phy ch 12 RG
advertisement

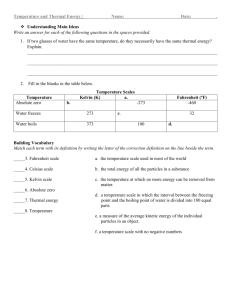
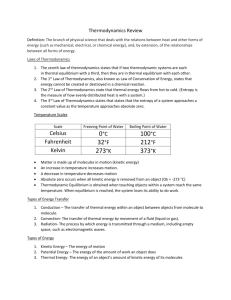
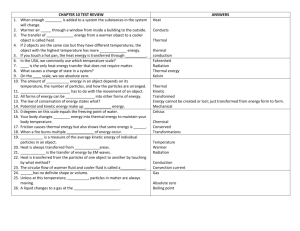
PHYSICS CHAPTER 12 (THERMAL ENERGY) READING GUIDE Pp. 313-331 1.a) _______________________ is the study of heat transformations into other forms of energy. B) During the Industrial Revolution (18th century), _________ engines were used to power trains, factories, and water pumps for _________ mines. C) In the early 1900’s, thermodynamics was first linked to the motions of ___________ and ___________ in the states of matter- gases, liquids, and solids. D) Today engineers use the laws of thermodynamics to develop high performance refrigerators, _____________, and ___________ engines. 2. Remember- when objects collide, they trade (transfer) _____________ energies. 3. The total energy (kinetic and potential) of the (gas)molecules is called _____________ __________ and the average kinetic energy per molecule is called the __________________ of a gas molecule. 4. Why do balloons in sunlight expand more than refrigerated balloons? 5. How do solids show an increase in kinetic energy since they are more dense and have less freedom of movement than gases? 6. Hot objects have greater ___________ ___________ than cold objects b/c their particles are moving faster (greater velocity). 7.Explain the difference in temperature and thermal energy in terms of number of particles. 8. Conduction is the heat transfer by actual ____________ of the particles (usually in a solid). Example- a metal spoon gets hot in warm soup. 9. Define thermal equilibrium10. Household thermometers operate by the colored _______________ expanding in the sealed tube when heated. 11.* FYI- The metric unit for temperature is the Kelvin (K); This is b/c the Celsius scale, used for experimentation, can be negative. Negative numbers cause problems for some mathematical operations and suggest that the __________ energy has a negative value which is not possible. 12.Conversion to and from Kelvin and Celsius scales involve these equations: Breakdown(remember units): Tk = Tc + 273 or Tc = Tk – 273 *must know* 13.a) Study fig 12-6; you must know these degree celsius and Kelvin values with respect to water: a) at 1000C or ____ K water boils(2120F).b)At 00C or ____ K, water freezes(320F).c) At -273.150C or ____ K, molecular motion is supposed to stop. This is called ___________ _________.b). How are these extremely cold temperatures(-2690C) almost reached? 14. a) Heat occurs when 2 objects of different temperatures come in contact with each other and _________ energy. B) This energy is always transferred from a _______ object to a ________ object. (2nd law of thermodynamics) c) The symbol “____” stands for heat of thermal energy, which is measured in metric units called _________. D) When thermal energy(Q) has a negative value, energy has been ____________ and when it has a positive value, energy has been _____________ *(hint: released/absorbed). 15. a) The 3 methods of heat transfer are conduction(see#8), _________________, and _____________. B)Conduction, which occurs best in solids, occurs b/c the molecules are in ___________ contact. C) Convection occurs best in a ____________, which is defined as a liquid or a gas. D) Convection occurs when the fluid actually moves from place to place. List 2 examples of this. E) How does radiation differ from convection and conduction? F) Radiation occurs as a result of ____________________ waves from the _______ moving through a vacuum. 16.a) The specific heat (capacity),”Cp”, (instead of just “C” b/c we will mix it up with the speed of light if you are not careful) is defined as the amount of ____________ needed to change the temperature of 1kg of any substance by 1 degree Celsius or 1 kelvin(see table 12-1)b) Water has a specific heat capacity of _________ j/kg0C or K(*must know), which is very high.c) The heat (thermal energy) absorbed or released by a substance as its temperature changes depends on its ______________, the change in ______________, and the ______________ ___________ of the substance.d) Water has a ___________ (high /low)specific heat, which is important b/c it makes water a great coolant due to the fact that it warms up slowly and cools down slowly. Why do metals like cooper make excellent cooking utensils? (hint- they are the opposite of water) 17.a) Breakdown(remember units): Q = mCpΔT b)Study ex prob #1(p318) 18.a) A calorimeter (see parts in fig 12-7) is a device used to measure _____________ in ____________ ______________. B) It is important that calorimeter provides a _______________, ______________ system, due to the conservation of energy. 19.a) Changes in state occur as a substances’ ______________ is changed;b) As the temperature increased(energy absorbed) in a solid, it becomes a ____________.c) As the temperature in a liquid is increased, it becomes a ___________.d) Remember that as the temperature is increased, the kinetic energy (motion) of the particles _________. 20.a) Define melting point (water=00C)b)boiling point (water=1000C)c) It is important to remember that the temperature during phase changes stays ______________ until the change of state has been completed. *This is shown in fig 12-10 as the flat lines (B to C and D to E)*know this graph* 21.Breakdown(remember units):a) Q = mHF b) Q = mHv *see table 12-2*(given on test) c) The (latent) heat of fusion is the amount of energy needed to __________ 1kg of a substance (occurs at 00C for water)----solid to liquid means energy is absorbed and liquid to solid means energy is released. D) The(latent) heat of vaporization is the amount of energy needed to __________ 1kg of a substance (occurs at 1000C)----liquid to a gas means energy is absorbed and gas to a liquid means energy is released.e)*FYI- latent means hidden, which is sometimes added due to absence of visible(temperature) change. 22.a) Breakdown: ΔU = Q – W b) This is called the ______ law of __________________.c) This law is just a restatement of the law of _______________________ of ___________________. 23.a) Define heat engine(we will learn the cyclic steps in a few days)b) What is the waste product of a heat engine?c)*FYI-remember-there are no ideal machines (100% efficiency) due to friction.c)see fig 12-13; describe what a refrigerator does. d)define heat pump25.a)Define entropy- b)What did Carnot prove? C)Breakdown; ΔS = Q/T d) The ____ law of thermodynamics states that entropy in the universe naturally _____________ and heat naturally flows from a _______ object to a __________ object, but is not reversible—no ideal (100% efficient) machine.


![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)