Burns Initial Evaluation and Management
advertisement

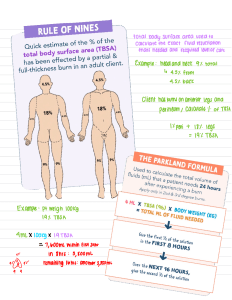
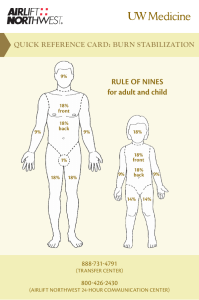
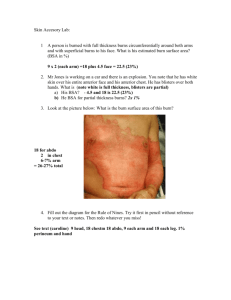
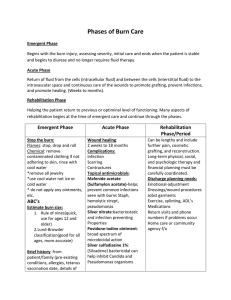
BURNS Initial Evaluation & Management Christopher P. Brandt M.D. Associate Professor of Surgery Case Western Reserve University Joseph B. Your patient is brought to the E.D. by the EMS service. He is a 14 year-old male who was involved in a house fire History What other points of history do you want to know? History, Joseph B. Neighbors heard an explosion Patient found confused, outside of the house Cannot remember what occurred Denies shortness of breath Transport time of twenty minutes PMH of ADHD Tetanus – up to date Physical Examination What would you look for? Physical Examination VS T=96.5 P=140 R=24 BP=90/60 Awake; No hoarseness or stridor Soot in mouth Clear breath sounds Burns involving face, neck, trunk, arms and upper legs (see photos) Doppler pulses in all extremities Physical Examination How do you determine the extent and depth of the burn injuries? What findings suggest inhalation injury? Extent of burn % total body surface area 1 8 Burn Depth Color Moistness Capillary refill/Blanching Sensation Blistering Superficial Second Degree Deeper second degree Third Degree Inhalation injury Indicators Occurred in closed space Cough, dyspnea, wheezing, hoarseness, stridor Facial burns / Singed facial hair Carbonaceous sputum Hypoxia Labs What would you obtain? Lab Results CBC - WBC-12.0 Hct-49% Electrolytes -Na-147 Cl-100 K-4.5 BUN-12 ABG - 7.31/35/125 on 50%VM Carboxyhemoglobin- 21% Tox. Screen - Negative U/A - Normal Interventions at this point? Interventions at this point? Assess airway; Intubation ? Oxygen Fluid resuscitation Foley Catheter NG tube Wound care Pain medication Interventions Why is fluid resuscitation important? How do you estimate fluid requirements? How do you monitor response to initial fluid therapy? What complications can occur from over- or under- resuscitation? Fluid Management Edema formation Systemic inflammatory response Capillary leak/ Increased vascular permeability Loss of skin barrier Zones of injury Parkland formula Crystalloid 4 x %TBSA x wt (kg) ½ of total in first eight hours Goal of ½ - 1 cc/kg/hr U.O. Studies What further studies/tests would you want at this time? Studies CXR – Basilar atelectasis EKG – Sinus tachycardia ? Bronchoscopy Management What would you do in the following scenarios? Low urine output Loss of Doppler signals in the hands Inadequate ventilation with high airway pressures? Management Escharotomy Management What are the principles of management of the inhalation injury? What will be the basic strategies for management of the burn wounds? Questions? Acknowledgment The preceding educational materials were made available through the ASSOCIATION FOR SURGICAL EDUCATION In order to improve our educational materials we welcome your comments/ suggestions at: feedbackPPTM@surgicaleducation.com