Programme Specification
advertisement
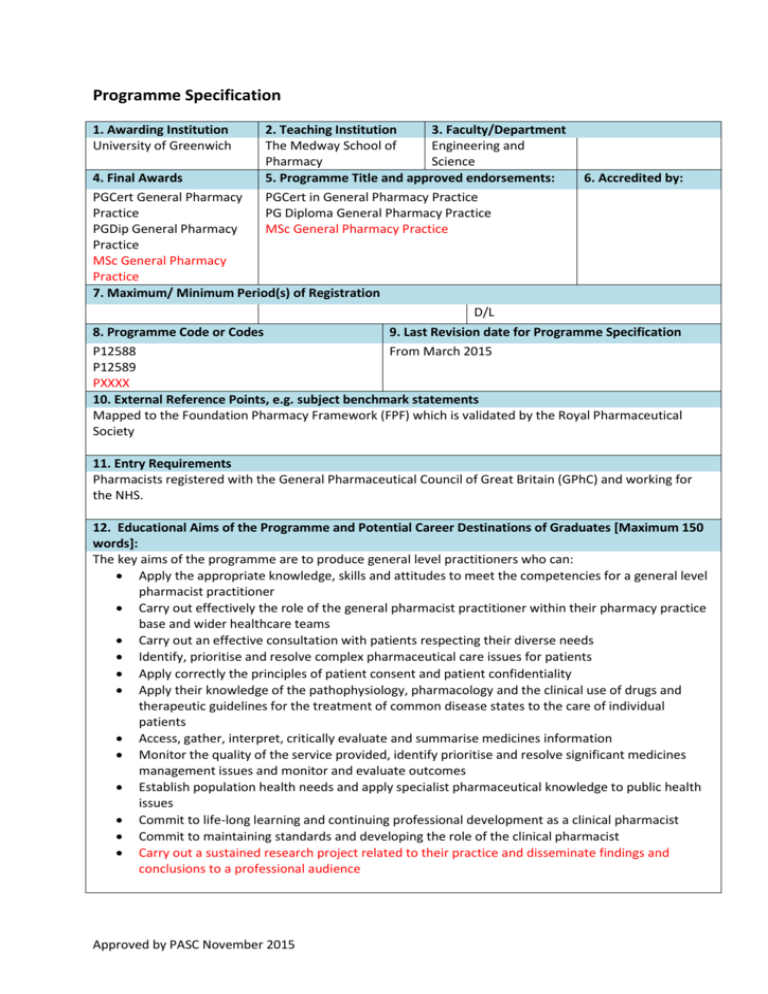
Programme Specification 1. Awarding Institution University of Greenwich 2. Teaching Institution 3. Faculty/Department The Medway School of Engineering and Pharmacy Science 5. Programme Title and approved endorsements: PGCert in General Pharmacy Practice PG Diploma General Pharmacy Practice MSc General Pharmacy Practice 4. Final Awards PGCert General Pharmacy Practice PGDip General Pharmacy Practice MSc General Pharmacy Practice 7. Maximum/ Minimum Period(s) of Registration 6. Accredited by: D/L 8. Programme Code or Codes 9. Last Revision date for Programme Specification P12588 From March 2015 P12589 PXXXX 10. External Reference Points, e.g. subject benchmark statements Mapped to the Foundation Pharmacy Framework (FPF) which is validated by the Royal Pharmaceutical Society 11. Entry Requirements Pharmacists registered with the General Pharmaceutical Council of Great Britain (GPhC) and working for the NHS. 12. Educational Aims of the Programme and Potential Career Destinations of Graduates [Maximum 150 words]: The key aims of the programme are to produce general level practitioners who can: Apply the appropriate knowledge, skills and attitudes to meet the competencies for a general level pharmacist practitioner Carry out effectively the role of the general pharmacist practitioner within their pharmacy practice base and wider healthcare teams Carry out an effective consultation with patients respecting their diverse needs Identify, prioritise and resolve complex pharmaceutical care issues for patients Apply correctly the principles of patient consent and patient confidentiality Apply their knowledge of the pathophysiology, pharmacology and the clinical use of drugs and therapeutic guidelines for the treatment of common disease states to the care of individual patients Access, gather, interpret, critically evaluate and summarise medicines information Monitor the quality of the service provided, identify prioritise and resolve significant medicines management issues and monitor and evaluate outcomes Establish population health needs and apply specialist pharmaceutical knowledge to public health issues Commit to life-long learning and continuing professional development as a clinical pharmacist Commit to maintaining standards and developing the role of the clinical pharmacist Carry out a sustained research project related to their practice and disseminate findings and conclusions to a professional audience Approved by PASC November 2015 13. Summary of Skills Development for Students within the Programme [Maximum 150 words]: On successful completion of the programme the graduate should be able to: Identify, prioritise and resolve the medicines management needs of patients, carers and other social and health care professionals. Consult effectively with patients, carers and the multi-disciplinary health care team, respecting diversity and confidentiality Independently develop their clinical pharmacy knowledge and skills in order to identify, prioritise and resolve complex pharmaceutical problems in a range of common conditions Demonstrate a systematic approach to medicines management for patients with a range of common conditions Demonstrate a proactive and critical approach to self-development and continue to advance their knowledge and understanding through continuing professional development and lifelong learning. Plan and conduct a sustained work-based research project 14. The programme provides opportunities for students to achieve the following learning outcomes: Knowledge and understanding of: 1. Organisation and structure of the NHS 2. Health policy and its impact on working practices 3. Medicines management and its application to individual patient care 4. Effective methods of working with patients, health and non-health professionals 5. Consultation methods and their applicability to patient care 6. Compliance, adherence and concordance` 7. Health beliefs: theories and models 8. Advantages and limitations of different methods of communication in the context of medicines management 9. Ethical issues influencing prescribing decisions 10. Evidence-based approach to drug therapy decisions 11. Application of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles to individual patient care 12. Systematic approach to the delivery of care to patients with complex needs 13. Systematic approach to drug and therapy monitoring in patients with complex conditions 14. Applied therapeutics 15. Systematic approach to complex queries about medicines use 16. Effective use of complex clinical data sets 17. Pharmaceutical public health 18. Clinical governance in the context of medicines management 19. Audit as a tool to improve quality of patient care 20. Change management as a tool to improve service provision 21. Use of CPD as a tool for lifelong learning 22. Research methods and tools 23. Ethical and legal issues related to research 24. Data analysis Approved by PASC November 2015 15. The programme provides opportunities for students to develop the following skills: Intellectual skills Work independently, efficiently and professionally within current NHS frameworks and the General Pharmaceutical council (GPhC) Standards of Conduct, Ethics and Performance, managing any conflicting priorities Demonstrate appropriate initiative whilst recognising personal and professional limitations Communicate clearly, precisely and appropriately with patients and all other healthcare professionals Recognise, value and use appropriate theories, concepts and principles from a range of disciplines Demonstrate effective application of patient confidentiality and the principles of patient consent Retrieve and document information in a clear and structured way Carry out effective