Ideal Gas Law
advertisement

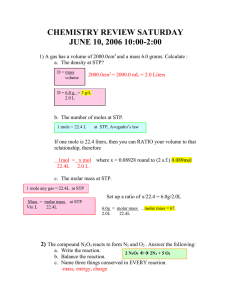
Ch. 11.3 Ideal Gas Law and Gas Stoichiometry Notes Bell work: The reaction shown represents the oxidation of ammonia (NH3). 4NH3 + 5 O24NO+ 6H2O 1. How many moles of water will be formed from 34 grams of ammonia? 2. What volume, in liters, will 75.4 grams of O2 occupy at STP? Ideal Gas Law • Ideal gas law: mathematical relationship among pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas. PV = nRT • R is known as the ideal gas constant. L atm R = 0.0821 --------------mol K • Be sure to match the units of the known quantities and the units of R. Comparing the Volumes of Reacting Gases • In the early 1800s, Gay-Lussac observed that when gases reacted, they did so in simple and definite volume proportions. • Example: hydrogen gas + oxygen gas → water vapor 2 L (2 volumes) +1 L (1 volume) 2 L (2 volumes) • Gay-Lussac’s law of combining volumes of gases states that at constant temperature and pressure, the volumes of gaseous reactants and products can be expressed as ratios of small whole numbers. • The coefficients in chemical equations of gas reactions reflect not only molar ratios, but also ________________ ________________. – Example: 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) 2 mole + 1 mole 2 mole 2 volumes + 1 volume 2 volumes Sample Problem The complete combustion of propane, C3H8, occurs according to the following balanced equation. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) How many liters of oxygen (O2) will be required for the complete combustion of 0.350 L of propane? Gas Stoichiometry The industrial production of ammonia (NH3) proceeds according to the following equation: N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2 NH3(g) If 20.0 mol of nitrogen (N2) is available, how many liters of NH3 can be produced at STP? EOC Sample Question The equation represents the breakdown of potassium chlorate (KClO3) 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 What volume of oxygen gas (O2) does 20.0 grams of potassium chlorate (KClO3) produce at STP based on the equation shown? A. 5.48 L C. 67.3 L B. 7.80 L D. 72.9 L Sample Problems 1. What is the pressure exerted by a 0.475 mol sample of nitrogen gas in a 10.0 L container at 25°? 2. Calculate the mass of 675 mL of NH3 at 725 mm Hg at 27°C.