May - the International Society for Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds!
advertisement

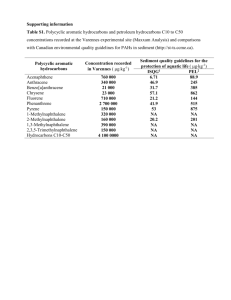
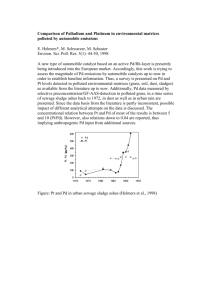
The May 2007 ISPAC newsletter This newsletter is for the benefit of ISPAC members. If you have information to share, such as your newest publications, a source of standards, news of new books, etc., please pass them along for including in the next issue. Call for Nominations for the 2007 Research Achievement Award for Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds We are soliciting nominations for the 2007 Research Achievement Award for Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds sponsored by ISPAC. This award was first given in 1987 and has been presented in alternating years at each of the subsequent ISPAC symposia (see http://www.ispac.org/ and click on conferences for options for a list of the past awardees). Please submit a nomination package consisting of a nomination letter summarizing the nominee's achievements in PAC research, a CV including publications, and a seconding letter (optional). Please send to Stephen A. Wise, chair of the award selection committee (stephen.wise@nist.gov) by May 12, 2007. The ISPAC webpages are at http://www.ispac.org/ ISPAC membership inquiries or refer potential members to either: Treasurer, Jocelyne Hellou HellouJ@mar.dfo-mpo.gc.ca Secretary, Dianne Poster poster@nist.gov Information on the Journal Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds will be found at: http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/titles/10406638.html For other inquiries, including volunteering to be a reviewer, contact Philippe Garrigues at p.garrigues@lptc.u-bordeaux1.fr Literature Review E Nagy, S Adachi, T TakamuraEnya, M Zeisig, L Moller DNA adduct formation and oxidative stress from the carcinogenic urban air pollutant 3nitrobenzanthrone and its isomer 2-nitrobenzanthrone, in vitro and in vivo Mutagenesis, 2007, Vol 22, Iss 2, pp 135-145 The carcinogenic vehicle emission product 3-nitrobenzanthrone (3-NBA) is known to rearrange in the atmosphere to the isomer 2-nitrobenzanthrone (2-NBA), which exists in 70-fold higher concentration in ambient air. The genotoxicity of 2-NBA and 3-NBA was studied both in vitro (human cell lines A549 and HepG2) and in vivo (F344 female rats intra-tracheally administered 5 mg/kg body weight of 3-NBA) models, using the P-32-HPLC and the single-cell gel electrophoresis (Comet assay) methods. In vitro, also the parent compound benzanthrone (BA) and the metabolite 3-aminobenzanthrone (3-ABA) were evaluated. 3-NBA gave highest levels of DNA adducts in the two cell lines, but significantly higher in HepG2 (relative adduct level similar to 500 adducts/10(8) normal nucleotides), whereas 2-NBA formed about one-third and onetwentieth of the DNA adduct amount in A549 and HepG2 cells, respectively. 3-ABA formed only minute amounts of DNA adducts and only in the A549 cells, whereas BA did not give rise to any detectable levels. The DNA adduct patterns from 3-NBA were similar between the two model systems, but differed somewhat for 2-NBA. The oxidative stress induced by BA was almost as high as what was observed for 3-NBA and 3-ABA in both cell lines, and 2-NBA induced lowest level of oxidative stress. The oxidative stress and DNA adduct level, in whole blood, was significantly increased by 3-NBA but not by 2-NBA. However, 2-NBA showed similar toxicity to 3NBA, with respect to DNA adduct formation in vivo, hence it is important to further study 2-NBA as a potential contributor to health risk. While DNA adduct level in the 3-NBA-exposed animals reached a peak around 1 and 2 days after instillation, 2-NBA-treated animals showed a tendency towards a continuing increase at the end of the study. V Pino, AM Afonso, JH Ayala, V Gonzalez Micellar solid-phase microextraction for determining partition coefficients of substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in micellar media: possible prediction of hydrocarbon-micelle behaviour Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2007, Vol 387, Iss 6, pp 2271-2281 Micellar solid-phase microextraction (MSPME) coupled to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) has been used to obtain partition coefficients of a group of 18 substituted aromatic hydrocarbons to ionic and nonionic micelles. Statistical and factor analyses have been utilized to establish some general equations relating molecular descriptors of non-substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their partition coefficients obtained by MSPME. The obtained equations have correlation coefficients higher than 0.94. They are used to predict hydrocarbon-micelle partition coefficients for a group of hydrocarbons with reported literature values giving a correlation coefficient of 0.98 and a standard deviation of the prediction of 0.182. The predictive model was also applied to substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with partition coefficient values obtained by MSPME, with a 69% level of success. SA Smyth, L Lishman, M Alaee, S Kleywegt, L Svoboda, JJ Yang, HB Lee, P Seto Sample storage and extraction efficiencies in determination of polycyclic and nitro musks in sewage sludge Chemosphere, 2007, Vol 67, Iss 2, pp 267-275 Analytical technology is continuously improving, developing better