Carbohydrate, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are 4 major groups
advertisement

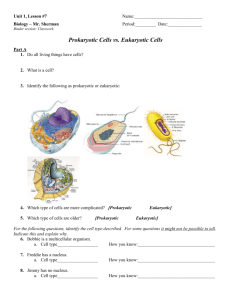
Carbohydrate, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are 4 major groups of biomolecules that make up cells in organisms. They are responsible for everything from the storage of energy to support structures within a cell system. The elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen, in different combinations, make up each of the molecules. How these elements are arranged dictates the type of molecule that’s formed. All organic compounds have a single basic building unit called a monomer. Monomer comes from the Greek words monos, meaning "single" and meros meaning "part." Monomers join together to form polymers. The prefix poly comes from the Greek word polus, meaning many," so polymer means "many parts." Monomers are put together to make variations and different forms of each organic compound. Nucleic Acids are biomolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon and phosphorous. Nucleic acids are polymers made from individual monomers called nucleotides. Nucleotides consist of three parts: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary or genetic information. There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Proteins are biomolecules made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. The monomers of proteins are amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids. The basic structure of an amino acid is a carbon bonded to hydrogen in the center joined with an amine group, a carboxyl, and a functional group. There are 20 different functional groups and they determine the type of amino acid. A generalized structure of an amino acid will show the functional group by using the variable "R" Lipids are large biomolecules that are insoluble in water meaning they do not dissolve in water. Lipids are made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms and can easily be identified by the long chains of carbon and hydrogen. The general shape of a lipid is like the capital letter E. Lipids are used to store energy and are an important part of the cell membrane. Examples of lipids are fats, oils, and waxes. Lipids are made up of 2 main parts a glycerol molecule and a fatty acid. Carbohydrates are compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Examples of carbohydrates are glucose, starch and cellulous. The monomer of a carbohydrate is a monosaccharide (a simple sugar). In monosaccharaides the elements hydrogen, carbon and oxygen make a circle or ring shape. Monosaccharides are bonded together to make other carbohydrates, such as disaccharides and polysaccharides. Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. There are 2 major groups of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek roots pro which means “before” and karyose which means “kernel.” In biology, we use this word root to refer to the nucleus of a cell. So prokaryotic means "before a nucleus." Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane bound nucleus. Instead their genetic material is in a circular loop in a region referred to as the nucleoid. (Nucleoid means nucleus-like.) Members of the kingdoms Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria) and Eubacteria (true bacteria) have prokaryotic cells. (You will learn more about these two kingdoms in another lesson.) Most bacteria come in one of three basic shapes: spirilla, bacilli, and cocci. As you can see in the picture below, spirilla are spiral shaped, bacilli are rod shaped and cocci are round. The word eukaryotic comes from the Greek roots eu means “true” and karyose which means “kernel.” (Remember in Biology we refer to this as the nucleus.) So, eukaryotic means “true nucleus.” Based on this definition what do you think the major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is? Members of the kingdoms Protista, Fungi, Plantae (plants) and Animalia (animals) all have eukaryotic cells. In this lesson we will focus on plant and animal cells. Review Questions: 1. What is the major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus and eukaryotic cells do. 2. What are the major differences between an animal cell and a plant cell? Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplast and animal cells do not. Plant cells typically have larger vacuoles than animal cells. 3. Identify what type of cell this is. It is a eukaryotic (because it has a nucleus) and it is a plant cell (because it has a cell wall and chloroplasts)