Chapters 4-5 - Xenia Community Schools
advertisement

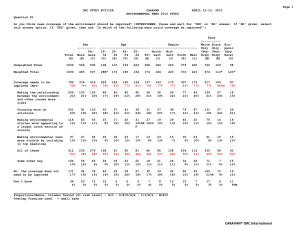
Spectra of Science Pacing Guide Quarter 1 Chapters Week 1-4 1.1 -1.3; OGT Chapter 12 Interaction of Science & Technology Week 5-7 2.1-2.3 Week 8-10 3.1, 13.1 & 13.2 Quarter 2 Chapters Week 1-4 4.1-3 Week 5-9 5.1-4 Quarter 3 Week 1-3 Chapters 6.1-4 Week 4 8.1 Week 5 9.1-2 Week 6&7 10.1-3 Week 8&9 11.1-3 Quarter 4 Chapters Week 1 12,3-4 Week 2-3 14.1-3; 15.1-2 Week 4 Week 5-7 16.1 19.3, 20.1, 20.3, 21.1-2 Week 8 Review Week 9 Exams Topics Theory and Law - Overview Measurement and Safety Scientific Method Graphing Mixtures Density Chemical/Physical Properties States of Matter Temperature Topics Atomic Models Ions/Isotopes Periodic Table - interpretation Physical properties of elements Naming Compounds - Writing Formulas Emphasize math skills - chem Topics Balancing Equations Types of Reactions Acids and Bases pH Nuclear Decay Transition Motion - speed velocity Newton's Laws of Motion Force Topics Energy - potential/kinetic Sound & Light Waves Electricity Plate Tectonics Formation of Solar System Universe Earth Spectra of Science Syllabus First Quarter - Chapters 1-3,13 Amole (2013-2014) Week Chapters and Sections Standards Covered Labs and Activities Week 1 Introduction/Safety Section 1.1 9.SWK.2-7 9.SI.1-3,6 9.PS.26-27 Lab- Observation and Inference Active Response- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Stations Lab-Science Skills Stations Station Activity- Analyzing Experiments Practice- Bikini Bottom Experiments Lab-Scientific Method Math Skills- Metric Conversion Lab- Measurement (Mini-Metric Olympics) Activity- Graphing Active Response- Accuracy vs. Precision Math Skills- Scientific Notation Math Skills- Significant Figures Short Cycle Q1A1 Chapter 1 Vocab. Quiz Practice- Standardized Question Sets Activity- Career Wanted Poster Lab- Technological Design Chapter 1 Test Practice- Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Lab- Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Active Response- Homogeneous/Heterogeneous Lab- Separation of a Mixture Math Skills- Calculating Density Lab- Sink or Float Lab- Density Cubes Short Cycle Q1A2 Science Show-Density Day Practice-Physical/Chemical Properties/Changes Demo Day- Physical vs. Chemical Changes Game- Physical & Chemical Changes Chapter 2 Vocab. Quiz Chapter 2 Test Demo Day- Types of Energy and Transformations Lab- States of Matter (Oobleck) Lab- Endo/Exothermic Reactions (In the Bag) Math Skills- Temperature Conversions Demo-Temperature Change and Changing States Practice- Types of Heat Transfer Demo Day- Heat Transfer Methods Short Cycle Q1A3 Chapter 3 Vocab. Quiz Chapter 3/13 Test Week 2 Section 1.2 9.SWK.2-4 9.SI.1-3, 6 Week 3 Section 1.3 9.SI.3-5 Week 4 OGT Book Ch. 12 9.SWK.1-9 9.ST.1-3 Week 5 Section 2.1 9.PS.9 9.SI.3 Week 6 Section 2.2 9.PS.9 Week 7 Section 2.3 9.PS.1,4,9,10 Week 8 Section 3.1 9.PS.1,9,15,16 Week 9 Section 13.1 9.PS.11 Week 10 Section 13.2 9.PS.17 Spectra of Science Syllabus Second Quarter - Chapters 4-5 Amole (2013-2014) Week Chapters and Sections Standards Covered Week 1 Section 4.1 9.PS.1-2, 26-27 Week 2 Section 4.2 9.PS.4-5 Week 3 Section 4.3 9.PS.9-10 Week 4 Section 4.1-4 9.PS.1-2,4-5,9-10 Week 5 Section 5.1-2 9.PS.1-2,4-5,7,9 Week 6 Section 5.2-3 9.PS. 1-2,4-5,7, 10 Week 7 Section 5.3 9.PS. 1-2,4-5,7 Week 8 Section 5.3-4 9.PS. 1-2,4-5,7 Week 9 Review for Semester Exams All standards from Q1 & Q2 Labs and Activities Lab- Anatomy of an Atom Lab- Bohr Models Activity- Color-coding Periodic Table Practice- Reading the Table Math Skills- P+N = mass Lab-Ions and Isotopes Baggie Challenge Short Cycle Q2A1 Practice-Properties of families Chapter 4 Vocab. Quiz Elements Quiz Mole Day- October 23- Introduction to the mole Game- Name that Element Chapter 4 Test Review- Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Station Lab- E, M, or C (compare contrast) Practice- Types of Bonds Activity-Lewis Dot Structures Practice- Reading Formulas Short Cycle Q2A2 Practice- Naming/Writing Ionic Compounds Chapter 5 Vocab. Quiz Practice- Naming/Writing Covalent Compounds Short Cycle Q2A3 Chapter 5 Test Semester Exam Spectra of Science Syllabus Third Quarter - Chapters 6, 8-11 Amole (2013-2014) Week Chapters and Sections Standards Covered Week 1 Section 6.1-2 9.PS.6-7 Week 2 Section 6.3 9.PS.7 Week 3 Section 6.4 9.PS.16 Week 4 Section 8.1 9.PS.8 Week 5 Section 9.1-2 9.PS.6-7,14-16 Week 6 Section 10.1-2 9.PS.21-23 Week 7 Section 10.3 9.PS.25 Week 8 Section 11.1 & 11.3 9.PS.21-27 Week 9 Section 11.2 9.PS.13, 21-27 Labs and Activities Practice- Parts of Reaction Formulas