Ch review answers
advertisement

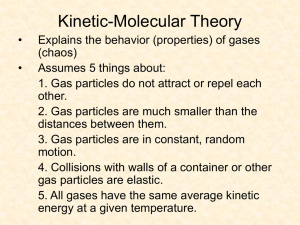
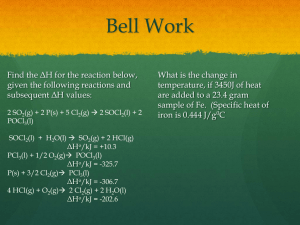
Name _______________________________ Gas Laws Review Chemistry 1. Complete this statement with the following words and phrases. Each is used once. absolute temperature increases constant temperature kinetic-molecular theory of gases decreases pressure elastic volume energy ideal gas According to the ____________________________, an __________________ consists of point-sized particles, with no _________________ whatsoever, that bounce off each other in perfectly _________________ collisions, without losing any _____________ in the process. The _______________ of a gas enclosed in a container results from the collisions of the particles with the walls of the container. If we increase the temperature of an ideal gas held in a container of constant volume, the pressure _____________ and always remains directly proportional to the _____________. If we increase the pressure on a gas held at _________________, the volume of the gas _____________ proportionately. 2. Describe the 5 properties of gases. a. b. c. d. e. 3. Explain how a barometer works. 4. How can we use atmospheric pressure to crush a can or push an egg into a flask? Explain what happens with the gas molecules. 5. What is STP? 6. Write the laws. Boyle’s Law Charles’ Law Gay-Lussac’s Law Combined Gas Law Dalton’s Law Ideal Gas Law Ideal Gas Law with Molar Mass Ideal Gas Law with Density Gas Stoichiometry Graham’s Law Explain how you will know when to use this law. Name _______________________________ Gas Laws Review Problems Chemistry page 2 Directions: Determine which law you will need to use. Then solve. Show work. 1. What pressure is needed to compress the air in a 1.105 L cylinder at 760 torr to a volume of 1.00 mL? 2. A 4.20 L sample of gas is collected over water at a pressure of 97 kPa. The pressure is adjusted to 101.325 kPa. What is the volume? The temperature of the gas is 20.0ºC. 3. When 500. mL of helium gas at 25ºC is cooled at constant pressure to 10.0 K, what does the volume of the gas become? 4. At what temperature does 100. mL of N2 at 305 K and 750 torr occupy a volume of 525 mL at a pressure of 1.89 atm? 5. What is the volume of 7.5 moles of methane gas under a pressure of 742 mm Hg and at 25ºC? 6. What is the molar mass of a gas at 32ºC and 0.785 atm and a volume of 2.5 L? The gas has a mass of 3.68 grams. 7. What will be the pressure of 150 grams of CCl2F2 at a temperature of 15ºC and a volume of 225 mL? 8. A weather balloon is filled with 1.0 L of helium at 23ºC and 1.0 atm. What volume does the balloon have when it has risen to a point in the atmosphere where the pressure is 220 torr and the temperature is –31 ºC? 9. At a temperature of 25 ºC, 125 mL of oxygen is collected over water at standard pressure. If we raise the temperature to 35ºC and expand the volume to 300 mL, what will be the pressure of the dry gas? 10. A sample of N2 gas is at a pressure of 475 torr and a temperature of 18ºC. What is the density of the gas? 11. How many grams of SO2 will be in a 2.5 L container at a pressure of 700 mm Hg and a temperature of 310 K? FSK Gas Laws Review Chemistry 1. Complete this statement with the following words and phrases. Each is used once. According to the kinetic-molecular theory of gases, an ideal gas consists of point-sized particles, with no volume whatsoever, that bounce off each other in perfectly elastic collisions, without losing any energy in the process. The pressure of a gas enclosed in a container results from the collisions of the particles with the walls of the container. If we increase the temperature of an ideal gas held in a container of constant volume, the pressure increases and always remains directly proportional to the absolute temperature. If we increase the pressure on a gas held at constant temperature, the volume of the gas decreases proportionately. 