consultations with patients and carers to encourage compliance Accept responsibility for own actions and for the care of patients assigned to his/her care Undertake a structured approach to problem solving, forming an appropriate judgement even in the absence of complete data Review, evaluate critically and synthesise sources of information and research methodologies cited in published literature to support the care of individual patients Accept responsibility for his/her own lifelong learning and continuing professional development Apply effective negotiating and influencing skills in order to achieve a definite outcome Assess the outcome of personal contributions to patient care Evaluate and discuss legal and ethical influences related to the pharmaceutical care of individuals Contribute to the improvement of healthcare outcomes through reflective practice and innovation Demonstrate a critical application of the evidence base to inform research design and delivery Subject practical skills Apply the principles of medicines management and pharmaceutical care in practice Interpret prescriptions for medicines and evaluate for safety, quality, efficacy, legality and economy Advise patients, carers and healthcare professionals about medicines usage and health promotion Identify, prioritise, analyse, evaluate and resolve pharmaceutical care issues (including social issues) related to real patients irrespective of complexity Perform complex pharmaceutical calculations in order to advise on safe drug administration Demonstrate respect for the patient irrespective of ethnic, cultural or religious background Carry out the role of the clinical pharmacist effectively within the multidisciplinary healthcare team Carry out a review of patients’ medication at a range of levels, document recommendations and influence prescribers and patients appropriately to institute agreed changes. Apply a knowledge of the pharmacology of drugs, pathophysiology of disease states and evidencebased treatment guidelines in the context of individual patients Select a range of biochemical, haematological, microbiological and near-patient tests in order to monitor efficacy and toxicity of drug therapy Conduct an analysis of a patient safety issue, evaluate options and draw an appropriate conclusion Investigate medicines information enquiries using an appropriate research strategy, and formulate and communicate responses to queries in a timely manner Advise on the clinical significance of drug-drug, drug-patient and drug-disease interactions and devise a course of action to minimise risk to the patient Investigate medicines information enquiries using appropriate evidence and formulate a response appropriate to the needs of the enquirer Advise on risk management issues and ways to minimise error Develop the pharmaceutical service and apply change management techniques Carry out a review of a clinical audit, evaluate the outcome and make recommendations for change Approved by PASC November 2015 Demonstrate an understanding of aspects of operational management including implementation of national drivers, drug budget management, use of productivity data and responding to complaints Contribute to the supervision and development of other members of pharmacy staff including provision of teaching, training and formative feedback on performance Identify and use appropriate methodologies and tools relevant to healthcare research Conduct a research project mindful of the ethical and legal issues that need to be taken into account when conducting healthcare research Manage and analyse data management to inform the interpretation of research findings Transferable/key skills Effective written and verbal communication with academic tutors, peers, practice tutors, patients, carers and the multi-disciplinary healthcare team Interpersonal skills: the ability to interact with patients, the public and other health and social care professionals Critical appraisal and summation of information from a variety of sources Interpretation of the significance of general, biological and medical statistics The ability to make appropriate decisions based on available information, with insight into the risks and benefits that may result from working with incomplete data Ability to work independently and as part of a team within professional standards of conduct, ethics and performance, with recognition of the moral and ethical issues related to medicines management issues Positive attitude and constructive approach to group discussions Reflective practitioner and autonomous learner with the ability to take responsibility for academic, professional and personal development High level information technology skills Time management and organisational skills High level problem solving skills 16. Teaching, Learning and Assessment Methods related to the programme learning outcomes and skills sets Teaching and Learning Guided, self-directed student learning is actively encouraged, supported by a range of resources including the library facilities at their practice base and/or Medway campus and the worldwide web. Students will be expected to develop the skill of critical evaluation of literature, and appropriate evaluation and application of web-based information will facilitate development of this skill. Students will undertake experiential learning under the guidance of a practice tutor in an accredited work base with set objectives. Blended learning will be essential. Formal teaching will be minimal but may include tutorials given by expert pharmacists or clinicians. Students will participate in action learning sets under the guidance of an academic facilitator to discuss evidence from their professional development portfolio. Students will have access to formative case studies intended to assist them