methods for isolating and concentrating trace compounds in environmental samples. Polycyclic and nitro musks (PNMs) are one group of emerging trace compounds detected in municipal wastewater. Differences in sample storage, preparation, and extraction methods for their measurement have led to variability in results. We analyzed 11 PNMs by GC/MS and compared the results of different storage times and extraction methods (supercritical fluid (SFE) or microwave-assisted (MAE)) for 202 samples of primary sludge, waste activated sludge (WAS), raw sludge, and aerobically/anaerobically digested biosolids collected from Canadian municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sixty-three air-dried :samples were extracted by SEE, and 139 air-dried, centrifuged, or filtered samples were extracted by MAE. The mean Surrogate recoveries were 89%,, (standard deviation (SD) = 11%) for d(10)-anthracene by SFE and 88% (SD = 14%) for d(10)-phenanthrene by MAE. Storage study results showed that PNM concentrations changed by a mean of 7% and 9% for primary sludge and WAS respectively after four weeks and decreased up to 25% after 13.5 months of storage in amber glass containers at -18 degrees C. Air-drying of sludge at room temperature caused losses of about 50% of PNM concentrations compared to centrifugation. The proportions of PNMs present in the liquid phase of sludge samples were less than 5% compared to proportions in the sludge solids. The most complete liquid-solid separation was achieved by filtration of frozen/thawed sludge samples, producing a liquid phase that contained less than 1% of the total musk content of the sample. YJ Xie, Y Zhu, FL Xu, XL Liu, B Xue, S Tao A method for determining pyrene in mucus using synchronous fluorimetry with multiple standard additions Chemosphere, 2007, Vol 66, Iss 10, pp 1878-1883 A new method was proposed to determine pyrene in mucus, which combined the synchronous fluorimetry with the multiple standard addition method (SFMSA). The method was used to determine pyrene in mucus directly without pretreatment. The method detection limit (MDL) for pyrene in mucus was measured as 0.47 ng/ml with a relative standard deviation of 12.7% (n = 7). The standard addition graph was linear in the range 0.05-50.00 ng/ml (r(2) = 0.9989). SFMSA was validated using a GC/MS method as a reference method, and nice agreement was found. The pyrene in mucus can be directly monitored by SFMSA without solvent extraction of samples. This indicates that SFMSA is more timesaving, less laborious and cheaper than the GC/MS method with solvent extraction. SFMSA has lower MDL and higher average recovery than the GC/MS method. C Pakou, M Fountoulakis, P Drillia, A Kampioti, K Stamatelatou, G Lyberatos Occurrence and fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sewage treatment plants using microwave-assisted extraction followed by liquid chromatography coupled with fluorescence detector Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 2007, Vol 16, Iss 2, pp 127-132 PAHs are highly persistent compounds in the environment, recalcitrant to biodegradation and highly lipophilic, while some of them cause acute carcinogenic and mutagenic toxicity. Due to the risk of soil contamination whenever sewage sludge is disposed to agricultural land, the investigation of their presence in sewage sludge is a priority need. This work concerns the occurrence of five PAHs, selected from the priority list of the US Environmental Protection Agency (phenanthrene, fluoranthene, pyrene, benzo[b]flouranthene, and benzo[a]pyrene), in municipal sewage sludge and to assess their fate in a sewage treatment plant. An analytical method based on microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), followed by HPLC-UV coupled with a fluorescent detector (FD) was used for their measurement. The method efficiency was evaluated as to its linearity, repeatability, accuracy and sensitivity. The contamination levels of the PAHs were determined in sludge from the sewage treatment plants of three main Greek cities: Athens, Patras and Heraklion. PAHs ranged from 0.2 to 4 mg kg(-1) d.m for each PAH in mixtures of primary and secondary sludge, while they were significantly lower in secondary sludge (less than 0.1 mg kg(-1) d.m). R Svabensky, K Koci, Z Simek The study of properties of HPLC determination of polycyclic aromatic nitrogen heterocycles International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2007, Vol 87, Iss 5, pp 337-349 The study of the separation of polycyclic aromatic nitrogen heterocycles (PANHs) by reversephase liquid chromatography with an octadecyl stationary phase is presented. The retention behaviour of a mixture of PANHs was studied under different chromatographic conditions. A mixture of phosphate buffer/acetonitrile was used as mobile phase in isocratic and gradient modes. The effect of different pH mobile phase in the range from 2.5 to 6.5 has been investigated to describe retention changes of PANHs as a function of their acid/base properties. Different concentrations of phosphate buffer as a component of the mobile phase were used to study the effect of ionic strength. Very good RP-HPLC separation of 24 PANHs and 16 EPA polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) was obtained without a pre-separation step in a test mixture and the extract of a real soil sample. Limits of