Covalent Bonding and Mixed Nomenclature Review
advertisement
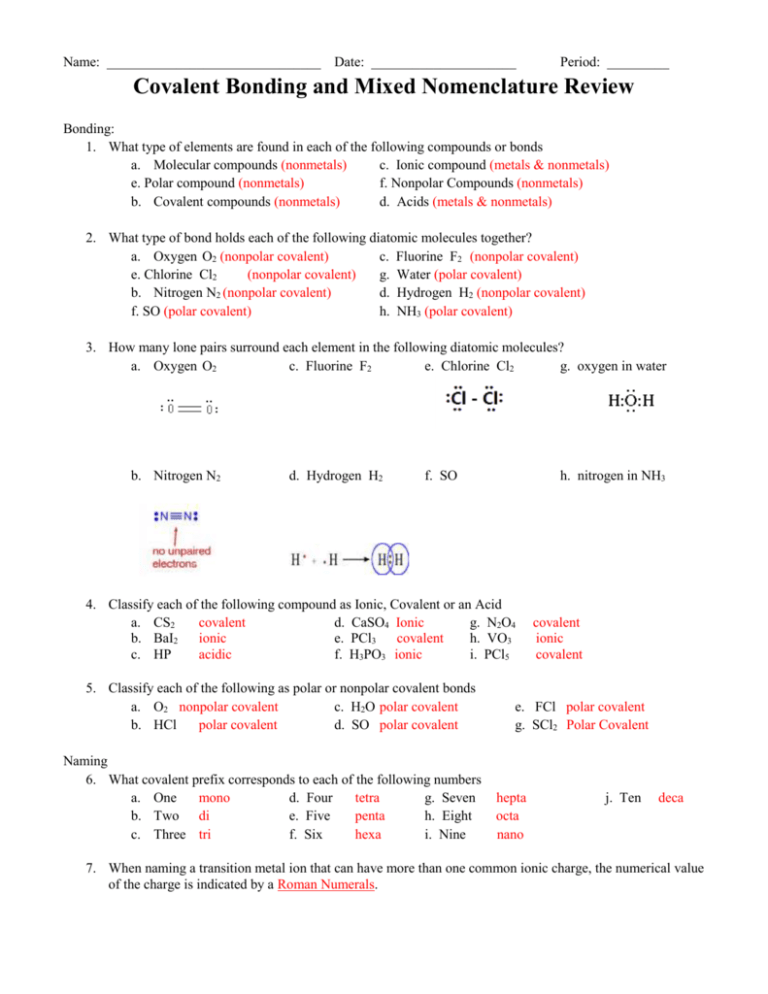
Name: _______________________________ Date: _____________________ Period: _________ Covalent Bonding and Mixed Nomenclature Review Bonding: 1. What type of elements are found in each of the following compounds or bonds a. Molecular compounds (nonmetals) c. Ionic compound (metals & nonmetals) e. Polar compound (nonmetals) f. Nonpolar Compounds (nonmetals) b. Covalent compounds (nonmetals) d. Acids (metals & nonmetals) 2. What type of bond holds each of the following diatomic molecules together? a. Oxygen O2 (nonpolar covalent) c. Fluorine F2 (nonpolar covalent) e. Chlorine Cl2 (nonpolar covalent) g. Water (polar covalent) b. Nitrogen N2 (nonpolar covalent) d. Hydrogen H2 (nonpolar covalent) f. SO (polar covalent) h. NH3 (polar covalent) 3. How many lone pairs surround each element in the following diatomic molecules? a. Oxygen O2 c. Fluorine F2 e. Chlorine Cl2 g. oxygen in water b. Nitrogen N2 d. Hydrogen H2 f. SO h. nitrogen in NH3 4. Classify each of the following compound as Ionic, Covalent or an Acid a. CS2 covalent d. CaSO4 Ionic g. N2O4 b. BaI2 ionic e. PCl3 covalent h. VO3 c. HP acidic f. H3PO3 ionic i. PCl5 5. Classify each of the following as polar or nonpolar covalent bonds a. O2 nonpolar covalent c. H2O polar covalent b. HCl polar covalent d. SO polar covalent Naming 6. What covalent prefix corresponds to each of the following numbers a. One mono d. Four tetra g. Seven b. Two di e. Five penta h. Eight c. Three tri f. Six hexa i. Nine covalent ionic covalent e. FCl polar covalent g. SCl2 Polar Covalent hepta octa nano j. Ten deca 7. When naming a transition metal ion that can have more than one common ionic charge, the numerical value of the charge is indicated by a Roman Numerals. 8. When the name of the polyatomic ion that is part of an acid ends in -ite, the acid name includes the suffix – ous acid. 9. When the name of the polyatomic ion that is part of an acid ends in -ate, the acid name includes the suffix - ic acid. 10. In naming a binary covalent compound, the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule is indicated by prefix. 11. For the following items if given the name write the chemical formula and if given the formula write the name 1. Phosphorous acid HPO3 9. S2F6 Disulfur Hexafluoride 2. Phosphorous pentachloride PCl5 10. Vanadium (IV) sulfide V2S4 3. Aluminum oxide Al2O3 11. HBr Hydrobromic Acid 4. Fe2(SO4)3 Iron (III) Sulfate 12. Calcium sulfate CaSO4 5. Iron (III) chloride FeCl3 13. Hydrosulfuric acid HS 6. SO3 sulfate (sulfur trioxide) 14. Sulfuric acid H2SO4 7. AlPO4 Aluminum Phosphate 15. KCl Potassium Chloride 8. H2SO3 sulfurous Acid 16. CoO2 Cobalt Oxide Properties 12. Ionic bonds form by transferring electrons, covalent bonds form by sharing electrons. 13. Ionic compound have high melting and boiling points while covalent compounds have low. 14. Ionic compound consists of bonds between metals and nonmetals, covalent compounds consist of bonds between two or more nonmetals. Lewis Structures 15. Draw the Lewis Structure for CF2S, and complete the table below showing number and types of bonds or lone pairs that each element has. Single Bond Double Bond Triple Bond Lone Pair Electrons C 2 1 F 2 S 1 6 16. Draw the Lewis Structure for CH3I, and complete the table below showing number and types of bonds or lone pairs that each element has. Single Bond Double Bond Triple Bond Lone Pair Electrons C 4 H 3 I 1 3 17. Draw the Lewis Structure for HCN, and complete the table below showing number and types of bonds or lone pairs that each element has. Single Bond Double Bond Triple Bond Lone Pair Electrons H 1 C 1 N 1 1 1