Practice- Types of Reactions Demo Day- Types of Reactions Math Skills- Balancing Chemical Equations Chapter 6 Vocab. Quiz Demo Day- Factors Affecting Rates of Reactions Short Cycle Q3A1 Chapter 6 Test Practice- Acids vs. Bases Lab- Testing pH of Household Supplies Activity- Personal Annual Radiation Dosage Practice- Radiation Types & Nuclear Reactions Lab- Modeling Half-life and Decay Practice- Fission vs. Fusion Chapter 8/9 Vocab. Quiz Chapter 8/9 Test Short Cycle Q3A2 Math Skills- Speed, Velocity, & Acceleration Lab- Wind-Up Velocity Activity- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Lab- Types of Friction Practice & Demos- Newton’s Laws Lab- Newton’s Toys Math Skills- Force & Momentum Chapter 10/11 Vocab. Quiz Math Skills- Weight vs. Mass Activity- Projectile Motion Short Cycle Q3A3 Chapter 10/11 Test Spectra of Science Syllabus Fourth Quarter - Chapters 12, 14-16, 19-21 Amole (2013-2014) Week Chapters and Sections Standards Covered Week 1 Section 12.3-4 9.PS.12-13,15 Week 2 Section 16.1 9.PS.2,5-7 Week 3 Section 14.1-3 9.PS.18-20 Week 4 Section 15.1-2 9.PS.18-20 Week 5 Section 19.3 9.ESS.1,3,8 Week 6 Section 20.1,3 9.ESS.2-3, 5, 8 Week 7 Section 21.1-2 9.ESS.4-8 Week 8 Section 21.4 9.ESS.4-8 Week 9 Review for Final Exams All standards from Q3 & Q4 Labs and Activities Math Skills- Work & Power Lab- Simple Machines (Mousetrap) Activity & Demo- PE & KE (King’s Island) Lab- Mechanical Energy Demo Day- Electric Force Chapter 12/16 Vocab. Quiz Chapter 12/16 Test Demo-Wave Part and Properties Math Skills- Wave Speed Lab- Spring Waves Station Lab- Sound Toys Station Lab- Light Toys Short Cycle Q4A1 Chapter 14/15 Vocab. Quiz Chapter 14/15 Test Activity- Nebular Theory Booklet Video- Formation of the Solar System Activity- Stars Life Cycle Lab- Galaxies Video-Formation of Universe Activity- Word Sorts for People and Theories Chapter 19/20 Vocab. Quiz Chapter 19/20 Test Short Cycle Q4A2 Activity- Earth Layers Model Activity- Pangaea Puzzle Lab- Plate Boundaries Lab- Seismic Waves/Hot Spots Stations Lab- Types of Weathering and Erosion Chapter 21 Vocab. Quiz Chapter 21 Test (?) Short Cycle Q4A3 Final Exam SCIENCE FAIR RESEARCH PROJECT TIMELINE (HONORS CURRICULUM) This is a tentative outline of the major dates involved in this year’s science research project. As we get closer to specific dates, details and guidelines of what is expected will be distributed. Be aware that any task with a due date will have pieces that must be turned in for a grade. Dates are subject to change. Quarter Q1 Q2 Q3 Task Due Date Introduce Project & Discuss Research Paper Guidelines Aug. 26 Topic and Question Due Sept. 3 Research Notes Due Sept. 20 Reference Page Due Sept. 27 Background Due Oct. 18 Hypothesis Statement Due Oct 25 Experimental Resources & Experimental Procedures Due Experimental Implementation Photo Evidence Due Nov. 8 Jan. 10 Appendix Due Jan. 17 Data Analysis Due Jan. 24 Conclusions Due Feb. 7 Title Page, Table of Contents, Abstract, and Introduction Due First Draft Due (with correct page numbers) Feb 21 Feb. 21 Poster Display Due March 7 Final Draft Due March 28 Present at Science Fair March 28 Q4 Completed? Ninth Grade Science Academic Content Standards Earth and Space Sciences 1. Describe that stars produce energy from nuclear reactions and that processes in stars have led to the formation of all elements beyond hydrogen and helium. (ORC Resources) 2. Describe the current scientific evidence that supports the theory of the explosive expansion of the universe, the Big Bang, over 10 billion years ago. (ORC Resources) 3. Explain that gravitational forces govern the characteristics and movement patterns of the planets, comets and asteroids in the Solar System. (ORC Resources) 4. Explain the relationships of the oceans to the lithosphere and atmosphere (e.g., transfer of energy, ocean currents, landforms). (ORC Resources) 5. Explain how the slow movement of material within Earth results from a. thermal energy transfer (conduction and convection) from the deep interior b. the action of gravitational forces on regions of different density (ORC Resources) 6. Explain the results of plate tectonic activity (e.g., magma generation, igneous intrusion, metamorphism, volcanic action, earthquakes, faulting and folding). (ORC Resources) 7. Explain sea-floor spreading and continental drift using scientific evidence (e.g., fossil distributions, magnetic reversals and radiometric dating). (ORC Resources) 8. Use historical examples to explain how new ideas are limited by the context in which they are conceived; are often initially rejected by the scientific establishment; sometimes