Organic Chemistry Exam Questions
advertisement
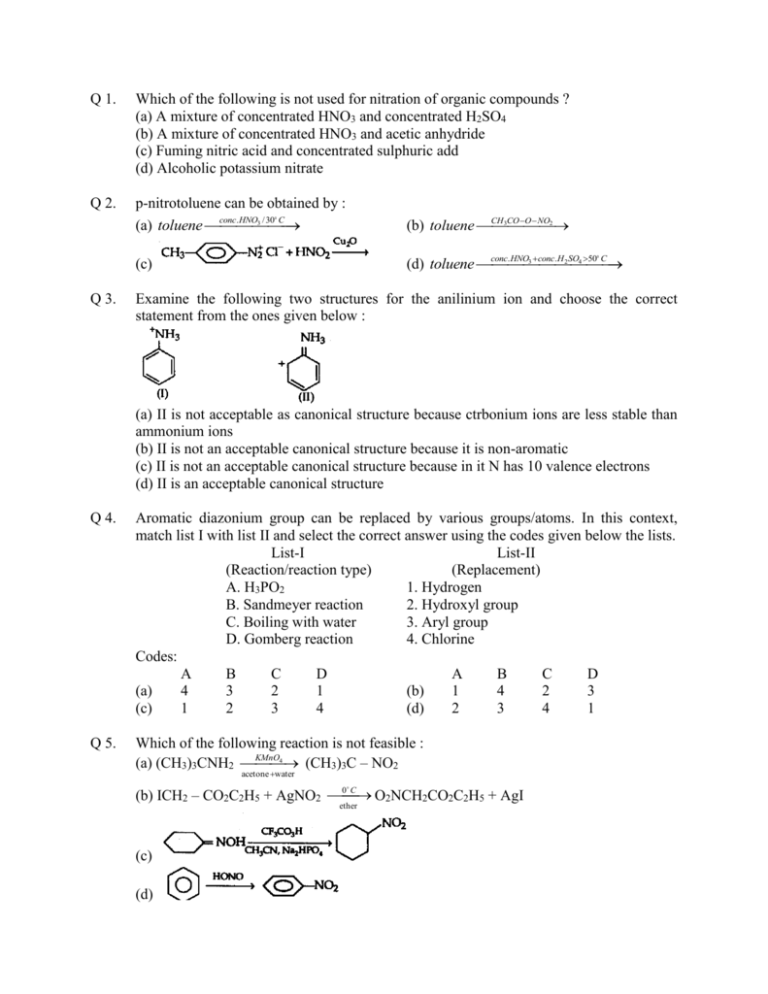
Q 1. Which of the following is not used for nitration of organic compounds ? (a) A mixture of concentrated HNO3 and concentrated H2SO4 (b) A mixture of concentrated HNO3 and acetic anhydride (c) Fuming nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric add (d) Alcoholic potassium nitrate Q 2. p-nitrotoluene can be obtained by : conc. HNO3 / 30 C (a) toluene CH 3CO O NO2 (b) toluene (c) conc. HNO3 conc. H 2 SO4 50 C (d) toluene Q 3. Examine the following two structures for the anilinium ion and choose the correct statement from the ones given below : (a) II is not acceptable as canonical structure because ctrbonium ions are less stable than ammonium ions (b) II is not an acceptable canonical structure because it is non-aromatic (c) II is not an acceptable canonical structure because in it N has 10 valence electrons (d) II is an acceptable canonical structure Q 4. Aromatic diazonium group can be replaced by various groups/atoms. In this context, match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists. List-I List-II (Reaction/reaction type) (Replacement) A. H3PO2 1. Hydrogen B. Sandmeyer reaction 2. Hydroxyl group C. Boiling with water 3. Aryl group D. Gomberg reaction 4. Chlorine Codes: A B C D A B C D (a) 4 3 2 1 (b) 1 4 2 3 (c) 1 2 3 4 (d) 2 3 4 1 Q 5. Which of the following reaction is not feasible : 4 (CH3)3C – NO2 (a) (CH3)3CNH2 KMnO acetone water (b) ICH2 – CO2C2H5 + AgNO2 0C O2NCH2CO2C2H5 + AgI ether (c) (d) Q 6. The product obtained in the reaction : (a) reaction (b) (c) (d) There is no Q 7. The reaction of CH3(CH2)6Br with NaNO2 in the presence of dimethylformaide gives : (a) CH3(CH2)6OH (b) CH3(CH2)6NO2 (c) CH3(CH2)6NO (d) There is no reaction Q 8. Which of the following statements is not correct? (a) Primary amines show intermolecular hydrogen bonding (b) Secondary amines show intermolecular hydrogen bonding (c) Tertiary amines show intermolecular hydrogen bonding (d) Amines have lower boiling points as compared to those of alcohols and carboxylic acids of comparable molar masses Q 9. The product not obtained in the reaction : CH3 – NO2 + Cl2 + NaOH (a) ClCH2NO2 (b) Cl2CHNO2 (c) Cl3CNO2 (d) CH3NH2 Q 10. Treatment of nitrobenzene with acetyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous MCI gives: (a) 2-nitroacetophenone (b) 3-nitroacetophenone (c) 4-nitroacetophenone (d) none of these Q 11. The conversion: can be brought about by reduction with : (a) Na3AsO3/NaOH (b) glucose/HCl (c) Zn/NaOH (d) LiAlH4/ether Q 12. Choose the incorrect statement (a) In the case of primary, secondary and tertiary amines, the basic strength depends on the extent of hydrogen bonding in the protonated amines (b) The presence groups like – OCH3 and – CH3 increases the basic strength of amines (c) The presence of groups like – NO2, - CN and halogens reduces the basic strength of amines (d) The basic strength of amines depends on their concentration Q 13. Amongst the following the most basic compound is: (a) benzylamine (b) aniline (c) acetanilide (d) p-nitroaniline Q 14. Which of the following reactions can be used to ethyl isocyanide ? 