Quiz 2 - Vocabulary Lesson 3 camelCase camelCase is the practice
advertisement
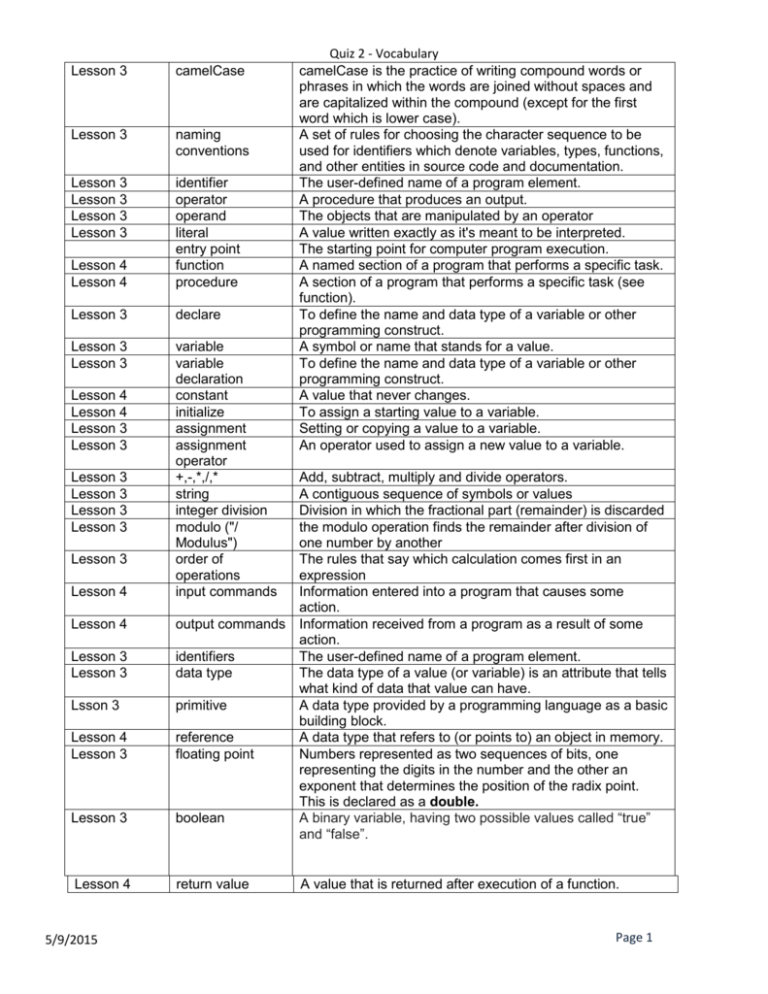
Lesson 3 camelCase Lesson 3 naming conventions Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 4 identifier operator operand literal entry point function procedure Lesson 3 declare Lesson 3 Lesson 3 variable variable declaration constant initialize assignment assignment operator +,-,*,/,* string integer division modulo ("/ Modulus") order of operations input commands Lesson 4 Lesson 4 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 4 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lsson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 3 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 5/9/2015 Quiz 2 - Vocabulary camelCase is the practice of writing compound words or phrases in which the words are joined without spaces and are capitalized within the compound (except for the first word which is lower case). A set of rules for choosing the character sequence to be used for identifiers which denote variables, types, functions, and other entities in source code and documentation. The user-defined name of a program element. A procedure that produces an output. The objects that are manipulated by an operator A value written exactly as it's meant to be interpreted. The starting point for computer program execution. A named section of a program that performs a specific task. A section of a program that performs a specific task (see function). To define the name and data type of a variable or other programming construct. A symbol or name that stands for a value. To define the name and data type of a variable or other programming construct. A value that never changes. To assign a starting value to a variable. Setting or copying a value to a variable. An operator used to assign a new value to a variable. Add, subtract, multiply and divide operators. A contiguous sequence of symbols or values Division in which the fractional part (remainder) is discarded the modulo operation finds the remainder after division of one number by another The rules that say which calculation comes first in an expression Information entered into a program that causes some action. output commands Information received from a program as a result of some action. identifiers The user-defined name of a program element. data type The data type of a value (or variable) is an attribute that tells what kind of data that value can have. primitive A data type provided by a programming language as a basic building block. reference A data type that refers to (or points to) an object in memory. floating point Numbers represented as two sequences of bits, one representing the digits in the number and the other an exponent that determines the position of the radix point. This is declared as a double. boolean A binary variable, having two possible values called “true” and “false”. return value A value that is returned after execution of a function. Page 1 Lesson 3 5/9/2015 local variable Quiz 2 - Vocabulary A variable that is known only within the current code. Page 2