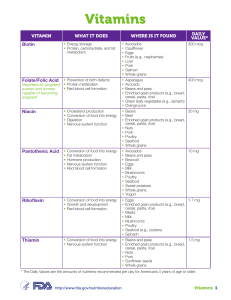
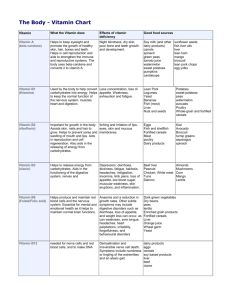
Vitamin and Mineral Functions, sources, DRI
advertisement
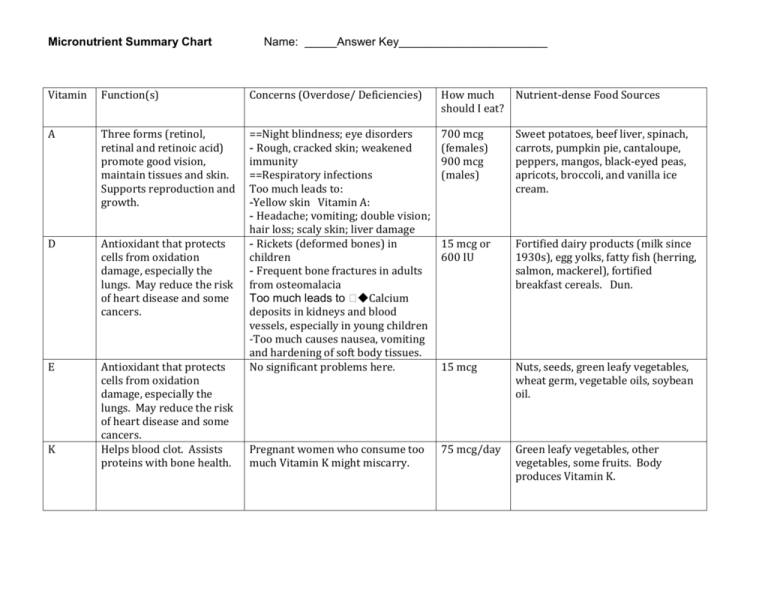
Micronutrient Summary Chart Name: _____Answer Key_______________________ Vitamin Function(s) Concerns (Overdose/ Deficiencies) How much Nutrient-dense Food Sources should I eat? A Three forms (retinol, retinal and retinoic acid) promote good vision, maintain tissues and skin. Supports reproduction and growth. 700 mcg (females) 900 mcg (males) Sweet potatoes, beef liver, spinach, carrots, pumpkin pie, cantaloupe, peppers, mangos, black-eyed peas, apricots, broccoli, and vanilla ice cream. D Antioxidant that protects cells from oxidation damage, especially the lungs. May reduce the risk of heart disease and some cancers. 15 mcg or 600 IU Fortified dairy products (milk since 1930s), egg yolks, fatty fish (herring, salmon, mackerel), fortified breakfast cereals. Dun. E Antioxidant that protects cells from oxidation damage, especially the lungs. May reduce the risk of heart disease and some cancers. Helps blood clot. Assists proteins with bone health. ==Night blindness; eye disorders - Rough, cracked skin; weakened immunity ==Respiratory infections Too much leads to: -Yellow skin Vitamin A: - Headache; vomiting; double vision; hair loss; scaly skin; liver damage - Rickets (deformed bones) in children - Frequent bone fractures in adults from osteomalacia Too much leads to �◆Calcium deposits in kidneys and blood vessels, especially in young children -Too much causes nausea, vomiting and hardening of soft body tissues. No significant problems here. 15 mcg Nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables, wheat germ, vegetable oils, soybean oil. Pregnant women who consume too much Vitamin K might miscarry. 75 mcg/day Green leafy vegetables, other vegetables, some fruits. Body produces Vitamin K. K Micronutrient Summary Chart Vitamin Function(s) Turns carbohydrates into B1 energy. Needed for muscle Thiamin coordination and healthy nerves. B2 Helps body release energy Riboflav from chos, fats and -in proteins. Helps body grow and contributes to red cell production. B3 Helps body release energy Niacin from chos, fats and proteins. Healthy nervous system and mucous membranes. B5 Helps body release energy Pantofrom chos, fats and thenic proteins. Helps body Acid produce cholesterol and promotes normal growth and development. Needed for healthy nerves. B6 Helps body release energy Pyridox- from carbs, fats and ine proteins. Promotes healthy nerves. Helps make nonessential amino acids used to build body cells and antibodies. Name: _____Answer Key_______________________ Concerns (Overdose/ Deficiencies) Nutrient-dense Food Sources Rare to have a deficiency. Light sensitivity, gritty eyes, sore tongue, mouth and lip sores and dry, flaky skin. How much should I eat? 1 mg (females) 1.2 mg (males) 1 mg (females) 1.3 mg (males) Pellegra (results in skin sores and mental/digestive problems). Rare when people eat enough protein because tryptophan makes niacin. 14 mcg females 15 mcg males Meat, poultry, fish, Enriched and whole-grain breads and cereals, dry beans, peas, peanuts, peanut butter. Rarely occur. Can be manufactured in intestinal bacteria. 5 mcg Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dry beans, peas, whole grain breads and cereals, enriched cereals, some fruits and vegetables. Skin disorders, confusion irritability and insomnia. Serious deficiencies result in convulsions. Too many supplements can cause nerve problems—difficulty in walking. Deficiencies are rare. 1.2 mg (females) 1.3 mg (males) Poultry, fish, pork, dry beans and peas, nuts, whole grains, enriched cereals, some fruits and vegetables, (avocados) liver and kidneys. Deficiency leads to nausea, apathy and loss of appetite. Beriberi (stiffness and weakness and joints.) Enriched and whole-grain breads and cereals, dry beans and peas, lean pork and liver. Enriched and whole-grain breads and cereals; dairy products, green leafy vegetables, eggs, meat, poultry, fish. Micronutrient Summary Chart Name: _____Answer Key_______________________ B12 Cobalamin Needed to process chos, proteins and fats. Helps maintain healthy nerves and red blood cells and used in making genetic material. Works with folate. Some people cannot absorb B12 well and results in pernicious anemia. 2.5 mcg C Maintains healthy blood vessels, bones (collagen needs this), skin and teeth. Helps you heal wounds and resist infection. Aids in the absorption of iron. An antioxidant. Scurvy. Also: poor appetite, weakness, bruising, soreness of joints. No scientific basis for cold connection. Large doses may cause nausea, cramps and diarrhea. 