detection of PANHs obtained by two detection techniques, ultraviolet-diode array detection (UV-DAD) and fluorescence detector (FD), are compared. The proposed method is tested with a real soil sample. R Ramos, E Garcia Induction of mixed-function oxygenase system and antioxidant enzymes in the coral Montastraea faveolata on acute exposure to benzo(A)pyrene Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C - Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2007, Vol 144, Iss 4, pp 348-355 Components of the cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase system (MFO) and antioxidant enzymes were investigated in the coral Montastraea faveolata exposed to the organic contaminant benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P). For bioassays the corals were exposed to increasing concentrations of B(a)P (0.01 and 0. 1 ppm) for 24 and 72 h, with water renewal every 24 h. Enzymatic activity of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) were measured in host (polyp) and hosted (zooxanthellae) cells. NADPH cytochrome c reductase activity and contents of cytochrome P-450 and P-420 were only measured in the polyp. Antioxidant enzymes CAT and SOD in polyps and zooxanthellae and GST in polyps increased significantly at the highest concentration and maximum time of exposure. Cytochrome P-420 was found in all colonies, and the cytochrome P-450 content was greatest in the colonies from the highest concentrations of contaminant. NADPH cytochrome c reductase activity and the concentration of pigments did not vary between treatments. This is the first report of the induction of both detoxifying mechanisms, the MFO system and antioxidant enzymes on acute exposure to an organic contaminant in the reef-constructing coral species M. Faveolata. QY Cai, CH Mo, QT Wu, QY Zeng, A Katsoyiannis Quantitative determination of organic priority pollutants in the composts of sewage sludge with rice straw by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry Journal of Chromatography A, 2007, Vol 1143, Iss 1-2, pp 207-214 In order to investigate the occurrence and distribution of organic contaminants in the compost of sewage sludge with rice straw, four different composting treatments at a low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio (13: 1) were conducted. Thirty semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) listed as priority pollutants by both China and the US EPA were Soxhlet-extracted, separated and analyzed by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The results showed that after composting (56 days) most of SVOCs were detected in the final composts. The total concentrations of PAHs and phthalic acid esters ranged from 1.8 to 10 mg/kg dry weight (d.w.) and from 9.8 to 18 mg/kg d.w., respectively, being significantly higher than those of chlorobenzenes and nitroaromatic compounds which were generally less than 1.0 mg/kg d.w. The concentrations and predominant compounds of organic contaminants in the different composts varied, and were affected by their physico-chemical properties and the composting processes. Concentrations of SVOCs in the static aerated composting processes especially intermittently aerated composting treatment were considerably lower than those in the manual-turned composting treatments. Concentrations of organic contaminants especially PAHs and di(2ethylhexyl) phthalate in the final composts were in agreement with the maximum permissible limits for agricultural purposes proposed by the European Union and by the EPA. C Champmartin, P Simon, P Delsaut, M Dorotte, B Bianchi Routine determination of benzo[a]pyrene at part-per-billion in complex industrial matrices by multidimensional liquid chromatography Journal of Chromatography A, 2007, Vol 1142, Iss 2, pp 164-171 A rapid and selective high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method using a columnswitching technique has been developed for the determination of benzo[a]pyrene in complex mixtures containing PAHs. The diluted sample is directly injected into the chromatographic system without pre-treatment. The purification is performed on-line using three cleaning columns filled with various stationary phases. The sample preparation, a simple dilution, and the analysis time do not exceed 45 min. The method developed was used to analyze industrial products such as oil, bitumen, etc. and was compared with an off-line method requiring treatment and extraction steps before the analysis. G Malloci, C Joblin, G Mulas On-line database of the spectral properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons Chemical Physics, 2007, Vol 332, Iss 2-3, pp 353-359 We present an on-line database of computed molecular properties for a large sample of PAHs in four charge states: -1, 0, +1, and +2. At present our database includes 40 molecules ranging in size from naphthalene and azillene (C10H8) up to circumovalene (C66H20). We performed our calculations in the framework of the density functional theory (DFT) and the time-dependent DFT to obtain the most relevant molecular parameters needed for astrophysical applications. For each molecule in the sample, our database presents in a uniform way the energetic, rotational, vibrational, and electronic properties. It is freely accessible on the web at http://astrochemistry.ca.astro.it/database/ and http://www.cesr.fr/-joblin/database/