7th Atmosphere Atmosphere Key Terms Density
advertisement

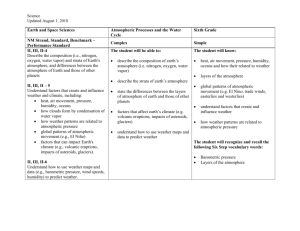
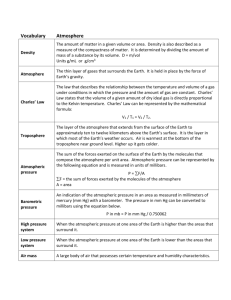
7th Atmosphere Atmosphere Key Terms 1. Density- The amount of matter in a given volume or area. Density is also described as a measure of compactness of matter. It is determined by dividing the amount of mass of a substance by its volume. D=m/v 2. Atmosphere- the thin layer of gases that surround the Earth. It is held in place by the force of the Earth’s gravity. 3. Charles Law- The law that describes the relationship between the temperature and the volume of a gas under the conditions in which the pressure and amount of a gas is constant. Charles’s Law states that the volume of a given amount of dry ideal gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin Temperature. Charles’ Law can be represented by the formula: a. V₁ / T₁ = V₂ / T₂ 4. Troposphere- the layer of the atmosphere extends from the surface of the Earth to approximately ten to twelve kilometers above the Earth’s surface. It is the layer in which most of the Earth’s weather occurs. 5. Stratosphere- The layer of the atmosphere that extends from the top of the troposphere to about 50 km above Earth’s surface. It is the layer where most clouds are formed. Stratosphere contains Ozone, which traps heat and warms the surrounding air. 6. Mesosphere- located above the stratosphere and much cooler, Begins 50 km above Earth’s surface and ends at 80 km. Most meteoroids burn up in the mesosphere, producing meteor trails. 7. Thermosphere- The outermost layer of the atmosphere. Extends from 80 km above Earth’s surface outward into space. Gas atoms and molecules there are so far apart that the air blends gradually into outer space. Even though the air in the thermosphere is thin, it is very hot, up to 1,800°C. 8. Exosphere- The outer most layer of the thermosphere. The exosphere extends from 550 km outward for thousands of kilometers. Satellites orbit in the exosphere making it possible for you to make a long distance phone call or watch television. 9. Atmospheric Pressure- the sum of forces exerted on the surface of the Earth by the molecules that compose the atmosphere per unit area. Atmospheric pressure can be represented by the following equation and is measured in units of millibars: a. P = ∑ F / A ∑ F = the sum of forces exerted by molecules of the atmosphere A = area 10. Barometric Pressure- An indication of the atmospheric pressure in an area as measure in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) with a barometer. The pressure in mm Hg can be converted to millibars using the equation : a. P in mm Hg / 0.750062 7th Atmosphere 11. High Pressure System- when the atmospheric pressure at one area of the Earth is higher than the area areas that surround it. 12. Low Pressure System- when the atmospheric pressure at one area of the Earth is lower than the areas that surround it. 13. Air Mass- a large body of air that possess certain temperature and humidity 14. Front- The boundary between air masses of different densities 15. Cold Front- The boundary between a cold air mass and a warm air mass. In a Cold Front, the colder air moves in behind the cooler air mass 16. Warm Front- The boundary between a cold air mass and a warm air mass. In a Warm Front, the warmer air mass moves in behind the cooler air mass. 17. Wind- Horizontal movements of air set into motion by pressure differences that exist within the Earth’s atmosphere 18. Pressure Gradient Force (PGF)- The difference in pressure between higher and lower areas of pressure and the distance between the two areas. a. PGF = area of higher pressure (mb) – area of lower pressure (mb) distance between areas of pressure (km) 19. Isobar- Lines on weather or atmospheric pressure map that indicate areas of equal atmospheric pressure 20. Barometer- One of the key instruments used by meteorologist to measure changes in the atmospheric pressure. Changes in atmospheric pressure measured with a mercury barometer are reported in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) 21. Evaporation- a change of phase in which the liquid phase of a substance is converted to its gaseous phase 22. Condensation- a change of phase in which the gaseous phase of a substance is converted to its liquid phase 23. Precipitation- Liquid and solid phases of water that fall from the sky. Precipitation includes rain, hail, snow, freezing rain, and sleet. 24. Meteorology- The study of the atmosphere and its associated phenomena