Answers to Assignment #2
advertisement

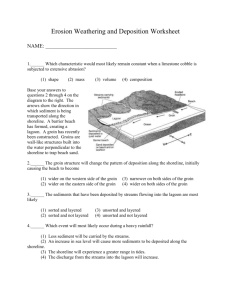
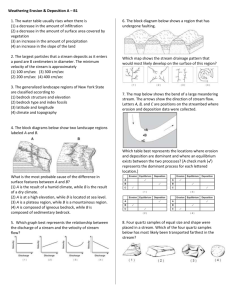
Answers to Assignment #2 182._______________ Gravity___________ is the force behind all erosion. 183._______________Running Water__________ is the primary agent of erosion. 184. Stream velocity depends on ________ gradient _______ and ______ volume (discharge) ___________. 185. The size of the particle transported depends on the stream’s _____ velocity _____________. 186. Heavy-dense-round particles settle _________ first _______ in water. 187. Graded bedding (vertical sorting) _____ large______ sediments are on the bottom. 188. Glacial sediments are _________ unsorted ______, scratched and form ________ “U” _________ shaped valleys. 189. Stream deposits are ______ sorted _______, round, and form _____ “V”________ shaped valleys. 212. Weathering- Break down of rocks at the earth’s surface into _________ sediments ____. 213. Sediments – broke down pieces of rock. 214. Soil- mixture of weathered rock (sediments) and organic remains that cover bedrock. 215. Chemical weathering dominates in _____ warm ________ and________ wet _____ climates. 216. Physical weathering dominates in _____ cold ____ and ____ wet __________ climates. (Good For Frost Wedging) 217. As the particle size decreases, the rate of weathering will _______ increases_________. 218. When particles are broken into smaller pieces, the surface area _____ increases _________. 219. Sediments are classified based on their _________ particle size__. (i.e. .02cm particles are sand) 220. Erosion- _____movement________ of sediments 221. ___________ Gravity _____ is the ultimate force behind erosion. 222. _________ Running Water _______ is the primary agent of erosion. 223. Dissolved mineral are carried in _____ solution_________. 224. Silt/Clay colloids are carried by _____ suspension _________. 225. Sand/ Pebbles slide and bounce along the bottom. 226. As the velocity increases, the size of the sediments a stream can transport _______ increases ________. 227. As the slope/gradient of a stream increases, the size of the sediments a stream can transport _____ increases_______. 228. As the discharge (an amount of water in a stream) increases, velocity will _______ increase ________. 229. The velocity of a stream is greatest on the _______ outside___ of a meander (bend). 230. Erosion occurs on the _____ outside________ of a meander where velocity is ____ fast __________. 231. Deposition occurs on the _____ inside _______ of a meander where velocity is ______ slow ________. 232. _____ Large______, _______ dense_______, _________ Round _____, particles are the first to settle out of water as the water slows down. (Sorting Sediments) 233. Sediments transported by water are _____ round_______ and _____ smooth_______ due to abrasion. 234. Streams erode a _ “V” ____ shaped valley. 235. Sediments deposited by glaciers are _______ unsorted _______, (all mixed up in size and shape.) 236. Glaciers erode a __ “U” __ shaped valley. 237. After a glacier has moved through an area the bedrock is _______ smooth___ and _______ polished____ with parallel glacial striations (scratches). 238. Wind deposits consist of fine grained well sorted particles (sand) particles exhibit a pitted/frosted appearance and cross bedded layers. 239. Residual soil- developed from the bedrock below it- _____ same _________ mineral composition as bedrock below. 240. Transported soil- transported from another location- _____ different______ mineral composition than bedrock below. 241. ______ Longshore _______ drift moves sand along the beach in the direction of the ocean current. 248. ______ Divergent ________ plate boundary – Two plates move apart. 249. ______ Convergent ________ - two plates move toward one another. 250. Proof of sea floor spreading -1- the age of the ocean floor is ______ younger____ at the mid ocean ridges and gets _____ older____ as you move away in either direction. 2. There is also a matching pattern of earth’s _____ magnetic__ polarity on either side of the ridge. 251. Inferences about Earth’s interior come from the study of ________ seismic waves _________. 252. Earthquakes and volcanoes happen in the same spot, near ________ plate boundaries________. 253. ______ Hot Spots________ are not associated with plate boundaries –magma burns through plate = a series of islands (Hawaii). 254. Continental crust is ______ older_______ with a density of ______ 2.7 g/cm3 ______ and is composed of ____granite __________. 255. Oceanic crust is ________ younger___, with a density of ___3.0 g/cm3 _____ and is composed of ___basalt____. 256. When a continental plate collides with an oceanic plate the ______ oceanic________ plate subducts because it ______more________ dense. 257. ______ Transform________ Boundary – Plates slide past each other (San Andres Fault). 258. Subduction zones/Trenches are where _________ oceanic crust_____________ is destroyed. (Recycled). 259. _____ Convection Currents_ in the asthenosphere (mantle) cause the plates to move. 260. P- Waves travel _____ faster _________ than S- waves. 261. P waves travel through ___ solids_______ & ______ liquids _____, but S- waves through _____ solids ____ only. 262. We can infer that the outer core is _____ liquid_________ because __ S__ waves cannot penetrate it. 263. One seismic station can determine the _____ distance _________ to the epicenter. 264. As the distance from the epicenter increases, the time lag between the P sand the S wave _______ increases_______. 265. You need ______ 3 ________ seismic stations to plot an epicenter. (Where three circles meet).