CIRCULATION Chap. 12-1 The Body*s Transport System
advertisement

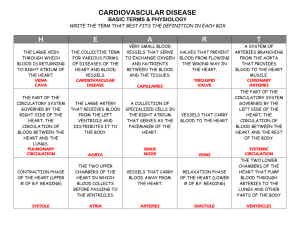
CIRCULATION Chap. 12-1 The Body’s Transport System Cardio-Vascular System • Also called the circulatory system. • Consist of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. • The cardiovascular system carries…….. Needed substances to all cells Waste products away from cells Cells that fight disease. White blood cells Movement of Materials • Needed materials: Blood carries oxygen from lungs to the cells Blood carries glucose to cells for energy • Waste products: Blood carries carbon dioxide from cells to lungs. • Disease fighters White blood cells attack disease causing microorganisms. Structure and Function • The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, about the size of your fist. It is located behind the sternum and inside the ribs. • Average heart beats per minute rate is 70-75 B.P.M. • Each heart beat pumps approximately 60 ml. (1/4 of a cup) of blood thru the vessels of your body. • DEMO: Can your hands work as fast as your heart? Try this at home. You need two containers. Fill one with water. Find a very small bowl that holds about ¼ of a cup. Every second use the small bowl to transfer water from one container to the other. How long can you las last? Structure and Function • The heart has 2 sides (right and left) Separated by wall of muscle called the septum. Each side has 2 chambers. • The upper chambers (called atria) receive blood coming into the heart. • The lower chambers (called ventricles) pump blood out of the heart. • Each atrium is separated from its ventricle by a one way valve that keeps blood from flowing backwards. One way valves also separate the ventricles from the two major arteries where blood Is pumped out of the heart. Demo: View arm one way valve Heart Works in 2 Phases • In phase 1, the heart atria relax and the atria are filled with blood. • In phase 2, the atria contract and fill the ventricles with blood, and the ventricles contract to pump the blood forward. • The “lubb-dubb” sound of the heartbeat is made as the valves slam shut. The Pacemaker • The pacemaker is a group of nerve cells located in the right atrium. • The pacemaker sends out electrical signals that makes the heart beat. • The pacemaker constantly receives stimuli from the brain about the body’s oxygen needs, and responds by adjusting the heartbeat to match the need. Two Loops • After leaving the heart, the blood travels three types of vessels thru-out the body Arteries take blood away from the heart Capillaries connect arteries to veins Veins bring blood back to heart • The pattern of the flow is like a figure 8. • Heart to lungs and back to heart • Blood thru aorta to cells of the body and back to heart Blood Vessels & Blood