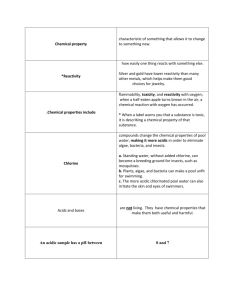
What are the Chemical Properties of Water?
advertisement

CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET What are the Physical Properties of Oxygen? Color Colorless Phase Gas Oxygen changes from a gas to a liquid at a temperature of -182.96°C (297.33°F) when it takes on a slightly bluish color Liquid oxygen can then be solidified or frozen at a temperature of -218.4°C *Allotropic There are several known allotropes including molecular oxygen O2 (aka normal atmospheric oxygen, dioxygen or triplet oxygen) and ozone (O3) Ozone is a colorless gas Odor Oxygen is an odorless gas Taste A tasteless gas Conductivity A poor conductor of heat and electricity Solubility Slightly soluble in water, alcohol and some other common liquids Density It is denser than air. The density of oxygen is 1.429 grams per liter Viscosity Resistance to flow - stickiness. The viscosity is 189 millipoises (at 0°C). What are the Chemical Properties of Oxygen? Chemical Formula O Oxygen gas (O2) Ozone (O3) Flammability Does not burn Combustion Supports combustion but does not burn Compounds Occurs in many compounds, including water, carbon dioxide, and iron ore Oxidation The common reaction in which it unites with another substance is called oxidation Oxides of some metals form peroxides by the addition of oxygen Ozone Properties - What are the Chemical Properties of Ozone? Ozone Ozone soluble in alkalis and cold water Oxidation A strong oxidizing agent Reactivity Can be produced by electric discharge in oxygen or by the action of ultraviolet radiation on oxygen in the stratosphere (where it acts as a screen for ultraviolet radiation) CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET What are the Physical Properties of Iron? Color Silver-gray metal Malleability Capable of being shaped or bent Ductility Easily pulled or stretched into a thin wire Luster Has a shine or glow Conductivity Good transmission of heat or electricity Allotropy It occurs in two or more crystalline forms in the same physical state Tensile It can be stretched without breaking Ferromagnetic Easily magnetized What are the Chemical Properties of Iron? Chemical Formula Fe Toxicity Non Toxic Reactivity with water Reacts with very hot water and steam to produce hydrogen gas Oxidation Readily combines with oxygen in moist air which produces iron oxide also known as rust Solubility Dissolves in acids What are the Physical Properties of Copper? Color Reddish-Brown metal Malleability Capable of being shaped or bent Ductility Easily pulled or stretched into a thin wire Luster Has a shine or glow Conductivity Excellent transmission of heat or electricity What are the Chemical Properties of Copper? Chemical Formula Cu Toxicity Poisonous in large amounts Reactivity with water It does not react with water Oxidation Readily combines with water and carbon dioxide producing hydrated copper carbonate Corrosion Corrodes when exposed to air CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET What are the Physical Properties of Sodium? Color Silver-White Malleability Capable of being shaped or bent Ductility Easily pulled or stretched into a thin wire Luster Has a shine or glow Conductivity Good transmission of heat or electricity Softness Soft enough to be cut with a knife What are the Chemical Properties of Sodium? Chemical Formula Na Reactivity with water Reacts explosively with water Oxidation Combines with oxygen at room temperature Reactivity with water Reacts violently with water Flammability Burns with a brilliant golden-yellow flame Reactivity with acids Reacts with acids to produce hydrogen gas Dissolves in mercury to form a sodium amalgam What are the Physical Properties of Carbon? *Allotropic Two allotropes of carbon have different crystalline structures: diamond and graphite The physical properties of carbon vary widely with the allotropic form. Forms of Carbon Graphite, diamonds and coal are all nearly pure forms of carbon Color Diamond is highly transparent. Graphite is opaque and black Hardness Diamond is one of the hardest substances known to man. Graphite is soft and often used as the "lead" in lead pencils Conductivity Diamond has a very low electrical conductivity. Graphite is a very good conductor Brittleness Very brittle, and cannot be rolled into wires or pounded into sheets Phase Solid What are the Chemical Properties of Carbon? Chemical Formula C CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET Oxidation Combines with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide (CO2 ) and carbon monoxide (CO) Reactivity Carbon does not dissolve in, or react with, water or acids Chains of Atoms Carbon has the ability to make long strings, or