spring from unexpected findings; and usually grow slowly through contributions from many different investigators (e.g., heliocentric theory and plate tectonics theory). (ORC Resources) Life Sciences None for grade 9 Science and Technology 1. Describe means of comparing the benefits with the risks of technology and how science can inform public policy. (ORC Resources) 2. Identify a problem or need, propose designs and choose among alternative solutions for the problem. (ORC Resources) 3. Explain why a design should be continually assessed and the ideas of the design should be tested, adapted and refined. (ORC Resources) Physical Sciences 1. Recognize that all atoms of the same element contain the same number of protons, and elements with the same number of protons may or may not have the same mass. Those with different masses (different numbers of neutrons) are called isotopes. (ORC Resources) 2. Illustrate that atoms with the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons are electrically neutral. (ORC Resources) 3. Describe radioactive substances as unstable nuclei that undergo random spontaneous nuclear decay emitting particles and/or high energy wavelike radiation. (ORC Resources) 4. Show that when elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), the repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements. Recognize that the periodic table was formed as a result of the repeating pattern of electron configurations. (ORC Resources) 5. Describe how ions are formed when an atom or a group of atoms acquire an unbalanced charge by gaining or losing one or more electrons. (ORC Resources) 6. Explain that the electric force between the nucleus and the electrons hold an atom together. Relate that on a larger scale, electric forces hold solid and liquid materials together (e.g., salt crystals, water). (ORC Resources) 7. Show how atoms may be bonded together by losing, gaining or sharing electrons and that in a chemical reaction, the number, type of atoms and total mass must be the same before and after the reaction (e.g., writing correct chemical formulas and writing balanced chemical equations). (ORC Resources) 8. Demonstrate that the pH scale (0-14) is used to measure acidity and classify substances or solutions as acidic, basic, or neutral. (ORC Resources) 9. Investigate the properties of pure substances and mixtures (e.g., density, conductivity, hardness, properties of alloys, superconductors and semiconductors). (ORC Resources) 10. Compare the conductivity of different materials and explain the role of electrons in the ability to conduct electricity. (ORC Resources) 11. Explain how thermal energy exists in the random motion and vibrations of atoms and molecules. Recognize that the higher the temperature, the greater the average atomic or molecular motion, and during changes of state the temperature remains constant. (ORC Resources) 12. Explain how an object's kinetic energy depends on its mass and its speed (KE = ½mv2). (ORC Resources) 13. Demonstrate that near Earth's surface an object's gravitational potential energy depends upon its weight (mg where m is the object's mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity) and height (h) above a reference surface (PE=mgh). (ORC Resources) 14. Summarize how nuclear reactions convert a small amount of matter into a large amount of energy. (Fission involves the splitting of a large nucleus into smaller nuclei; fusion is the joining of two small nuclei into a larger nucleus at extremely high energies.) (ORC Resources) 15. Trace the transformations of energy within a system (e.g., chemical to electrical to mechanical) and recognize that energy is conserved. Show that these transformations involve the release of some thermal energy. (ORC Resources) 16. Illustrate that chemical reactions are either endothermic or exothermic (e.g., cold packs, hot packs and the burning of fossil fuels). (ORC Resources) 17. Demonstrate that thermal energy can be transferred by conduction, convection or radiation (e.g., through materials by the collision of particles, moving air masses or across empty space by forms of electromagnetic radiation). (ORC Resources) 18. Demonstrate that electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy. Recognize that light acts as a wave. Show that visible light is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum (e.g., radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays). (ORC Resources) 19. Show how the properties of a wave depend on the properties of the medium through which it travels. Recognize that electromagnetic waves can be propagated