2 H 5OH / H 2O (a) CH3CH2I + NaCN C (b) CH3CH2I + KCN alcohol (c) CH3CH2NH2 + CHCl3 + KOH (d) None of the above alcohol Q 15. In the reaction between CH3NC and HgO, the product obtained is: (a) methyl isothiocyanate (b) methyl isocyanate (c) methylamine (d) methyl cyanide Q 16. Among the following, the strongest base is: (a) C6H5NH2 (b) p-NO2C6H4NH2 (c) m-NO2C6H4NH2 (d) C6H5CH2NH2 Q 17. An aliphatic nitro compound turns red with the addition of a concentrated NaOH solution, followed by the addition of an excess of an NaNO2 solution and then dilute H2SO4. The colour disappears with the addition of the excess of an acid but reappears if the solution is made alkaline. The aliphatic nitro compound is: (a) CH3CH2NO2 (b) (CH3)2CHNO2 (c) (CH3)3CNO2 (d) all of these. Q 18. The product obtained in the reduction : (a) not reduced (b) (c) (d) The compound is KOH 2 CH3NH2 the intermediates involved is: Q 18. In the reaction CH3CONH2 Br (a) CH3CH2NHBr (b) CH3NHBr (c) CH3N = C = O (d) CH3CONBr2 Q 19. Which of the following amines form maximum hydrogen bonds within themselves? (a) CH3NH2 (b) (CH3)2NH (c) (CH3)3N (d) None of these Q 20. A positive carbylamine test is given by: (a) N, N-diemthylaniline (c) N-methyl-o-mehtylaniline (b) 2, 4-dimethylaniline (d) p-methylbenzylamine Q 21. Which of the following represents electrophilic substitution? (a) (b) (c) (d) Q 22. Which of the following reactions is an example of Sandmeyer reaction ? (a) (b) (c) (d) Q 23. Which of the following statements is correct? (a) Thiol esters ale less susceptible to nucleophilic attack than normal esters (b) Thiol esters are not susceptible at all to nucleophilic attack than normal esters (c) The a-hydrogens of thiol esters are more acidic than those of ordinary esters (d) The carbon-sulphur bond of a thiol ester is weaker than the carbon-oxygen bond of an ordinary ester Q 24. Which of the following statements are correct? (a) Aniline is a stronger base than ethyl amine (b) Aniline is a stronger base than p-methoxyaniline (c) Aniline must be acetylated before nitration with an acid mixture (d) Aniline is soluble in an ammonium hydioxide solution Q 25. Benzenediazonium chloride on reaction with phenol in weakly basic medium gives: (a) diphenyl ether (b) p-hydroxyazobenzene (c) chlorobenzene (d) benzene Q 26. In the reduction of nitrobenzene into aniline, the intermediates formed are: (a) (b) (c) (d) Q 27. The products obtained in the reaction : (a) (b) (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these. Q 28. The red coloured compound formed during the Victor Meyer’s test for ethyl alcohol is: (a) (b) Q 29. Benzylamine cannot be prepared by: 4 (a) C6H5CONH2 LiAlH ether 4 (c) C6H5CN LiAlH (c) (d) (b) C6H5CH2CONH2 + Br2 + KOH 4 (d) C6H5CH2NC LiAlH Q 30. Which of the following statements is incorrect? (a) Thiols do not form as strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds as do alcohols (b) Thiols are considerably stronger acids than the corresponding alcohols (c) Thiols are much weaker acids than the corresponding alcohols (d) Thiols form insoluble salts with heavy metals, e.g., mercury Q 31. The oxidation of aniline with paracetic acid in the presence of acetic acid by refluxing gives: (a) (b) (c) (d) None of these. Q 32. A nitroalkane produces a ketone when it is boiled with HCl. The nitroalkane could be: (a) CH3CH2NO2 (b) (CH3)2CHNO2 (c) (CH3)3CNO2 (d) Q 33. The final product (III) obtained in the reaction sequence is: (a) (b) (c) (d) none of these Q 34. When is heated then : (a) propene is the major product (b) ethene and C3H7N(CH3)2 are the only product (c) ethene and propene are obtained with ethene and propene are obtained with ethene as the major product (d) equimolar amounts of ethene and propene are obtained Q 35. The conversion of m-dinitrobenzene into m-nitroaniline can be brought about with : (a) Sn/HCl (b) Zn/NH4Cl (c) (NH4)2S (d) None of these. Answers 1. 9. 17. 25. (c) (d) (b) (a) 2. 10. 18. 26. (a) (c) (a) (d) 3. 11. 27. (c) (d) (b) (a) 33. (b) 34. (c) 35. (b) 19. 4. 12. 20. 28. (b) (d) (a) (a) 5. 13. 21. 29. (c) (c) (b) (b) 6. 14. 22. 30. (b) 7. (a) (a) 15. 23. 31. (d) (a) (b) (d) (a) 8. 16. 24. 32. (c) (b) (b) (d)