Problem04-t-test
advertisement

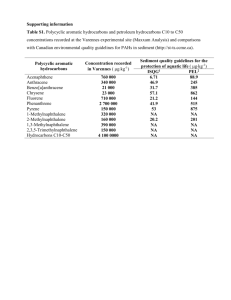
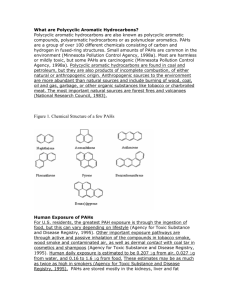
Perera et al, in "Prenatal Airborne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Exposure and Child IQ at Age 5 Years" (2009), evaluated the relationship between prenatal exposure to airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and child intelligence (a number of PAHs are considered to be reproductive and developmental toxicants), adjusted for certain covariates, including the Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment (HOME) score. HOME is a standard assessment of the quality of the home environment for children. In this problem, we will make inference on the HOME score. In Perera et al, the study sample of 249 children from New York City had a mean HOME score of 40.67 and standard deviation of 5.63. Let's assume that the average HOME score for children of a similar age in all US metropolitan areas is 55, with unknown standard deviation. We would like to determine whether the mean HOME score for the 249 NYC children is significantly different from the US metropolitan area average. (a) State the null and alternative hypotheses for this test. (b) What is the appropriate test to use? What assumptions are made in this test? (c) Find the value of the test statistic and determine the p-value. (d) Write the conclusion of this test. (e) Construct a 95% confidence interval for the mean HOME score for NYC children.