Names and Formula Packet key
advertisement

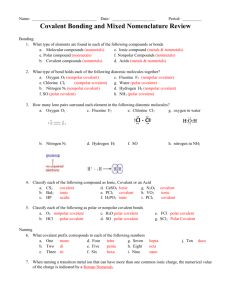
Matter Unit Names and Formulas for Compounds Key Matter Unit Rules for Naming Compounds Covalent Ionic Two or more Nonmetals Metal and Nonmetal Formed Between: Cation (positive ion) name. When Naming: If the cation can have more than one charge, a roman numeral is used to denote the charge in that compound. Anion (negative ion) name. End the name of binary (2 elements) compounds with”ide” Compounds with Polyatomic ions end with “ate” or “ite” Use prefixes to tell how many of each element. nd End the name of the 2 particle with “ide” mon (1) di (2) tri (3) tetra (4) penta (5) hex (6) hept (7) oct (8) non (9) dec (10) P2Cl5 diphosphorous pentachloride NaBr sodium bromide Example: FeS iron(II) sulfide CaCO3 calcium carbonate Memorize the following polyatomic ions names and corresponding formula and charge (make flash cards!): acetate hypochlorite chlorite chlorate perchlorate carbonate permanganate cyanide chromate dichromate bicarbonate hydrogen phosphate hydrogen sulfite hydrogen sulfate ammonium nitrate nitrite peroxide hydroxide phosphate sulfite sulfate oxalate Assignment 1: Name the following binary compounds: Identify each as ionic or covalent. CS2 carbon disulfide (covalent) MgSe magnesium selinide (ionic) CuCl2 copper(II) chloride (ionic) SO2 sulfur dioxide (covalent) FeS iron(II) sulfide (ionic) CaCl2 calcium chloride (ionic) PbF2 lead(II) fluoride (ionic) KI potassium iodide (ionic) Na2O sodium oxide (ionic) CBr4 carbon tetrabromide (covalent) Fe2O3 iron(III) oxide Cl2O7 dichlorine heptoxide (covalent) CaO calcium oxide (ionic) Al2S3 aluminum sulfide (ionic) Cu2O copper(I) oxide (ionic) (ionic) Why do the elements iron, copper, and lead have a roman numeral in the name while the other metals do not? What does the roman numeral tell you? Assignment 2: Name the following compounds: Identify as ionic or covalent; binary or ternary. NaCl sodium chloride (binary ionic) NaHCO3 sodium bicarbonate (ternary ionic) CaO calcium oxide (binary ionic) NaClO sodium hypochlorite (ternary ionic) CaCO3 calcium carbonate (ternary ionic) Al2O3 aluminum oxide (binary ionic) CO2 carbon dioxide (binary covalent) Fe2S3 iron(III) sulfide (binary ionic) XeF6 xenon hexafluoride (binary covalent) NaNO2 sodium nitrite (ternary ionic) LiCN lithium cyanide (ternary ionic) K2S potassium sulfide (binary ionic) NH3 nitrogen trihydride (binary covalent) NaOH sodium hydroxide (ternary ionic) CO carbon monoxide (binary covalent) SO2 sulfur dioxide (binary covalent) TiO2 titanium(IV) oxide (binary ionic) KNO3 potassium nitrate (ternary ionic) KClO3 potassium chlorate (ternary ionic) SiO2 silicon dioxide (binary covalent) Assignment 3: Name the following compounds of all types including acids: MgSO4 magnesium sulfate H3PO3 phosphorous acid CuBr2 copper(II) bromide HI hydroiodic acid Mn3(PO4)2 manganese(II)phosphate Na2SO4 sodium sulfate Al2(CO3)3 aluminum carbonate Fe2SO3)3 iron(III) sulfite HClO3 chloric acid NaHSO4 sodium bisulfate (sodium hydrogen sulfate) SnO tin(II) oxide Bi2(SO4)3 bismuth(III) sulfate HNO3 nitric acid Cd(NO2)2 cadmium(II) nitrite H2S hydrosulfuric acid How do you know when to name a compound as an acid? Assignment 4: Write formulas for the following compounds of all types including acids: sodium phosphite Na3PO3 hydrochloric acid HCl copper(I) nitrate CuNO3 carbon tetrachloride CCl4 dinitrogen trioxide N2O3 strontium chlorate Sr(ClO3)2 iron(III) chromate Fe2(CrO4)3 cobalt(II) chloride CoCl2 sulfuric acid H2SO4 disulfur difluoride S2F2 chromic acid H2CrO4 oxalic acid H2C2O4 manganese(III) sulfate Mn2(SO4)3 phosphoric acid H3PO4 chromium(III) oxide Cr2O3 Assignment 5: Naming and Formulas Part 1: Naming Part 2: Formulas 1. Fe(NO3)2 iron(II) nitrate 11. cadmium(II) fluoride CdF2 2. Mg(NO2)2 magnesium nitrite 12. barium phosphate Ba3(PO4)2 3. KOH potassium hydroxide 13. copper(I) chloride CuCl 4. NH4NO3 ammonium nitrate 14. barium nitrate Ba(NO3)2 5. CaSO4 calcium sulfate 15. iron(III) carbonate Fe2(CO3)3 6. PbF2 lead(II) fluoride 16. calcium sulfite CaSO3 7. PbO2 lead(IV) oxide 17. copper(II) hydroxide Cu(OH)2 8. Ba(HCO3)2 barium bicarbonate 18. aluminum phosphate AlPO4 9. Al2(CO3)3 aluminum carbonate 19. zinc sulfite ZnSO3 10. Cu(OH)2 copper(II) hydroxide 20. zinc chloride ZnCl2 Part 3: What’s Wrong With These Formulas? 21. (NH3)2CO3 NH3 is not an ion. NH4 is ammonium. 22. Na2PO4 Because Na has a charge of +1 and phosphate is -3, the charges are not equal. Should be Na3 PO4. 23. K(OH)2 Because K has a charge of +1 and hydroxide is -1, the charges are not equal. Should be KOH. Assignment 6: Naming and Formulas Name Use Formula calcium sulfate plaster CaSO4 calcium carbonate chalk CaCO3 aluminum sulfate deodorant Al2(SO4)3 potassium nitrate saltpeter KNO3 silicon dioxide amethyst SiO2 cobalt(II) chloride CoCl2 CuSO4 aluminum chloride foam stabilizer in beer controls algae in tropical fish aquariums antiperspirant nitrogen dioxide Los Angeles smog NO2 sulfur dioxide London smog SO2 nitrogen monoxide auto exhaust NO carbon tetrachloride CCl4 tin(II) fluoride once used as cleaning fluid fluoristan in toothpaste tin(IV) fluoride toothpaste additive SnF4 iron(II) sulfate iron pills, dyes, inks FeSO4 ammonium nitrate fertilizer ingredient NH4NO3 silver bromide photographic emulsion AgBr lead(IV) oxide electrode in car battery PbO2 sodium phosphate grease cleaner Na3PO4 copper(II) sulfate AlCl3 SnF2