chains, of atoms Compounds Carbon forms more compounds than all other elements combined; several million carbon compounds are known Buckminsterfulleren C60 Carbon also occurs in a newly discovered form known as fullerenes or buckyballs. A fullerene is any molecule composed entirely of carbon. Fullerenes are similar in structure to graphite What are the Physical Properties of Hydrogen? Color Colorless Phase Gas Hydrogen changes from a gas to a liquid at a temperature of 252.77°C (-422.99°F) It changes from a liquid to a solid at a temperature of -259.2°C (434.6°F) Odor Hydrogen is an odorless gas Taste A tasteless gas Density The lowest of any chemical element, 0.08999 grams per liter - the least dense of all gases Solubility Slightly soluble in water, alcohol and some other common liquids What are the Chemical Properties of Hydrogen? Chemical Formula H Hydrogen gas (H2) Oxidation It burns in air or oxygen to produce water H2 reacts with every oxidizing element Reactivity with gases Combining hydrogen and nitrogen at high pressure and temperature produces ammonia (NH3) Combined with carbon monoxide produces methanol (CH3OH) Reactivity with nonmetals It combines readily with non-metals, such as sulfur and phosphorus It combines readily with the halogens which include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine Flammability Highly Flammable, a highly combustible diatomic gas CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET Combustion When mixed with air and with chlorine it can spontaneously explode by spark, heat or sunlight. Example: the destruction of the Hindenburg airship Acid Compounds Common acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), nitric acid (HNO3), acetic acid (HC2H3O2) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4) What are the Physical Properties of Chlorine? Color Greenish-yellow Phase Gas Odor Disagreeable, suffocating smell Density About two and one-half times as dense as air Solubility Is soluble in water. Its aqueous solution is called chlorine water which consists of a mixture of chlorine, hydrochloric acid, and hypochlorous acid Boiling Point The boiling point of chlorine is –34.05°C Melting Point The melting point is –101°C. What are the Chemical Properties of Chlorine? Chemical Formula Cl Corrosion Highly corrosive Toxicity Highly Toxic Compounds PVC, hydrochloric acid and Sodium chloride (table salt) Reactivity with metals Most metals react with dry chlorine only upon heating Combustion Alkali metals react with chlorine by combustion when tiny amounts of moisture are present Explosive Specific mixtures of chlorine and hydrogen can be explosive Oxidation It forms the oxides Cl2O, ClO2, O2O6, Cl2O7, and Cl2O8, as well as hypochlorites (salts of hypochlorous acid), chlorites and chlorates What are the Physical Properties of Lead? Color Bluish-White Malleability Capable of being shaped or bent Conductivity Poor transmission of heat or electricity Softness Relatively Soft CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET Tensile It can be stretched without breaking Luster A shine or glow Crystalline structure Face-centered cubic crystalline structure What are the Chemical Properties of Lead? Chemical Formula Pb Reactivity with water Dissolves slowly in water Oxidation Does not readily react with oxygen in the air Flammability Does not burn Reactivity with acids Reacts quickly with hot acids but slowly to cold acids Corrosion Very resistant to corrosion but tarnishes upon exposure to air Toxicity Toxic What are the Physical Properties of Calcium? Color Silvery-white metallic Phase Solid Hardness Relatively soft metal Crystalline structure Cubic Ductility It can be beaten into extremely thin sheets. It can be pressed, rolled, and cut Malleability Capable of being shaped or bent Melting point Melting point is 851°C Boiling point Boiling point is 1482°C What are the Chemical Properties of Calcium? Chemical Formula Ca Oxidation Used as a deoxidizer in steel Isotopes Six Compounds Compounds include limestone, marble, and gypsum Flammability When heated in air or in oxygen it ignites Reactivity with water Reacts with cold water rapidly at first, but the reaction is then slowed due to the formation of a film of Calcium hydroxide - Ca(OH)2. Reactivity with acids Highly reactive CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET What are the Physical Properties of Sulfur? Color Pale yellow - Non-metallic Phase Solid Crystalline structure & Forms Rhombic, Amorphous and Prismatic *Allotropic There are several known allotropes including brimstone Odor Odorless Taste Tasteless Solubility Insoluble in water Boiling point The boiling point of sulfur is 444.6°C Conductivity A poor conductor of heat