Unit 6 Regular Review Key
advertisement

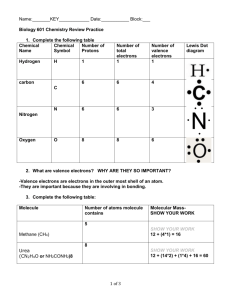
Name:__[KEY]____________________ Date:___________ Period:____ Review Chemistry I Unit 6: Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature 1. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds with other atoms rather than remaining as single atoms? Atoms form covalent bonds to obtain more stable electron arrangements. 2. A molecule is a neutral group of atoms held together by ______ . A. B. C. D. ionic bonds unshared electrons partial charges covalent bonds 3. Compounds formed by covalent bonds usually contain _______________. A. B. C. D. halogens and oxygen two or more nonmetals a metal and a nonmetal positive and negative ions 4. Which of the following is a molecular compound? A. B. C. D. Na2O AlCl3 SCl6 CuO 5. How do atoms form covalent double bonds? A. B. C. D. C C One atom loses two electrons to the other atom in the bond. Two atoms share two pairs of electrons. Two atoms share two single electrons. Two atoms share one electron. 6. Which of these elements does NOT exist as a diatomic molecule? A. B. C. D. P Cl O N ? ? 1 7. A bond formed between a carbon atom and hydrogen atom is likely to be ____. A. B. C. D. polar covalent dipolar ionic nonpolar covalent 8. Which of the following bonds is the most polar (i.e. has the greatest difference in electronegativity)? A. B. C. D. C—C H—N O—H H—Cl 9. Which of the following covalent bonds is the least polar? A. B. C. D. H—Cl H—C Cl—Cl H—N 10. Which is TRUE of a nonpolar covalent bond? A. B. C. D. electrons are shared unequally between atoms a cation is bonded to an anion electrons are transferred between atoms electrons are shared equally between atoms 11. Draw the Lewis dot structure for CO2 in the box: Does CO2 contain polar bonds? _Yes_ If so, how many? _2__ Is CO2 a polar molecule? No If not, explain why not. The polar bonds are arranged symmetrically and cancel out. 12. The following molecules contain polar bonds. Which is the only nonpolar molecule? A. HCl B. NH3 C. H2O D. CBr4 (hint: drawing the Lewis structures can help) 2 water molecule water molecule 13. Water molecules are polar because they have polar bonds (due to different electronegativities) that are arranged asymmetrically (do not cancel out). 14. Describe properties that are common in typical molecular compounds. conductor: good or poor melting point: high or low boiling point: high or low net charge: neutral or charged #15-20 Write the NAME or FORMULA for the following molecular compounds: 15. CS2 carbon disulfide 16. CCI4 carbon tetrachloride 17. S2O6 disulfur hexoxide 18. triboron monoxide B3O 19. tetraphosphorus pentoxide P4O5 20. arsenic trihydride AsH3 21. In drawing a Lewis structure, what is special about hydrogen (H) ? A. B. C. D. It achieves an octet of 8 electrons. It can form up to four bonds with 8 shared electrons. It can only form one double bond. It can only form one single bond with no unshared electrons around it. 3 For #22-27, -Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following compounds. -List how many unshared pairs of electrons are in the molecule. -Identify the molecule as polar or nonpolar by circling the correct label. 22. HBr unshared pairs: _3_ polar or nonpolar 23. NI3 unshared pairs: _10_ polar or nonpolar 24. N2 unshared pairs: _2_ polar or nonpolar 25. Cl2 unshared pairs: _6_ polar or nonpolar 26. SO2 unshared pairs: _6_ polar or nonpolar 27. CH2F2 unshared pairs: _6_ polar or nonpolar 4




![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-300x300.png)