File - Mr Liang`s Science
advertisement

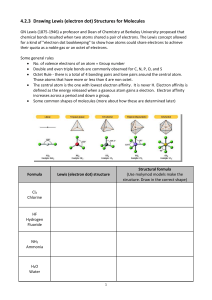
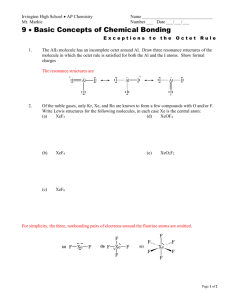
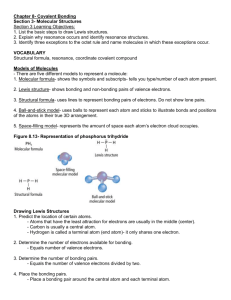
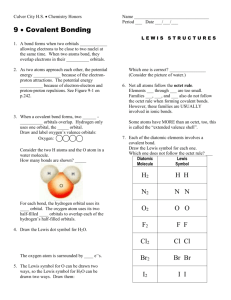
1 Chemical Bonding 3: Writing Lewis Diagram (a) The Lewis Structures of Simple Ionic Compounds Extend from the previous class Draw Lewis Structure for MgCl2 (b) The Lewis Structure of Covalent Compound that obey the Octet Rule Lewis Structure show how the VALENCE electrons are distributed in a molecule. The octet rule states that most atoms, other than hydrogen, ten to attain an octet of electrons as a result forming covalent bonds For example: H2O The “Rule of the Game” a. Count up the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Adjust number by subtracting one electron for every positive charge and adding one electron by every negative charge b. Determine which atomes are bonded together and put 2 electrons into each bonds. (NOTE: you will always be shown which atoms are connected to which other atoms) c. Use the remaining valence electrons to complete the octets of the atoms surrounding central atom(s). Then place any remaining electrons, in pairs, on the central atom(s). d. If a central atom has less than an octet of electrons, have a neighbour share electrons with the deficient atom by putting an extra pair (or pairs) of electrons into the shared bond e. Tidy up: replace each pair of electron engaged in a bond with a dash “-” 2 Example: NH4+ CHO2- HOPO 3 (c) Extension: The Lewis Structure of Covalent Compound that Violates the Octet Rule 1) Electron deficient molecule In addition to H, the atoms Be, B and Al are exception to the dendency for covalentlybonded atom to complete their octets. These atoms have such low electronegativites that the best that they can do is to GAIN ONE EXTRA ELECTRON IN A COVALENT BOND FOR EVERY ELECTRON THEY CAN CONTRIBUTE TO THE BONDS. (They do not have sufficient electronegativity to pull extra electrons on an adjacent atom into covalent bonds) Definition: a molecule in which one or more atoms (other than hydrgoen) does not possess a full octet of electron is called an ELECTRON-DEFICIENT molecules For example, BF3 2) Atoms having an expanded octet of valence electrons Elements in the third and four period of the periodic table frequently attain more than an octet of valence electrons when they vorm covalent compounds. (The extra electrons are placed in low-lying d-orbitals.) Other than the fact that the central atom will end up with more than eight valence electrons, the same rules are used for forming the Lewis Structure. For example PCl5 4 Exercise