and electricity Viscosity (resistance to flow - stickiness) Upon melting, sulfur is converted into a mobile yellow liquid, which turns brown and becomes a viscous, dark brown mass at about 190°C. The viscosity decreases above 190°C, and at 300°C sulfur again becomes a flowing liquid What are the Chemical Properties of Sulfur? Chemical Formula S Compounds Familiar compounds are Sodium sulfite, hydrogen sulfide (a poisonous gas that smells like rotten eggs) and sulfuric acid Oxidation The oxides are sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide, which when dissolved in water make sulfurous acid and sulfuric acid, respectively Reactivity It is chemically reactive, especially upon heating, and combines with almost all the elements. Upon heating, sulfur reacts with metals, forming the corresponding sulfides What are the Physical Properties of Potassium? Color Silver-white Phase Solid Melting point Melting point of 63°C (145°F) - very low for a metal Color Silvery-white metal Density Less than water What are the Chemical Properties of Potassium? Chemical Formula K CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET Reactivity with water It reacts with water violently and gives off hydrogen gas Reactivity It reacts readily with all acids and with all non-metals, such as sulfur, chlorine, fluorine, phosphorus, and nitrogen Highly or explosively reactive Compounds Useful compounds include the bromide, KBr, the cyanide, KCN, Potassium carbonate K2CO3 Substances containing potassium impart a purple color to a flame Oxidation Rapidly oxidizes in air Alloys Alloyed with sodium as a cooling medium in nuclear reactors What are the Physical Properties of Mercury? Color Silver-White mirror-like appearance Luster Mirror like Conductivity Good transmission of heat or electricity Surface Tension High surface tension. When mercury is spilled, it breaks up into tiny beads which often become lodged in cracks Density High Density What are the Chemical Properties of Mercury? Chemical Formula Hg Toxicity Highly toxic Reactivity with acids Reacts with some acids when they are hot, but does not react with most cold acids Oxidation Does not readily react with oxygen in the air Compounds Many of mercury's compounds are pigments, pesticides and medicines. Vermilion, a vivid red pigment is a chemical compound of mercury and sulfur and is known as red sulfide of mercury Mercuric chloride HgCl2, is used as an insecticide, in rat poison Amalgam Mercury forms a special type of alloy called an amalgam which is an alloy containing mercury. An amalgam of mercury, silver and tin is used in dentistry for filling teeth. What are the Physical Properties of Silicon? Color Pure silicon is a hard, dark gray solid Phase Solid Luster A metallic shine or glow CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET *Allotropic Silicon has two allotropic forms, a brown amorphous form, and a dark crystalline form Solubility Soluble in hydrofluoric acid and alkalis Melting point Melts at 1417°C Boiling point Boils at 2600°C Conductivity It is a semi-conductor What are the Chemical Properties of Silicon? Chemical Formula Si Compounds Silicon forms compounds with metals (silicides) and with non-metals Oxidation Combined with oxygen as silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) or with oxygen and metals as silicate minerals. It is stable in air even at elevated temperatures owing to the formation of a protective oxide film Flammability Dark-brown crystals that burn in air when ignited Is transparent to long-wavelength infra-red radiation Reactivity with acids Dissolves only in a mixture of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid What are the Physical Properties of Iodine? Color Violet black. A sgray solid that changes into purple vapors when heated Luster Has a shine or glow Odor Strong, harsh odor Crystalline structure Rhombic Density Heavy What are the Chemical Properties of Iodine? Chemical Formula Hg Toxicity Poisonous halogen Oxidation It does not combine directly with oxygen Compounds With hydrogen it forms hydrogen iodide, which in water solution becomes hydriodic acid. Its compounds are used in medicine and photography and in dyes Corrosion Highly corrosive Reactivity with water Dissolves only slightly in water CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET Reactivity with heat Moves from the solid to the vapor state (sublimation) What are the Physical Properties of Water? Color Nearly colorless with a hint of blue Odor None Taste Bland Density 1.000 g/ml. The density of water is approximately one gram per cubic centimeter Boiling Point 100 °C Conductivity Water is a good conductor of heat Compressibility The compressibility of water reduces