Avogadro*s Law and Molar Volume
advertisement
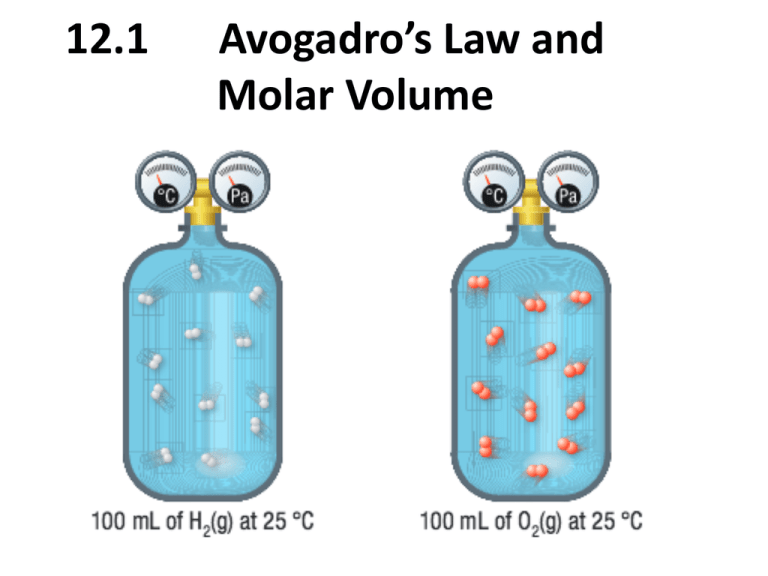
12.1 Avogadro’s Law and Molar Volume The Law of Combining Volumes • Water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity 2H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g) • H2O consists of 2 H atoms and 1 O atom. • When water decomposes twice the volume of hydrogen as oxygen is produced The Law of Combining Volumes • Proposed by Joseph Gay-Lussac • The Law of Combining Volumes: When measured at the same temperature and pressure, volumes of gaseous reactants and products of chemical reactions are always in simple ratios of whole numbers • Example: Combining 1.0 unit of H2(g) and Cl2(g) produces 2.0 units of HCl(g) The Law of Combining Volumes • Ammonia gas can be produced by combining nitrogen, N2(g), and hydrogen, H2(g) N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Coefficients: Mole Ratio: Volume Ratio: 1 1 1 3 3 3 2 2 2 • While Gay-Lussac Proposed the law, he was unable to explain it Avogadro’s Law • Avogadro’s law: the volume (V) of a gas is directly related to the amount (n) of the gas when temperature and pressure remain constant V1/n1 = V2/n2 Where: V is the Volume in L n is the amount in mol Avogadro’s Law • Explains the law of combing volumes: – Equal volumes of gases, at the same temperature and pressure, contain the same number of molecules. – The mole ratios provided by the balanced equation are also the ratios of volumes – Example: 100mL of H2(g) at 25°C contains the same number of molecules as 100mL of O2(g) at 25°C Example A balloon with a volume of 34.5 L is filled with 3.2 mol of helium gas. To what volume will the balloon expand if another 8.0 g of helium is added? (Assume that pressure and temperature do not change.) Molar Volume • Molar Volume: the volume occupied by one mole of a gas. It is the same for all gases. – One mole of any gas at STP (0°C, 101.3kPa) occupies 22.4L – One mole of any gas at SATP (25°C, 100kPa) occupies 24.8L Example 1. A party balloon has 2.50 mol of helium gas in it at STP. What is the volume of the balloon?(at STP 1mol = 22.4L) 1. A sample of helium at SATP has a mass of 32.0 g. What volume does this mass of gas occupy? (at SATP 1mol = 24.8L) Homework Read Section 12.1 Questions p. 579 #1-3 p. 580 #1-3 p. 581 #4