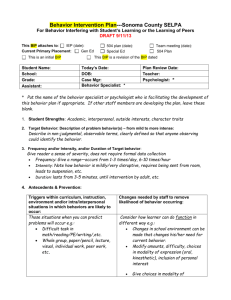
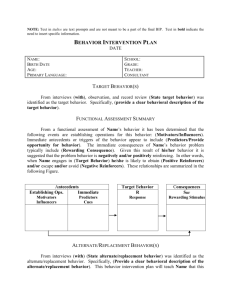
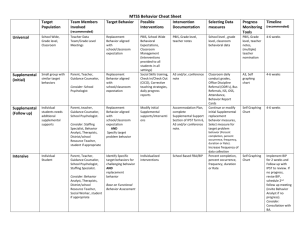
Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP)
advertisement
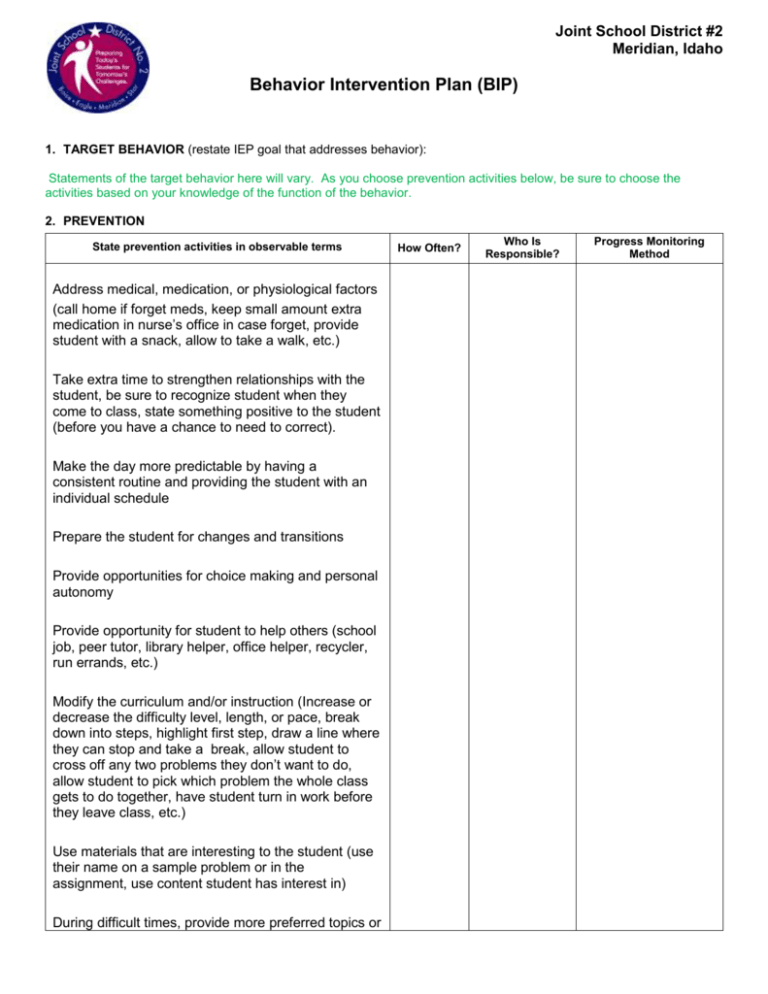
Joint School District #2 Meridian, Idaho Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) 1. TARGET BEHAVIOR (restate IEP goal that addresses behavior): Statements of the target behavior here will vary. As you choose prevention activities below, be sure to choose the activities based on your knowledge of the function of the behavior. 2. PREVENTION State prevention activities in observable terms Address medical, medication, or physiological factors (call home if forget meds, keep small amount extra medication in nurse’s office in case forget, provide student with a snack, allow to take a walk, etc.) Take extra time to strengthen relationships with the student, be sure to recognize student when they come to class, state something positive to the student (before you have a chance to need to correct). Make the day more predictable by having a consistent routine and providing the student with an individual schedule Prepare the student for changes and transitions Provide opportunities for choice making and personal autonomy Provide opportunity for student to help others (school job, peer tutor, library helper, office helper, recycler, run errands, etc.) Modify the curriculum and/or instruction (Increase or decrease the difficulty level, length, or pace, break down into steps, highlight first step, draw a line where they can stop and take a break, allow student to cross off any two problems they don’t want to do, allow student to pick which problem the whole class gets to do together, have student turn in work before they leave class, etc.) Use materials that are interesting to the student (use their name on a sample problem or in the assignment, use content student has interest in) During difficult times, provide more preferred topics or How Often? Who Is Responsible? Progress Monitoring Method State prevention activities in observable terms activities Alternate preferred and less preferred tasks. (try a first____, then ____ schedule) Analyze and sequence tasks Increase reinforcement for correct responses Teach skills within typical daily routines Get typical peers to provide modeling Organize the physical environment Allow student to alternate between two approved work areas (2 desks, allow to stand at table at back of room, etc.) Organize the student’s tasks and work materials; then teach him/her to do it. Clarify with the student what is expected before each task or activity. Develop or modify routines. Create an individual written picture, or object schedule for the student. Prepare the individual for changes ahead of time. Minimize waiting periods or provide other activities. Have alternate plan in place for substitutes (maybe goes to class in another room with familiar teacher, stay in smaller group instruction, etc.) Use Positive Phrasing (rather than Negative) Positive phrasing: “If you finish your reading by lunch, we can all go outside together and play a game.” Negative phrasing: “If you do not finish your reading by lunch, you will have to stay inside until it’s done.” Humor directed either at the teacher or the situation— How Often? Who Is Responsible? Progress Monitoring Method Joint School District #2 Meridian, Idaho Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) State prevention activities in observable terms How Often? Who Is Responsible? never at the child—can defuse tensions as well as redirect children. Humor must never be used to demean a child or be used in a manner that might encourage others in the class to ridicule the child. Copy to the confidential folder, each service provider, and the parent/adult student. XIII - 3 Progress Monitoring Method Document date: Student’s Name: Native Lang: District: Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) District ID: Ethnicity: State ID: Birth Date: Page ___ of ___ Grade: Sex: Age: School: 3: WHAT WILL BE TAUGHT? What Will Be Taught? (What other behaviors or skills will be taught so that the student can meet his or her needs in an acceptable manner?) How Often? Who Is Responsible? Progress Monitoring Method Hint: Teach adaptive skills in the natural context Create opportunities to practice skills Teach self-management skills Choose skills to teach that the student can use across settings when possible Identify skills/behaviors that produce the same outcome/function for the student as the target behavior (replacement behavior) Teach replacement behaviors and other positive skills when the student is not in crisis Prompt the student to use replacement skills when it is predictable that the target behavior will occur (i.e., before the behavior occurs or very early in a chain) Increase reinforcement for replacement and other positive behaviors (i.e., reinforce more often, quicker, more reliably, with more powerful reinforcers) Te Teach student to request a short break when he/she is beginning to feel overwhelmed (can be in class or out of class in specified location) Teach student to recognize physical changes in body when he/ she is beginning to feel agitated Preteach expectations for behavior for new situations and practice with student Teach student self-monitoring strategies (how am I feeling, am I paying attention, etc.) Teach Stop, Relax and Think method: 1. Define problem 2. Decide who “owns” the problem 3. Think of as many solutions as possible to solve the problem 4. Select a solution to try 5. Use the solution 6. Evaluate its success Form 520b Copy to the confidential folder, each service provider, and the parent/adult student. Joint School District #2 Meridian, Idaho Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) XIII - 4