the sea level Specific Heat Water has a high specific heat. Specific heat is the amount of energy required to change the temperature of a substance Surface Tension Water has a high surface tension - it is adhesive and elastic Cohesion Water is attracted to other water Adhesion Water can also be attracted to other materials What are the Chemical Properties of Water? Chemical Formula H2O - two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom Solvation Water dissolves more substances than any other liquid pH Pure water has a neutral pH of 7, which is neither acidic nor basic Ionization Water weakly ionizes Reactivity Metals such as gold, silver, copper, tin, etc. do not react with water CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET Examples of Physical Properties Examples of Physical properties are: Color (vividness of visual appearance) Luster (a shine or glow) Hardness (rigid and resistant to pressure) Odor (distinctive smell) Luminescence (emitting light not caused by heat) Conductivity (transmission of heat or electricity or sound) Solubility (ability to be dissolved) Malleability (capable of being shaped or bent) Ductility (easily pulled or stretched into a thin wire) Density (the measure of the relative "heaviness" of objects with a constant volume) Viscosity (resistance to flow - stickiness) Compressibility (made more compact) Freezing point (temperature below which a liquid turns into a solid) Boiling point (temperature at which the vapor pressure is large enough that bubbles form inside the body of the liquid) Melting point (temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid) Crystalline structure (geometric pattern e.g. rectangular, hexagonal) Allotropic - Allotropes are forms of an element with different physical and chemical properties occurring in two or more crystalline forms in the same physical state. The physical properties can vary widely with the allotropic form. Example: Forms of Carbon are graphite and diamonds. Diamond is highly transparent. Graphite is opaque and black In a physical change, the substances are not altered chemically, but merely changed to another phase (i.e. gas, liquid, and solid) or separated or combined. Examples of Chemical Properties Examples of chemical properties are: Flammability (the ability to catch on fire) Toxicity (the ability to be poisonous) Radioactivity (giving off ionizing radiation) Heat of combustion (amount of heat released when the substance is completely burned) Reactivity with water (what happens when a substance reacts with water) Reactivity with acids (what happens when a substance reacts with an acid) Oxidation (the combination of a substance with oxygen) Corrosion (a corrosive substance that will destroy or irreversibly damage another surface) CLASSROOM SET DO NOT WRITE ON THIS SHEET Elements -vs. - Compounds Computer Search Physical and Chemical Properties All substances have properties that we can use to identify them. For example we can identify a person by their face, their voice, height, finger prints, DNA etc... The more of these properties we identify, the better we know the person. In a similar way matter has properties - and there are many of them. There are two basic types of properties that we can associate with matter. These properties are called Physical properties and Chemical properties: You can find examples of chemical and physical properties on the back of these lab instructions. Purpose: Students will compare the chemical and physical properties of a compound and the elements that make it up. Procedures: 1. Choose an element from the following list: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, sodium, potassium, iron, calcium, nitrogen, fluorine, chlorine, sulfur, Bromine, Iodine, lithium, magnesium. 2. Find the physical and chemical properties of the element. 3. Choose two compounds that contain the element you researched. For example; if I chose hydrogen as my element, then I could choose water (H2O) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) as my compounds. 4. Find some physical and chemical properties of each of the compounds. 5. Use the internet to search the chemical and physical properties of the element and compounds. a. You may use the following sites to research the elements or compounds. These are only a few of the sites you could use. http://chemistry.about.com/library/blperiodictable.htm http://www.webelements.com/ http://www.chemicalelements.com/index.html http://www.chemspider.com/ http://www.elementalmatter.info Element: _______________ Physical Properties Compound: ______________ Physical Properties Chemical Properties Chemical properties Compound: ______________ Physical Properties Chemical Properties