Population Biology Concepts Population Ecology Factors Affecting
advertisement

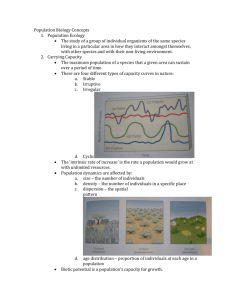
7/12/2011 Population Biology Concepts y Population Ecology y Carrying Capacity (K) Day 1: Population Biology D P l ti Bi l y Reproductive Strategies y Survivorship Population Ecology y Population ecology plays a large role in POPULATION VIABILITY ANALYSIS (PVA) Factors Affecting PVA Increase Viability Decrease Viability y Favorable environment y High natality y The goal of PVA is to predict the long‐term probability of a species persisting in a given habitat. y Generalized niche G li d i h y Satisfactory habitat y Predatory defense mech. y Resistance to disease y Ability to migrate y Adaptability y Sufficient Food Supplies Factors Affecting PVA Increase Viability Decrease Viability y Favorable environment y Unfavorable environment y High natality y Low natality y Generalized niche G li d i h y Specialized niche S i li d i h y Satisfactory habitat y Unsatisfactory habitat y Predatory defense mech. y Unsuitable predatory defense y Resistance to disease y Little resistance to disease y Ability to migrate y Unable to migrate y Adaptability y Inflexible (not adaptable) y Sufficient Food Supplies y Deficient food supply Carrying Capacity y Time for a short game. 1 7/12/2011 Carrying Capacity Carrying Capacity y Carrying capacity refers to the number of organisms a y Biotic Potential is the maximum rate at which a given area can sustain. y Factors that help regulate population include: F h h l l l i i l d population can grow. y What factors likely influence biotic potential? Wh f lik l i fl bi i i l? y Food availability, space, O2 content in waters y Nutrient levels in soils, amount of sunlight Carrying capacity Carrying Capacity y When left with unlimited resources, populations grow y No population is truly unlimited though exponentially Carrying Capacity Carrying Capacity y Values fluctuate over time, hovering around the carrying capacity 2 7/12/2011 Growth Rates Growth Rates y The “Rule of 70” tells us that: y Population as a system… what factors affect population size? y If a population is growing at a rate of x% y Then it takes approximately 70/x years for the population to double Growth Rates Growth Rates y Population as a system… what factors affect population y Population as a system… what factors affect population size? size? y Population Size (P) can be calculated as: P l i Si (P) b l l d y Population Size (P) can be calculated as: P l i Si (P) b l l d P=Original Size + Births – Deaths + immigration ‐ emmigration P=Original Size + Births – Deaths + immigration – emmigration y Net growth rate is a slope: New / Old Reproductive Strategies Reproductive Strategies y Organisms have adapted either to: y Maximize growth rates in environments that lack limits y Maintain population size at close to the carrying capacity in stable environments r‐strategists y Species with high reproductive rates are r‐strategists y y y y y Species that reproduce later in life with fewer offspring are k‐strategists y y y y Mature rapidly Short lived Tend to be prey Have many offspring and overproduce Low parental care Are generally not endangered Tend to be small Population size limited by density 3 7/12/2011 Reproductive Strategies r‐strategists k‐strategists y y y y y Mature slowly y y y y Mature rapidly Short lived Tend to be prey Have many offspring and overproduce Low parental care Are generally not endangered Tend to be small Population size limited by density y Long lived Survivorship Curves y Survivorship curves show age distribution characteristics of species, reproductive strategies, and life history y Tend to be both prdeator T d t b b th d t and d prey y Have few offspring y High parental care y Reproductive success is measured by how many organisms are able to mature and reproduce y Population size stabilizes near carrying capacity y Tend to be large Survivorship Curves Survivorship Curves y Type 1: Late Loss y Reproduction occurs early in life y Most deaths occur at the M d h h limit of lifespan y Low mortality at birth Survivorship Curves Survivorship Curves y Type 2: Constant Loss y Type 3: Early Loss y Death rates uniform y Typical of species that y Predation affects all ages have many offspring y Typical of organisms that y Species that reproduce S i h d reach adulthood quickly for most of their lifetime y Death is prevalent for younger members of species and declines with age 4