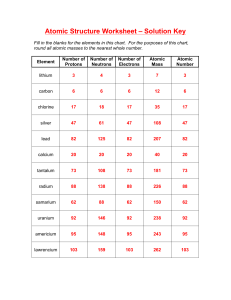
Periodic Trends Worksheet Review
advertisement

Periodic Trends Worksheet Review 1. Rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius: carbon, aluminum, oxygen, potassium (Hint: Determine which atom has the smallest radius and then use the trend). 2. Rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity: sulfur, oxygen, neon, aluminum (Hint: Determine which atom has the smallest electronegativity and then use the trend). 3. What is the difference between electronegativity and ionization energy? 4. Why does fluorine have a higher ionization energy value than iodine? Handout #117 5. Why do elements in the same family generally have similar properties? 6. Rank the following elements by decreasing atomic radius: magnesium, silicon, calcium, aluminum. 7. For the following pairs of atoms and their corresponding ions, determine which one is larger. & Na+ a. Na b. Ba2+ & Ba c. O & O2- d. Cl- & Cl e. Al f. N3- & N & Al3+ 8. Rank the following elements by decreasing electronegativity: sulfur, silicon, phosphorus. germanium, 9. Why does the atomic radius increase as you go down a group or family? 10. Why does the atomic radius generally decrease as you go across a period in the periodic table? Handout #117 Periodic Trends Worksheet - Solutions 1) Rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius: carbon, aluminum, oxygen, potassium. From smallest to largest: oxygen < carbon < aluminum < potassium 2) Rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity: sulfur, oxygen, neon, aluminum. From smallest to largest: neon < aluminum < sulfur < oxygen 3) What is the difference between electron affinity and ionization energy? Electron affinity is a measure of the energy change that occurs when an atom grabs an electron. Ionization energy is a measure of how much energy it takes to pull electrons off of an element. Both values are for atoms in the gas phase. 4) Why does fluorine have a higher ionization energy than iodine? It is harder to pull electrons off of fluorine because fluorine has a higher electronegativity than iodine. Iodine has a much lower electronegativity than fluorine because of the shielding effect, which states that the electrons in inner energy levels tend to push electrons in outer energy levels away from the nucleus. This pushing makes it harder for iodine to grab electrons. 5) Why do elements in the same family generally have similar properties? Because they have similar electron configurations and the same number of valence electrons. Because valence electrons are responsible for most of the chemistry we observe, this similarity causes the properties of the elements to also be similar. Handout #117