in applying theoretical knowledge in the context of the care of patients. Intellectual skills are developed through reflective practice and learning activities. Participation in case presentations and case study analysis will necessitate critical appraisal of the literature and provide opportunities for peer review, critical discussion and reflective learning. Subject practical skills will be developed in a co-ordinated manner throughout the programme. These skills are highlighted through the practical sessions as part of the action learning sets. Investigations will be carried out as part of the work-based assignments. The portfolio of evidence, the opportunity to work with pharmacists from different hospital practice backgrounds, and the practical placements within the multi-disciplinary team will all provide Approved by PASC November 2015 students with an excellent foundation for CPD in their future careers as clinical pharmacists. Students will work with their academic and work-placed supervisors to design and deliver a research project. This will involve interrogation of the evidence base, and investigation of research methods and tools. The academic supervisor and student will work together to plan an appropriate, flexible method of learning research skills. Appropriate facilities and support will be made available to the student, together with access to research expertise within the university and practice base. Assessment The assessment methods associated with each course are given in the course specifications. A variety of assessment methods are used to test the clinical knowledge, skills and attitudes of the practitioners, including objective structured clinical examinations, multiple choice questions, case based questions, pharmaceutical calculation questions, project work, compilation of a portfolio to demonstrate competency attainments. One of the key characteristics of assessment within the programme is the element of negotiation. This allows students to construct their own evidence of achievement of key learning outcomes under the guidance of an accredited practice tutor using experiences from their chosen area of clinical practice and application of their knowledge and skills to the care of actual patients. Methods used to assess intellectual skills include intensive workshops during action learning sets, oral presentations, case study analysis, and portfolio entries, all set within the context of practice based reflective learning. A variety of assessment methods are used to assess subject practical skills. The reflective portfolio is a vital component in the assessment of the skills required and will include reflection upon practice within the workplace and reflection upon communication skills in practice. Assessed tasks include a literature review of an area of prescribing or a therapeutic dilemma, and a critical review of an aspect of the pharmaceutical service provided in the work-base applying change management theory. A variety of assessment methods are used to assess transferable key skills. The emphasis throughout the course on the development of transferable skills will ensure that these outcomes are met in master’s level graduates. Communication skills will be demonstrated with patients, peers, tutors and in the workplace. Different methods of communicating results are encouraged including written reports, oral presentations and oral discussion of a patient’s case with an assessor. IT competence will be demonstrated through investigation of medicines information queries and presentation of written responses, presentation of the practice portfolio, the use of the worldwide web and the analysis and presentation of pharmaceutical literature. The ability to solve problems, communicate appropriately and work with others will be demonstrated though the competence framework assessments. Self-directed learning and CPD will be demonstrated through the reflective portfolio The research project thesis, poster, abstract and 2 personal reflections will form the assessment of the research component. 17. Programme Structure: Levels, Courses and Credits Level 7 Award(s) and Credits The PGCert/Diploma/MSc General Pharmacy Practice is only offered in the part-time mode. Students must pass the requirements for the award of PG Certificate in order to progress to PG Diploma level and must have completed the Diploma before progression to the MSc Compulsory course PHAM1028 Approved by PASC November 2015 MSc General Pharmacy Practice 180 credits at M level Pass: Minimum of 50% overall on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment Merit: 60% and over on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment Distinction: 70% overall on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment Compulsory Courses Stage 2 PHAM1134: Developing Self, Others and Your Operating Management Skills (Foundation Stage 2) (30 credits) “Module A” PHAM 1135: Ensuring Patient Safety and a Quality Service (Foundation Stage 2) (30 credits) "Module B”: Stage 1 PHAM1133: Practitioner Development and Establishment of Professional and Clinical practice (Foundation Stage 1) (60 credits) Approved by PASC November 2015 PG Diploma General Pharmacy Practice 120 credits at M level Pass: Minimum of 50% overall on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment Merit: 60% and over on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment Distinction: 70% overall on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment PG Certificate in General Pharmacy Practice 60 credits at M level Pass: Minimum of 50% on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment Merit: 60% and over on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment Distinction : 70% and over on marked assignments plus satisfactory portfolio assessment