ES 2014 FRG in progress
advertisement

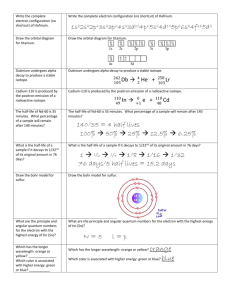
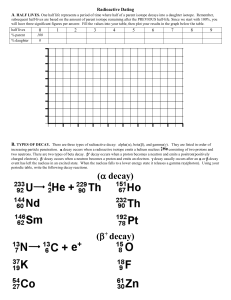
Name__________________ EARTH SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW PHYSICS UNIT TERMS AND CONCEPTS: Distance vs displacement Speed vs displacement Force Newton’s 2nd Law Potential energy Trough Frequency Speed of light Opaque speed gravity friction Newton’s 3rd Law kinetic energy amplitude transverse wave transparent velocity “g” Newton’s first law energy crest wavelength longitudinal wave translucent Some Additional Things to Know: How to label a standard wave Choose which of Newton’s laws is represented in a situation Distinguish whether common materials are opaque, transparent, or translucent Work velocity problems solving for any of the three variables Work gravitational potential energy problems Work kinetic energy problems Practice Problems: 1. How far has a dog run if he is travelling at a speed of 5.3 m/s for 44 s? 2. How fast is a car travelling if it has gone 70 m in 52 s? 3. What is the kinetic energy of a jogger with a mass of 85 kg traveling at a speed of 3.6 m/s? 4. What is the kinetic energy of a baseball with a mass of 2 kg that is traveling at 14 m/s? 5. What is the potential energy of a 5 kg rock that is at the top of a 175 m high cliff? 6. What is the potential energy of a 2 kg textbook if it is held at 2.3 m above the floor? Name________________ EARTH SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW CHAPTERS 17,18,and 19 Terms and Concepts: Continental drift Asthenosphere Mantle Divergent boundary Shield volcano Terrane Pyroclastic flow s-waves epicenter tsunami Alfred Wegner inner core crust convergent boundary cinder cone volcano viscosity earthquake Richter scale focus seismic gap plate tectonics outer core evidence for PT transform boundary composite volcano types of plutons p-waves Modified Mercalli seismometer causes of earthquakes Some Additional Things to Know: What happens at each type of plate boundary? What process do scientists use to tell epicenter of earthquake? What does each type of volcano look like? Name___________________ EARTH SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW WEATHER--CHAPTERS 11-14 Terms and Concepts: Conduction Ozone Heat condensation nuclei Dew point Hail Coriolis effect Blizzard Storm surge Anemometer convection troposhere stratosphere thermosphere sleet relative humidity jet stream front squall line barometer radiation temperature mesosphere cloud types freezing rain psychrometer prevailing winds hurricane climate Some Additional Things to Know: Four types of fronts Absolute zero Causes of global warming Effects of global warming An Inconvenient Truth Descriptions of the four layers of the atmosphere How clouds are formed Three temperature conversion formulas and how to work problems: 1. 500 K =___________C 2. 39 F =______________C 3. 90 C = ____________F 4. 350 C = _____________K Name_______________________ EARTH SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW GEOLOGIC TIME ( CHAPTERS 21-24) RESOURCES (CHAPTERS 25-27) TERMS AND CONCEPTS: Fossils Molds and casts Relative dating original remains carbonaceous films principle of superposition Embedded fragments rule absolute dating Parent isotope daughter isotope Beta particle electron capture Pre-cambrian era Paleozoic era Cenozoic era resource Nonrenewable resource ore Fossil fuels solar energy Geothermal energy nuclear energy Carrying capacity point source pollution replaced remains trace fossils principle of cross-cutting relationships radioactive decay alpha particle half-life Mesozoic era renewable resource gangue wind energy hydroelectric energy nonpoint source pollution Some Additional Things to Know: Examples of each fossil type How to read a rock-layer diagram How to balance nuclear reactions How to do half-life problems A brief history of the earth including descriptions of each era Advantages and disadvantages of various alternative energy sources Analysis of our everyday choices and the impact they make on the environment Write the balanced equation for each of the following nuclear decays please. 1. Alpha decay of Thorium—233. Thorium is Th. 2. Beta decay of Uranium—238. Uranium is U. 3. Electron capture by Radium—226. Radium is Ra. 4. Alpha decay of lead—208. Lead is Pb. 5. Electron capture by Americium—243. Americium is Am. Begin by determining the number of half lives that have passed. Then answer each question please. 6. If an isotope with a half-life of 20 days has been decaying for 60 days, how much remains of a 180 g sample? 7. An isotope with a half-life of 22 minutes has decayed from a 22 g sample to a 2.75 g sample. How long has it been decaying? 8. How many half-lives does it take for only 6.25% of an original sample to remain? 9. What was the original sample size if an isotope with a half life of seven minutes has been decaying for 56 minutes and has only 2.5 grams remaining? Name__________________ EARTH SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW CHAPTERS 28-31 Terms and Concepts: Rotation Winter solstice Apogee Lunar eclipse Solar eclipse Waxing Corona Geocentric Constellations Absolute magnitude Mercury Sputnik Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram revolution vernal equinox perigee maria umbra aurora fusion photosphere Big Bang AU’s Gemini Alan Shepard Some Additional Things to Know: Three types of galaxies What determines color of a star? Eight planets in order from sun Descriptions of each of the eight planets Apollo 13 Diagram of moon phases Diagram of sun summer solstice autumnal equinox tides penumbra waning chromosphere heliocentric solar wind light year Neil Armstrong Apollo Yuri Gagarin