Enter Topic Title in each section above
advertisement
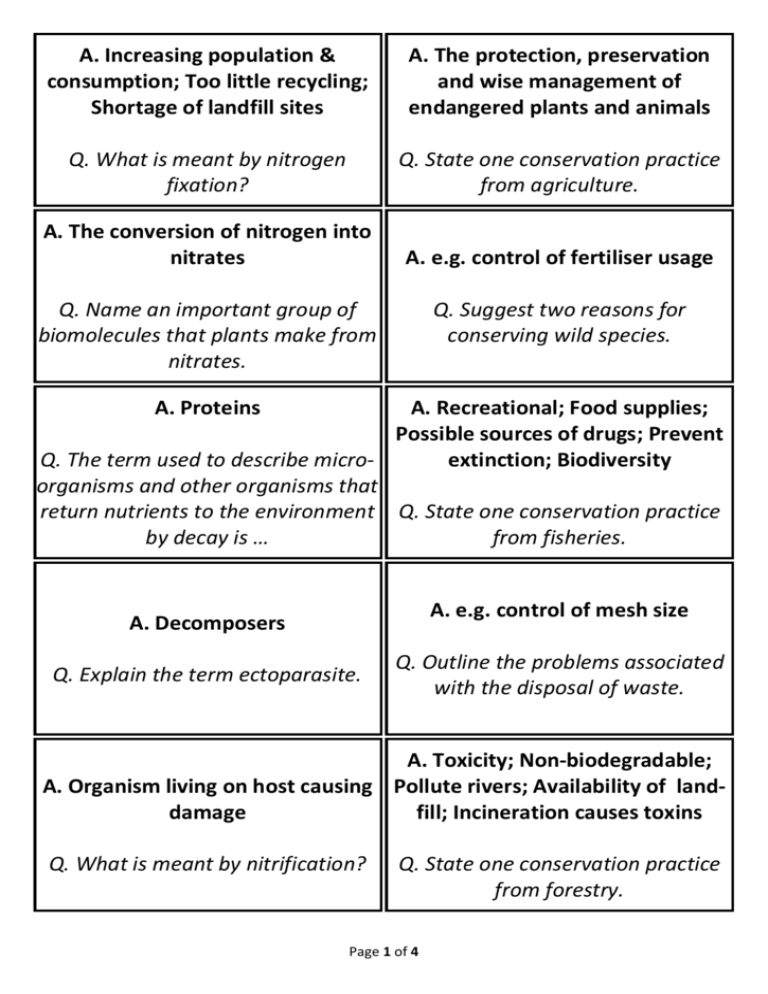
A. Increasing population & consumption; Too little recycling; Shortage of landfill sites A. The protection, preservation and wise management of endangered plants and animals Q. What is meant by nitrogen fixation? Q. State one conservation practice from agriculture. A. The conversion of nitrogen into nitrates A. e.g. control of fertiliser usage Q. Name an important group of biomolecules that plants make from nitrates. Q. Suggest two reasons for conserving wild species. A. Proteins A. Recreational; Food supplies; Possible sources of drugs; Prevent Q. The term used to describe microextinction; Biodiversity organisms and other organisms that return nutrients to the environment Q. State one conservation practice by decay is … from fisheries. A. e.g. control of mesh size A. Decomposers Q. Explain the term ectoparasite. Q. Outline the problems associated with the disposal of waste. A. Toxicity; Non-biodegradable; A. Organism living on host causing Pollute rivers; Availability of landdamage fill; Incineration causes toxins Q. What is meant by nitrification? Q. State one conservation practice from forestry. Page 1 of 4 A. The process of converting ammonia into nitrites and/or A. e.g. plant trees nitrites to nitrates Q. Farmers add nitrates as fertilizers Q. Suggest two ways of minimising to the soil, but not when heavy rain waste. is forecast. Why not? A. Fertiliser may be washed off the land; Eutrophication Q. Name a group of organisms involved in nitrogen fixation. A. Reduce; Recycle; Re-use Q. Give an example of the use of micro-organisms in waste management. A. Landfill sites; Sewage treatment plants; Digesters; Compost heaps A. Bacteria; Monera; Lichens; Clover; Legumes Q. Explain the term decomposition. A. Decaying; Rotting Q. Why are elements recycled in nature? Q. Give an advantage for the incineration of domestic waste. A. Amount of waste greatly reduced; Useable heat; Reduced landfill Q. Suggest why continual monitoring of the environment is valuable. A. To detect change(s) early; To remedy effect of change; To detect levels of pollutants A. Limited supply or words to that affect or reused Q. What is meant by pollution? Q. Give a disadvantage for the incineration of domestic waste. Page 2 of 4 A. The harmful addition to the environment by humans Q. Give an example of a human activity that results in the pollution of air. A. Harmful products produced Q. Give an example of a human activity that results in the pollution of water. A. e.g. fertiliser run-off A. e.g. burning fossil fuels Q. Explain conservation in relation to wild plants and animals. Q. Why is waste management becoming an increasingly difficult problem? Page 3 of 4 Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem 1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling 1.4.9 Human Impact on an Ecosystem Enter Topic Title in each section above Page 4 of 4





![School [recycling, compost, or waste reduction] case study](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/005898792_1-08f8f34cac7a57869e865e0c3646f10a-300x300.png)

