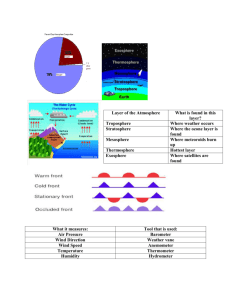
Cut and Paste in the “Earth Systems” part of the foldable: Layer of
advertisement

Cut and Paste in the “Earth Systems” part of the foldable: Layer of the Atmosphere Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere What it measures: Air Pressure Wind Direction Wind Speed Temperature Humidity What is found in this layer? Where weather occurs Where the ozone layer is found Where meteoroids burn up Hottest layer Where satellites are found Tool that is used: Barometer Weather vane Anemometer Thermometer Hydrometer Storms Storm Thunderstorm Tornado Hurricane Snow storm “Electrical storms”- presence of lightning and thunder. Brief , intense and effect a small area Violent whirling winds sometime visible as a funnel shaped cloud. Huge, rotating storms that form over the ocean near the equator. They produce very strong winds , heavy rains, and very powerful waves. Quickly moving cold fronts and they produce high winds, and very low temperatures feature Cloud types associated with these are the cumulonimbus. Strong winds, heavy rain and sometimes hail, snow or no precipitation at all. Spiraling high winds and extremely low pressure Flooding is what does the most damage and causes the most deaths during a hurricane. This happens mostly when people choose to ignore the evacuation demands. Can result in blizzards, ice storms and a large accumulation of snow. Clouds Type stratus Location High level clouds. Almost always frozen to form ice crystals Low level Weather If isolated- clear weather If dense- stormy weather ahead Layered- brings drizzle and near the ocean- heavy rain cumulus Low level Neutral weather cirrus Weather map satellite radar Ways to Forecast Weather Useful for making predictions. Can show precipitation, wind direction, temperature, cloud cover, high or low pressure, cold or warm fronts, stationary or occluded fronts. A satellite image is a picture of the earth taken from an earth orbital satellite. Most modern weather radars use the pulsedoppler technique to examine the motion of precipitation, but it is only a part of the processing of their data Cut and paste notes in the “Earth Systems” section of the foldable Air Quality affects the quality of life for all organisms. Good health of individuals requires monitoring of the soil, air, and water and taking steps to make sure they are safe. Technology has helped monitor the air quality. Best way to improve air quality is to stop the Burning of fossil Fuels (transportation) Smog-smoke and fog Acid rain- caused by the burning of fossil fuels EPA-Environmental protection agency- protects air quality Natural pollutants-radon, mold, spores, volcanic eruptions, forest fires, plant pollen Ways to Forecast Weather Weather systems generally move west to east across the US. Long range weather forecasting is more difficult than short range. Satellite images and radar – enable forecasters to track movements of large scale weather systems like air masses and fronts. Data such as wind direction, wind speed, air temperature, humidity and air pressure 3 Ways heat is transferred Conduction- transfer of heat from one object to another through DIRECT CONTACT -warmer object transfers energy to cooler object until equal temp - Conductors – transfers heat well like metals - Insulators – poor conductors of heat such as wood, paper, and plastic foam - Convection- transfer of heat by movement of liquid or gas - Increase temp of causes density of substance to decrease and move upward - Radiation- transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves - Sun is biggest source of radiation heat transfer The gases of the atmosphere are used than renewed by the process of respiration, photosynthesis, evaporation and condensation. Air Pressure- refers to the weight of the earth’s atmosphere pressing down on everything at the surface. Low pressure systems- associated with storms High pressure systems- associated with clear and dry conditions Relative humidity- compares the actual amount on water in the air to the amount that the air can hold at that temperature. Meteorologists- study and predict weather. Differences in air pressure causes of weather. The uneven heating of the earth’s surface causes winds Air has weight Air changes with elevation. As you move up in the atmosphere, air molecules move farther apart. So, as air pressure decreases, distance above the earth’s surface increases. Warm air is less dense than cool air (higher temperature=lower air pressure) The cycling of water into and out of the atmosphere makes weather. The more energy the molecules in air have, the hotter it feels. Winds are caused by differences in air pressure.