be prepared to explain what you know
advertisement

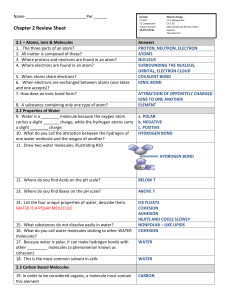
Name: Biochemistry –Chapter 2 Review BE PREPARED TO EXPLAIN WHAT YOU KNOW 1. Explain the relationship among atoms, elements, and compounds. Elements are composed of atoms. Compounds are composed of atoms of two or more elements combined in definite proportions 2. How are atoms in a compound held together? Explain the two type of bonds we learned in class. Atoms in a compound are held together by a chemical bond. Covalent- shares electrons, ionic- transfers- electrons. 3. Distinguish between single double and triple covalent bonds. Two electrons are shared in a single covalent bond, four is a double and six in a triple bond. 4. Explain what a hydrogen bond is, and how it works to hold water molecules together. Because of their partial positive and negative charges, polar molecules such as water can attract teach other. The attraction between the hydrogen atom of a water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water is an example of a hydrogen bond. 5. Explain the properties of cohesion and adhesion. Give an example of each property. Cohesion is an attraction between molecules of the same substance. Water forming beads on a smooth surface. Adhesion is an attraction between molecules of different substances. Glass and water. 6. What is polarity? An uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. 7. What is the relationship among solutions, solutes and solvents? A solution is a mixture in which one substance is dissolved in another. The solute is the substance that is dissolved. The solvent is the substance in which the solute is dissolved. 8. How are acids and bases different? How do their pH values differ? An acid is any compound that produces H+ ions in solution: acidic solutions have pH values below 7. A base is a compound that produces hydroxide ions OH- in solutions. Basic solutions have pH values above 7 9. Give two examples of each acid and base. Acid- acid rain, lemon juice Base – oven cleaner, ammonia, bleach 10. Explain the relationship between monomers and polymers, using polysaccharides as an example. Polymers are large macromolecules made up of smaller molecules called monomers. For example, monomers called monosaccharides are joined together to form polymers called polysaccharides. 11. Identify three major roles/functions of proteins. Proteins control the rate of chemical reactions, regulate cell processed, form tissues, transport substances, and help fight disease. 12. Name the two basic kinds of nucleic acids. What sugar does each contains? Nucleotides consist of a 5carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. DNA- deoxyribose RNA- ribose 13. Draw all 4 macromolecules? 14. What are amino acids? Monomers of proteins. Compound with an amino group, on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end. R-group differs. 15. How does the body use carbohydrates? Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plant and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. 16. Give two examples of carbohydrates. Sugars – glucose fructose starches- glycogen and cellulose 17. What relationship exists between an enzyme and a catalyst? An enzyme is a biological catalyst. 18. Describe some factors that may influence enzyme activity. Factors that can influence enzyme activity include pH, temperature, and proteins in that help with the rate of reaction. 19. Why are enzymes important for all body functions? Enzymes are biological catalysts. Living cells use enzymes to speed up virtually every important chemical reaction that takes place in cells. 20. Explain why a lock and key are used to describe the way an enzyme works. The fit of an enzyme and a substrate at the enzymes’ active site is so precise that the substrate is lie a key and the enzyme is like a lock. Like a key in a lock, only a substrate of a certain shape can fit into the active site of the enzyme. 21. What is the difference between unsaturated and saturated fat. At least one Carbon-carbon double bond- unsaturated. Saturated – the max possible number of hydrogen atoms. 22. List three lipids. Oils, waxes, butter, phospholipid, sterols. 23. Draw out the four macromolecule structures. 24. Why is it important that energy-releasing reactions take place in living organisms? To carry out all life processes, living things need the energy released in the chemical reactions involved in digesting food. 25. What element identifies that a substance is organic? Carbon 26. What molecules is made up of glycerol and fatty acids? Lipids 27. What do nucleotides consist of? 5carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. 28. What are nucleic acids used for in the body? Store and transmit hereditary, or genetic information *****You also need to study the biochemistry vocabulary and notes*******