. In general, there are four forces that stabilize protein structure during folding: 1. _______________ effect: Water forces the nonpolar side chains to associate with one another, causing the protein to _______________ into a more compact globule. a. This decrease in disorder (or _______________) is the driving force for protein folding. 2. _______________ bonding: These interactions in helices and sheets are the first to form, giving rise to secondary structure. These also form between these secondary structures, giving rise to _______________ structure and eventually the final __________ structure. 3. _____ _____ __________ Interactions: Another name for London dispersion forces, the cumulative effect of all of these nonpolar forces contribute significantly to the stability of a protein. 4. __________-__________ Interactions: These may occur between oppositely-charged side chains, and contribute minimally to the stability of a protein. Molecular Chaperones Folding is not a __________ search for its native conformation. It is a cooperative, sequential process in which a few initial interactions lead to the formation of subsequent structural features. Folding is assisted by molecular _______________, which… o Increase the __________ of folding. o Prevent the formation of _______________ folded intermediates. o Prevent protein subunits from aggregating incorrectly and _______________ before they are completely assembled. Read pages 113 (2nd full paragraph) through the end of the section on page 115 to learn more about molecular chaperones.