XistAR write up
advertisement

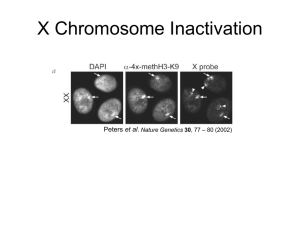
William Ou 55614127 November 24, 2015 News & Views Just a month ago, a paper titled: An Xist-activating antisense RNA required for X-chromosome inactivation, was published on Nature Communications. Contrast to our understanding of X-inactivation via Xist thus far, these researchers found an additional novel piece of long non-coding RNA expressed from the inactivated X chromosome. They identified this lncRNA to be antisense of Xist, and that its expression is required for proper Xist functioning. Here, I will explain the paper in 3 steps, 1) How they identified the novel antisense Xist RNA, 2) How they mapped it and 3) How the function of the lncRNA is characterized. First, as you can see from the diagram depicting the X inactivation center(XIC), Tsix is a gene antisense of Xist, which have been shown from other literature and as discussed in class, is a gene transcribed only from the active X chromosome in either iXCI or random XCI. Since Tsix is also antisense to Xist, the researchers distinguished the novel antisense lncRNA by breeding F1 rats with a mutant Tsix allele (XΔTsix) such that the maternal X(Xm)is the containing the mutant allele. In these rats, Tsix is expected to not be expressed, which they confirmed by RT-PCR and sequencing RNA/DNA of male rats, since no inactivation is required in male rats, Tsix is only expressed from that mutant allele (Figure 1b). However, in the female versions of these rats, there appears to be an antisense transcript present, which can only be transcribed from the WT inactivated Xp. This claim was conclusively determined through sequencing by utilizing known SNPs in the Xist/Tsix sequence. Next, to distinguish parent-of-origin-specific from strainspecific bias in expression, they compared RNAs produced from WT F1 hybrids and their reciprocal counterpart. Through SNP profiling, they found Xist antisense transcripts in both X chromosomes (active and inactive). In addition, they did a FISH analysis, by probing the XistAR (probe shown in Figure 1a). Green is a probe for Xist, red is for XistAR and white is for Atrx (transcribed from active X). Consistent with speculations, XistAR probes coincided with Xist probes (as in figures). So far the cells analyzed were from TS (trophoblast stem) and XEN (extra-embryonic endoderm) which both exhibit iXCI. To examine the involvement of XistAR in random inactivation, they examined antisense expression in EpiSC (epiblast stem cells). Since it is impossible to deduce allele-specific expression in random inactivation cell lines, they utilized F1 hybrids that are Tsix-heterozygous. In these hybrids, X inactivation would be in favor the X-chromosome with mutant Tsix(XΔTsix). Again, XistAR was detected only from inactivated X (XΔTsix). This was further confirmed by FISH of WT hybrid EpiSCs(lower % because XistAR from different chromosomes have different sequences and the probe only probes one of them). Now that the antisense Xist RNA is confirmed, the researchers set to map it out. First, they used 5’ and 3’ RLM-RACE and found a 5’ cap on the RNA but failed to find a poly-A tail on the 3’ end. The researchers also sequenced XistAR by RNA FISH (as shown on the slide). Primers used that resulted in amplification, corresponds to the sequence of the XistAR gene. The 5’ end mapped out to be bp 2802 of Xist and 3’ end bp13 which is within exon 1 of Xist. Lastly, the function of XistAR was characterized by insertion of intronic cassette sequence containing multiple polyadenlyation (mpA) in the antisense orientation. This intron insertion would lead to Xist RNA unharmed and XistAR truncated (XXpA). William Ou 55614127 November 24, 2015 News & Views As a control they analyzed a strain with the same intronic cassette but with no mpA(XXIVS). As you can see on the graphs, the truncated XistAR resulted in decrease in Xist expression. Since no Xist means no X-inactivation, ultimately means increase expression of genes that are normally expressed from the active X. This is consistent with data shown in Figure 6d. (RNF12, Atrx, Pdha1 are expressed from active X, utx escapes inactivation shown by other papers). The researchers had to determine the role of XistAR in both imprinted X-inactivation and random X-inactivation. To do so they utilized a number of techniques. Select all that apply. 1) In FISH analysis, the EpiSC cells showed a lower percentage of XistAR associated with the silenced X chromosome (and Xist) compared to TS and XEN cells because X-inactivation in EpiSC doesn’t normally happen 2) The researchers were able to utilize intronic cassettes to truncate XistAR and not Xist because the double-stranded cassette has different splice sequences on each strand. 3) A mouse heterozygous for a mutant Tsix was used to study random inactivation because this mutant phenotype would knockout random inactivation 4) In this paper SNPs allowed researches to study the effects of single nucleotide base pair changes on gene expression 5) Through RT-PCR analysis, the researches found another piece of Xist antisense RNA and that it is the same size as Tsix. Answer : False, True, false, false, false.