Chapter 9: Burns
advertisement

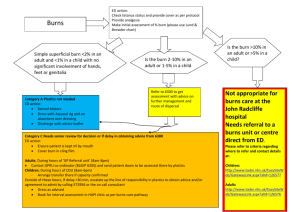
Chapter 9: Burns Types of Burns: Thermal burns: caused by flames, contact with hot objects, flammable vapor that ignite and causes a flash or an explosion, steam, or hot liquid Chemical burns: Can cause tissue damage and death if they come in contact with the skin. Three types of chemicals, acids, alkalis, and organic compounds are the most common chemical burns Electrical burns: The severity of the injury from electric current depends on the type of current (direct or alternating), the voltage, the area of the body exposed, and the duration of contact. Depth of Burns: First degree(superficial): Affect the skin’s outer layer Characteristics include redness, mild swelling, tenderness and pain Second-degree (partial-thickness) burns: Extend though the skin’s entire outer layer and into the inner layer Blisters, swelling, weeping of fluids Third-degree (full thickness) burns: Severe burns that penetrate all the skin layers and the underlying fat and muscle The skin looks leathery, waxy, or pearly gray, sometimes charred The victim feels no pain from a third degree burn because the nerve endings have been damaged or destroyed Extent of Burns: Determine the severity of the burn Rule of the Hand: The victim’s entire hand represents about 1% of his or her total body surface area (BSA) Burns on the face, hands, feet, and genitals are more severe than on other body parts Care of Thermal Burns: First-Degree Burns: Cool the burn with cold water until the part is pain free (at least 10 minutes) After the burn cools, apply an Aloe Vera gel or skin moisturizer to keep skin moistened and reduce itching and peeling Give ibuprofen to relieve pain and inflammation. Give acetaminophen to children Second Degree Burns: Remove clothing and jewelry from the burned area Cool the burn with cold water until the part is pain free After the burn has been cooled, apply antibiotic ointment Cover the burn loosely with a dry, nonstick, sterile or clean dressing to keep the clean Give ibuprofen to relieve pain and inflammation. Give acetaminophen for children Large Second Degree and All Third Degree Burns Monitor breathing Remove clothing and jewelry that is not stuck to the burned area Cover the burn with a dry, nonstick, sterile or clean dressing Care for shock Seek medical care Chemical Burns: a chemical burn results when a caustic or corrosive substance touches the skin Remove as fast as possible Care for Chemical Burns: Immediately flush the area with a large quantity of water for 20 minutes, if the chemical is a dry powder brush the powder from skin before flushing Remove the victims contaminated clothing and jewelry while flushing with water Cover the affected area with a dry, sterile or clean dressing Seek medical care Electrical Burns: Thermal (flame): clothing or objects in contact with the skin are ignited by an electric current Arc burn (flash): when electricity jumps from one spot to another True electrical injury (contact): when an electric current passes directly through the body, which can disrupt the normal heart rhythm and cause cardiac arrest and burns Care for Electrical Burns: Make sure the area is safe, unplug, disconnect, or turn of the power, if that is possible call 9-1-1 Monitor breathing If the victim fell, check for a possible spinal injury Care for shock Call 9-1-1 for medical care Chapter 9: Burns Types of Burns: Thermal burns: _______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Chemical burns: Can cause tissue damage and death if they come in contact with the skin. Three types of chemicals, acids, alkalis, and organic compounds are the most common chemical burns Electrical burns: The severity of the injury from electric current depends on the type of current (direct or alternating), the voltage, the area of the body exposed, and the duration of contact. Depth of Burns: First degree(superficial): ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Second-degree (partial-thickness) burns: Extend though the skin’s entire outer layer and into the inner layer Blisters, swelling, weeping of fluids Third-degree (full thickness) burns: ________________________________________ ________________________________________ The skin looks leathery, waxy, or pearly gray, sometimes charred The victim feels no pain from a third degree burn because the nerve endings have been damaged or destroyed Extent of Burns: Determine the severity of the burn ______________________The victim’s entire hand represents about 1% of his or her total body surface area (BSA) Burns on the face, hands, feet, and genitals are more severe than on other body parts Care of Thermal Burns: First-Degree Burns: Cool the burn with cold water until the part is pain free (at least 10 minutes) After the burn cools, apply an Aloe Vera gel or skin moisturizer to keep skin moistened and reduce itching and peeling ________________________________________ ____________________________ Second Degree Burns: Remove clothing and jewelry from the burned area ________________________________________ After the burn has been cooled, apply antibiotic ointment Cover the burn loosely with a dry, nonstick, sterile or clean dressing to keep the clean Give ibuprofen to relieve pain and inflammation. Give acetaminophen for children Large Second Degree and All Third Degree Burns ________________________________________ Remove clothing and jewelry that is not stuck to the burned area Cover the burn with a dry, nonstick, sterile or clean dressing ________________________________________ Seek medical care Chemical Burns: a chemical burn results when a caustic or corrosive substance touches the skin Remove as fast as possible Care for Chemical Burns: ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Remove the victims contaminated clothing and jewelry while flushing with water Cover the affected area with a dry, sterile or clean dressing Seek medical care Electrical Burns: Thermal (flame): ________________________________________ Arc burn (flash): when electricity jumps from one spot to another ________________________________________when an electric current passes directly through the body, which can disrupt the normal heart rhythm and cause cardiac arrest and burns Care for Electrical Burns: Make sure the area is safe, unplug, disconnect, or turn of the power, if that is possible call 9-1-1 ________________________________________ If the victim fell, check for a possible spinal injury Care for shock ________________________________________