65 mg (females) 75 mg (males) Poultry, fish, pork, dry beans and peas, nuts, whole grains, enriched cereals, some fruits and vegetables, (avocados) liver and kidneys. Meat, poultry, fish, shellfish, eggs, dairy, some fortified foods, some nutritional yeasts. Only available in fortified cereals—no other vegetable sources. Citrus, cantaloupe, guava, kiwi, mango, papya, strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli, cabbage, kale, plantains, potatoes, tomatoes. Vitamin Questions: 1. What are the two main groups of vitamins called? (Clue- where are these absorbed and stored in the body?) Water soluble (B vitamins and Vitamin C) and Fat Soluble (Vitamins A, D, E, and K) 2. What is the main role of B vitamins? (Healthy nerve functioning.) 3. Which minerals work with Vitamin D to contribute to bone health? (Calcium and Phosphorus) Micronutrient Summary Chart Name: _____Answer Key_______________________ Mineral Function(s) Calcium Builds and maintains bones Osteoporosis with deficiency. Works and teeth. Assists with with Vitamin D and phosphorus. blood clotting and nerve functioning. Chloride Part of stomach juices. Needed for proper fluid balance. Copper Helps form red blood cells and functioning of circulatory system. Also assists immune system and bone health. Fluoride Found in the body as calcium fluoride. Prevent tooth decay. Component of thyroid hormones: Needed for thyroid functioning. Helps immune system. Iodine Concerns (Overdose/ Deficiencies) How much should I eat each day? 1300 mg Increased blood pressure with too much and build up of fluid with congestive heart failure, kidney and liver problems Male infants may develop kinky hair syndrome (rare). Lack of copper associated with anemia and osteoporosis. Copper is poisonous in large amounts. Large amounts associated with hepatitis, kidney problems, and brain disorders. Deficiency: cavities, weak bones and teeth. 2.3 g Goiter is the deficiency disease. Large amounts associated with high blood pressure. Nutrient-dense Food Sources Yogurt, mozzarella cheese, sardines, cheddar cheese, milk, soymilk (fortified), orange juice (fortified), tofu, salmon, turnip greens, kale. Table salt or sea salt as sodium chloride. Seaweed, rye, tomatoes, lettuce, celery and olives. 890 mcg Oysters and other shellfish, whole grains, beans, nuts, poultry 3 mg Fluoridated water. 150 mcg Iodized salt Micronutrient Summary Chart Mineral Iron Function(s) Important part of hemoglobin. Also needed for growth and development of cells and hormone synthesis. Magnesium Helps cells use energy nutrients, regulate body temperature, helps muscles and nerves work, and improves the acid-alkali balance in the body Phosphorus Helps to build strong bones and teeth. Potassium Selenium Name: _____Answer Key_______________________ Concerns (Overdose/ Deficiencies) Dietary forms: heme and nonheme. Non-heme is not absorbed as readily by the body. Deficiency is anemia. Difficult to assess blood serum levels of magnesium. How much should I eat each day? 15 mg females 11 mg males 410 mg males Nutrient-dense Food Sources Plants and iron-fortified foods contain non-heme iron. Meats, seafood and poultry contain heme and non-heme iron. Liver is one of the best sources of iron Beans,dark green leafy vegetables, meat, nuts and whole grains 360 mg females Helps build strong bones and teeth, regulates many internal bodily activities. Deficiency: hypokalemia related to weak muscle, abnormal heart rhythm, and rise in blood pressure. One of the body’s electrolytes. That helps to build proteins, break down and use carbohydrates, build muscles, maintain normal body growth, Overdose: hyperkalemia: control the electrical activity abnormal heart rhythms. of the heart, control the acid-base balance in the body. Important for reproduction and hormone metabolism. 1250 mg Protein and calcium food sources. Dairy produts. 4.7 g All meats (red meat and chicken), fish (salmon, cod, flounder, and sardines) are good sources. Soy , citrus fruits, cantaloupe, bananas, kiwi, prunes, and dairy products also have potassium. 55 mcg Seafood and organ meats are the richest sources. Also found in cereal and whole grains and eggs. Micronutrient Summary Chart Name: _____Answer Key_______________________ Mineral Function(s) Concerns (Overdose/ Deficiencies) Sodium Controls blood pressure and blood volume. Helps muscles and nerves work properly. Cellular metabolism , protein synthesis, wound healing, DNA synthesis. May have too much in processed foods. Zinc How much should I eat each day? 2300 mg or less Nutrient-dense Food Sources 11 mg males Oysters, beef, crab, fortified breakfast cereals, lobster, pork, baked beans, chicken, yogurt, cashews, chickpeas, Swiss cheese, milk, almonds, among others. Processed foods, table salt. Overdose: high pressure, edema. Information excerpted from the NIH Database (2015)s 9 mg females