CHH Review Unit 7
advertisement

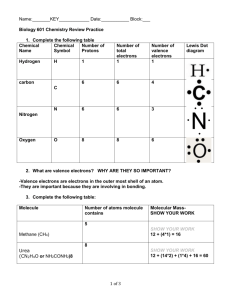
Name:____________________________ Date:___________ Period:____ Review Chemistry I Honors Unit 7: Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature 1. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? ________________________________________________________________ 2. A molecule is a neutral group of atoms held together by ______ . A. B. C. D. ionic bonds unshared electrons partial charges covalent bonds 3. Compounds formed by covalent bonds usually contain _______________. A. B. C. D. halogens and oxygen two or more nonmetals a metal and a nonmetal positive and negative ions 4. Which of the following is a molecular compound? A. B. C. D. Na2O AlCl3 SCl6 CuO 5. Carbon can form up to 4 bonds on each atom so it can form _________________. A. B. C. D. 8 valance electrons large, long chain biomolecules ionic bonds easily metallic compounds 6. How do atoms form double covalent bonds? A. B. C. D. C C One atom loses two electrons to the other atom in the bond. Two atoms share two pairs of electrons. Two atoms share two single electrons. Two atoms share one electron. 7. Which of these elements does NOT exist as a diatomic molecule? A. B. C. D. P Cl O N ? ? 1 8. A bond formed between a carbon atom and hydrogen atom is likely to be ____. A. B. C. D. polar covalent dipolar ionic nonpolar covalent 9. Which of the following bonds is the most polar (i.e. has the greatest difference in electronegativity)? A. B. C. D. C—C H—N O—H H—Cl 10. Which of the following covalent bonds is the least polar? A. B. C. D. H—Cl H—C Cl—Cl H—N 11. Which is TRUE of a nonpolar covalent bond? A. B. C. D. electrons are shared unequally between atoms a cation is bonded to an anion electrons are transferred between atoms electrons are shared equally in atoms 12. Draw the Lewis dot structure for CO2 in the box: Does CO2 contain polar bonds? _____ If so, how many? ____ Is CO2 a polar molecule? _____ If not, explain why not. _____________________ _______________________________________ 13. The following molecules contain polar bonds. Which is the only nonpolar molecule? A. B. C. D. HCl NH3 H2O CBr4 2 14. Describe how London dispersion forces occur between two atoms or molecules. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 15. Describe dipole-dipole interactions. ___________________________________________________________________ 16. Describe how a hydrogen bond forms between two molecules. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 17. List the intermolecular attractions in decreasing order from strongest to weakest: _____________________ < _____________________ < _____________________ Weakest Strongest water molecule water molecule 18. Water molecules are polar because they have _____________________________ that are arranged _____________________________. 19. There are strong attractions between polar water molecules which cause water to have all of the following properties EXCEPT ____. A. B. C. D. surface tension liquid of greater density than solid (ice) attraction to nonpolar molecules higher boiling point 21. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) boils at –60oC. Even though water is a smaller molecule that should become a gas more easily than H2S, water doesn’t boil until it reaches 100oC. Why are water molecules so difficult to separate from liquid phase to form a gas? ___________________________________________________________________ 3 22. Which substance has hydrogen bonding as its main intermolecular force? A. B. C. D. SO2 HCl F2 NH3 How do you recognize a molecule that can form hydrogen bonds? ___________________________________________________________________ 23. Describe properties that are common in typical molecular compounds. conductor: good or poor melting point: high or low boiling point: high or low net charge: neutral or charged #24-29 Write the NAME or FORMULA for the following molecular compounds: 24. CS2 ______________________________ 25. CCI4 ______________________________ 26. S2O6 ______________________________ 27. triboron monoxide _______ 28. tetraphosphorus pentoxide _______ 29. arsenic trihydride _______ 30. In drawing a Lewis structure, what is special about hydrogen (H) ? A. B. C. D. It achieves an octet of 8 electrons. It can form up to four bonds with 8 shared electrons. It can only form one double bond. It can only form one single bond with no unshared electrons around it. 4 For #31-36 , Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following compounds. List how many unshared pairs of electrons are in the molecule. Label the molecule as polar or nonpolar. Name the molecular geometry and list the bond angle. 31. HBr unshared pairs: ___ polar or nonpolar geometry: ____________________ bond angle: _____o 32. NI3 unshared pairs: ___ polar or nonpolar geometry: ____________________ bond angle: _____o 33. BF3 unshared pairs: ___ polar or nonpolar geometry: ____________________ bond angle: _____o 34. SO2 unshared pairs: ___ polar or nonpolar geometry: ____________________ bond angle: _____o 35. CH2F4 unshared pairs: ___ polar or nonpolar geometry: ____________________ bond angle: _____o 36. C2H4 unshared pairs: ___ polar or nonpolar (around one of the C atoms) geometry: ____________________ bond angle: _____o 5



![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-300x300.png)