without a medium. (ORC Resources) 20. Describe how waves can superimpose on one another when propagated in the same medium. Analyze conditions in which waves can bend around corners, reflect off surfaces, are absorbed by materials they enter, and change direction and speed when entering a different material. (ORC Resources) 21. Demonstrate that motion is a measurable quantity that depends on the observer's frame of reference and describe the object's motion in terms of position, velocity, acceleration and time. (ORC Resources) 22. Demonstrate that any object does not accelerate (remains at rest or maintains a constant speed and direction of motion) unless an unbalanced (net) force acts on it. (ORC Resources) 23. Explain the change in motion (acceleration) of an object. Demonstrate that the acceleration is proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. (Fnet = ma. Note that weight is the gravitational force on a mass.) (ORC Resources) 24. Demonstrate that whenever one object exerts a force on another, an equal amount of force is exerted back on the first object. (ORC Resources) 25. Demonstrate the ways in which frictional forces constrain the motion of objects (e.g., a car traveling around a curve, a block on an inclined plane, a person running, an airplane in flight). (ORC Resources) 26. Use historical examples to explain how new ideas are limited by the context in which they are conceived; are often initially rejected by the scientific establishment; sometimes spring from unexpected findings; and usually grow slowly through contributions from many different investigators (e.g., atomic theory, quantum theory, Newtonian mechanics). (ORC Resources) 27. Describe advances and issues in physical science that have important, long-lasting effects on science and society (e.g., atomic theory, quantum theory, Newtonian mechanics, nuclear energy, nanotechnology, plastics and ceramics and communication technology). (ORC Resources) Scientific Inquiry 1. Distinguish between observations and inferences given a scientific situation. (ORC Resources) 2. Research and apply appropriate safety precautions when designing and conducting scientific investigations (e.g., OSHA, Material Safety Data Sheets [MSDS], eyewash, goggles, ventilation). (ORC Resources) 3. Construct, interpret and apply physical and conceptual models that represent or explain systems, objects, events or concepts. (ORC Resources) 4. Decide what degree of precision based on the data is adequate and round off the results of calculator operations to the proper number of significant figures to reasonably reflect those of the inputs. (ORC Resources) 5. Develop oral and written presentations using clear language, accurate data, appropriate graphs, tables, maps and available technology. (ORC Resources) 6. Draw logical conclusions based on scientific knowledge and evidence from investigations. (ORC Resources) Scientific Ways of Knowing 1. Comprehend that many scientific investigations require the contributions of women and men from different disciplines in and out of science. These people study different topics, use different techniques and have different standards of evidence but share a common purpose - to better understand a portion of our universe. (ORC Resources) 2. Illustrate that the methods and procedures used to obtain evidence must be clearly reported to enhance opportunities for further investigations. (ORC Resources) 3. Demonstrate that reliable scientific evidence improves the ability of scientists to offer accurate predictions. (ORC Resources) 4. Explain how support of ethical practices in science (e.g., individual observations and confirmations, accurate reporting, peer review and publication) are required to reduce bias. (ORC Resources) 5. Justify that scientific theories are explanations of large bodies of information and/or observations that withstand repeated testing. (ORC Resources) 6. Explain that inquiry fuels observation and experimentation that produce data that are the foundation of scientific disciplines. Theories are explanations of these data. (ORC Resources) 7. Recognize that scientific knowledge and explanations have changed over time, almost always building on earlier knowledge. (ORC Resources) 8. Illustrate that much can be learned about the internal workings of science and the nature of science from the study of scientists, their daily work and their efforts to advance scientific knowledge in their area of study. (ORC Resources) 9. Investigate how the knowledge, skills and interests learned in science classes apply to the careers students plan to pursue. (ORC Resources)