FUNDING AND FTE Christopher J. Lemons, Ph.D. CURRENT
advertisement

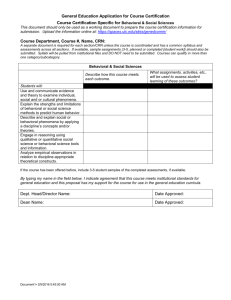
FUNDING AND FTE Christopher J. Lemons, Ph.D. CURRENT RESEARCH GRANTS Puranik, C., Lemons, C.J., & Al Otaiba, S. (Under Review). Peer-assisted writing strategies for Kindergarten (PAWS). Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. ($1,117,128). Co-principal Investigator. 0.10 FTE 7/2012 – 6/2015. Lemons, C.J., Puranik, C., Al Otaiba, S., & Fidler, D. (2011-2014). Enhancing reading instruction for children with Down syndrome: A behavioral phenotypic approach (Project ERIC). Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. ($1,445,011). Principal Investigator. 0.25 FTE 07/2011 – 06/2014. ABSTRACTS PAWS Purpose: While both reading and writing are necessary for success in school and the workplace, the vast majority of research and intervention development has focused on reading skills. Most of this research suggests that early intervention is important to improving reading achievement. However, less is known about writing, and fewer interventions have been developed to help students learn to write. Still, research in writing that has been completed to date suggests that early intervention may be important. Before learning how to compose long texts, children must first learn skills such as transcription (mechanics of writing, such as spelling and handwriting) and text-generation (translating thoughts into text). The current project aims to develop a writing intervention for kindergarten children. Building on the Peer-Assisted Learning Strategies (PALS) framework, this new writing intervention, Peer Assisted Writing Strategies (PAWS) will allow for increased learning time as pairs of students are asked to work together to complete highly structured activities aimed at increasing writing skill. Intervention: The intervention will incorporate five principles of instructional design: (1) explicit instruction with extensive modeling by the teacher; (2) multiple opportunities for children to practice; (3) integration of reading and writing through unifying themes; (4) brief, developmentally-appropriate activities to boost engagement; and (5) use of peer assisted learning strategies. Lessons will be designed to last approximately 30 minutes, and will occur three days each week over 16 weeks. Weekly lessons will include letter writing automaticity instruction, spelling lessons, and instruction regarding composition of sentences and paragraphs. Students will work in pairs to practice writing. High achieving and low achieving students will be paired together, with the higher-achieving student first serving as a Coach and the lower-performing student first serving as Writer. Children in each pair will take turns being Coach and Writer, and pairs will be reassigned every 4–6 weeks. Research Design: This project involves an iterative developmental design including the development of lessons, two phases of implementation, a feasibility pilot study, and final revisions. During the two implementation phases, students receiving the intervention will be compared to students in regular classrooms on improvement in writing skills, based on a pre-test. Interviews and focus groups with teachers will help the researchers to determine revisions to be made to the intervention. The feasibility pilot phase will also use pre- and post-intervention assessments of students' writing in treatment and comparison classrooms, and focus groups with teachers will provide information regarding feasibility. Classroom observation and videotaping will be used to assess fidelity of implementation. Project ERIC Purpose: Enhancing Reading Instruction for Children with Down Syndrome: A Behavioral Phenotypic Approach (Project ERIC), is to develop an innovative early reading intervention for children with Down syndrome based upon the distinct profile of behavior, or behavioral phenotype, for this group of children. Setting: This research will be conducted in urban and sub-urban school districts in the Pittsburgh area. Population: Participants will be 30 children with DS (ages 5-17) from a variety of ethnic and socio-economic backgrounds. Intervention: The purpose of Project ERIC is to enhance reading instruction for children with Down syndrome (DS) by making adaptations and modifications based on behavioral characteristics shared by many children with DS, the behavioral phenotype. The reading intervention will include components targeting essential early reading skills including phonological awareness, decoding, sight word reading, fluency, and vocabulary. To enhance the likelihood of success for children with DS, several aspects of the behavioral phenotype including cognition, language development, and personality-motivation, will be considered in the development of the intervention. The goal is to determine whether reading instruction can be improved for children with DS by adapting the instruction based on specific characteristics shared by this group. Project ERIC has the potential to enhance the reading outcomes for children with DS as well as provide information regarding the effectiveness of developing reading interventions for specific groups of children who share common characteristics and struggle with learning to read through current approaches. Research Design: An iterative process will be used to guide development and data regarding feasibility of implementation and promise of positive student outcomes will be collected. The intervention will be developed based on input from advisory board members and 10 children with DS will receive 16-weeks of one-on-one instruction provided by project staff in an exploratory phase in which instruction will be modified based on student response.