4-6 ch5
advertisement

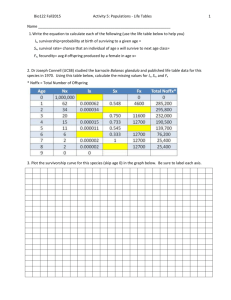
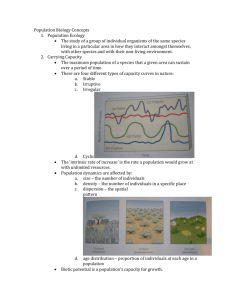
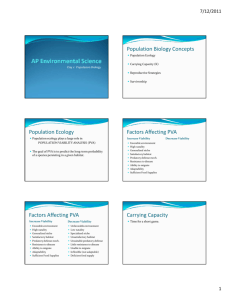
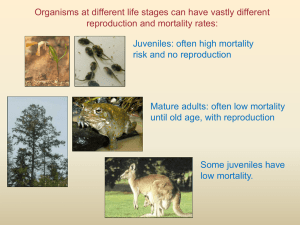
Warm-up: (10-21-15) *Ferret Article/rubric out for stamp! 1. Read the article and answer the questions in your warm-up. No complete sentences. Do not copy the questions. _________________________________ Copy hw. Chapter 5-6 Population Ecology Goals for today: Contrast top down and bottom up population controls Identify the pros/cons of sexual and asexual reproduction Identify the 3 types of survivorship curves Be able to give examples of “r” and “K” strategists Top-down or bottom-up? Evidence seems to show both happening Top-down – predators hunt and kill prey keeping prey pop. stable Bottom-up – prey are the food source that determine predator pop. Can you think of a bottom up example? REPRODUCTIVE PATTERNS Asexual reproduction: reproduce without exchanging genetic material. Offspring are exact genetic copies (clones). Ex. Bacteria, some plants. “a” in front of a word means… What is a disadvantage to asexual reproduction? Sexual reproduction: reproduction with exchange of genetic material What are some advantages? Disadvantages? Disadvantages: males do not give birth (female needs to produce two offspring to replace parents) increase chance of genetic defects Courtship/mating rituals can be costly (energy) Major advantages: genetic diversity offspring protection Sexual Reproduction: Courtship Courtship rituals consume time/energy Inflict injury on males during competition What are some examples of characteristics/rituals that consume time/energy? Opportunists: reproduce rapidly when conditions are favorable, or a new niche opens up Ex. Pioneer species Examples??? Survivorship curves Survivorship curves: show how likely an organism is to survive at different times in its life. 3 types of curves.(type I, II, and III) 100 % surviving 10 1 Age Type I survivorship curve (late loss) Ex. Humans or elephants Other examples? Type II survivorship curve (constant loss) % surviving 100 10 1 Age Probability of dying doesn’t change throughout life, simple decline day to day. Ex. Some birds Type III survivorship curve (early loss) % surviving 100 10 1 Age Probability of dying is high when young, but if it survives, it has a high probability of living to old age. Ex. Sea turtles, insects, oak trees What are some differences between type 1 and 3? r and K strategists r strategist: species that produce many "cheap" offspring. Little/no parental care Small, short-lived adults Reach reproductive age rapidly Ex. Type III survivorship Pioneer species would be (r,K) strategists. K strategist: species that produce few "expensive" offspring. Ex. Type I and II survivorship (humans) Lengthy parental care High ability to compete Reproduce later in life Low ability to adapt to change compared to r strategists. Why? r or K strategist? Reach reproductive age rapidly Reproduces later in life Less adaptable to change High biotic potential Opportunists Small, short-lived Fewer offspring No/little parental care Does not usually live in a rapidly changing environment Pioneer species Reproductive Patterns r-selected: opportunists K-selected: competitors. Check for Understanding: 1. Wolves controlling a deer population is an example of what type of population control? 2. Describe an r-selected organism. 3. Which is better at adapting to environmental changes, r or K strategists. Why?