Tenses of Verbs - Saint John the Beloved School
advertisement

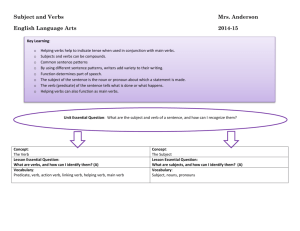
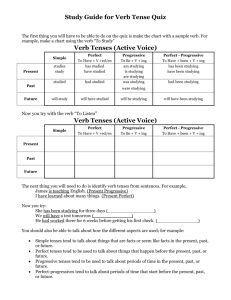
Tenses of Verbs Tense Definition / Rules Example Simple Present happening right now - add s to regular verbs that are singular, do not add s to verbs that are plural Simple Past already happened - add ed to regular verbs to make them past tense Simple Future will happen later - use the helping verb will or shall to make the verb future tense Present Perfect expresses an action that took place at an indefinite time in the past. The action may still be going on. - always includes has or have - -ed ending (if regular verb) Past Perfect an action in the past that was completed before another action took place - always includes had - -ed ending Future Perfect an action that will be completed before another action in the future -always includes will and have - ed ending She has raised the money. They have raised the money. She has started her lifelong biography. Progressive Tenses show continuing or ongoing action. Use a form of be and the present participle form of the verb (-ing ending). Present Progressive use is or are before the main verb She is studying. Past Progressive use was or were before the main verb He was studying. Future Progressive use will be before the main verb We will be studying all week. Present Perfect Progressive use have been before the main verb They have been studying for days. Past Perfect Progressive use had been before the main verb We had been studying before the weekend. Future Perfect Progressive use will have been before the main verb We will have been studying for weeks by the time the project is done. Principal Parts of Verbs Verb Present Participle (is) -ing ending Past - ed ending Past participle (have) -ed ending paint (is) painting (has) painted painted worry (is) worrying worried (has) worried hope (is) hoping hoped (has) hoped