2. Describe the 5 properties of gases. a. Gases Expand to fill their containers b. Gases will diffuse or effuse from their containers c. Gases are compressible d. Gases have a mass and a low density e. Gases like liquids are considered fluids. 3. Explain how a barometer works. A column of Hg is placed above a pool of Hg that is supported by the push of atmospheric pressure any change in that pressure is shown by a change in height of the column of Hg 4. How can we use atmospheric pressure to crush a can or push an egg into a flask? Explain what happens with the gas molecules. By decreasing the pressure inside the can or flask would allow atmospheric pressure to push in the can or egg. 5. What is STP? Standard temp and Pressure or 101.3kPa 760 torrs 273K or 0C & 760 mm Hg, 1.00 atm 6. Write the laws. Boyle’s Law P1V1 = P2V2 Explain how you will know when to use this law. Pressure and Volume will be changing Charles’ Law V1 = V2 T1 Temperature and Volume will be changing T2 Gay-Lussac’s Law P1 = P2 T1 Pressure and Temperature will be changing T2 Combined Gas Law Temperature, Pressure and Volume will be changing Dalton’s Law PT=P1+P2+P3+… See the words collected over water, or have two or more gases being measured. Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT Ideal Gas Law with Molar Mass PV = mRT M Ideal Gas Law with Density Not at STP and all 4 variables are involved. Know the specific gas and its mass. (got the formula) D = PM Need or have Density RT Gas Stoichiometry Using the balanced chemical equation & If at STP 1 mole = 22.4L Or if not then use PV=nRT Graham’s Law 𝒗𝒆𝒍𝟏 𝒗𝒆𝒍𝟐 𝑴 = √𝑴𝟐 𝟏 To determine the relative speed of a gas molecule Name _______________________________ Gas Laws Review Problems Chemistry page 2 Directions: Determine which law you will need to use. Then solve. Show work. 1. What pressure is needed to compress the air in a 1.105 L cylinder at 760 torr to a volume of 1.00 mL? Boyles solve for P2 P2 = 839,800 Torr 2. A 4.20 L sample of gas is collected over water at a pressure of 97 kPa. The pressure is adjusted to 101.325 kPa. What is the volume? The temperature of the gas is 20.0ºC. Dalton’s law 1st then Boyle’s solve for V2 V2 = 3.92 L 3. When 500. mL of helium gas at 25ºC is cooled at constant pressure to 10.0 K, what does the volume of the gas become? Charles Law solve for V2 V2 = 16.78 ml 4. At what temperature does 100. mL of N2 at 305 K and 750 torr occupy a volume of 525 mL at a pressure of 1.89 atm? Combined gas law solve for T2 Convert 750 torr to 0.987 atm T2 = 3066 K 5. What is the volume of 7.5 moles of methane gas under a pressure of 742 mm Hg and at 25ºC? V= nRT/P V = 187.96 L 6. What is the molar mass of a gas at 32ºC and 0.785 atm and a volume of 2.5 L? The gas has a mass of 3.68 grams. M = mRT/PV M = 46.95 g/mol 7. What will be the pressure of 150 grams of CCl2F2 at a temperature of 15ºC and a volume of 225 mL? P = mRT/MV P = 130 atm or 99,009 torr M of CCl2F2 = 121 g/mol 8. A weather balloon is filled with 1.0 L of helium at 23ºC and 1.0 atm. What volume does the balloon have when it has risen to a point in the atmosphere where the pressure is 220 torr and the temperature is –31 ºC? Combined gas law solve for V2 220 torr = 0.289 atm V2 = 2.82 L 9. At a temperature of 25 ºC, 125 mL of oxygen is collected over water at standard pressure. If we raise the temperature to 35ºC and expand the volume to 300 mL, what will be the pressure of the dry gas? Combined gas law solve for P2 P1 = 760 mmHg – 23.8 mmHg = 736.2 mmHg P2 = 317 mmHg or 0.417 atm 10. A sample of N2 gas is at a pressure of 475 torr and a temperature of 18ºC. What is the density of the gas? D = PM/RT D = (475 torr)(28 g/mol) (62.4 R )( 291 K) D= 0.732 g/ L 11. How many grams of SO2 will be in a 2.5 L container at a pressure of 700 mm Hg and a temperature of 310 K? m = RT/PVM Molar mass of SO2 =64.1 m = 0.172 g of SO2