1.Synth_of_Sodium_Chloride_Selbstlern
advertisement

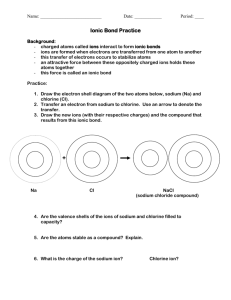
THE IONIC BOND (The 3rd substance class: SALTS) Repetition: The ionic bond is formed between metal and non-metal atoms. Example: Synthesis of cooking salt from the elements Na + Cl Na—Cl wrong, why? Na ... sodium Cl ... chlorine Between sodium and chlorine atoms, no covalent bond is formed because: 1. Noble gas state: With the virtual molecule above the chlorine atom reaches the noble gas-state, the sodium atom does not. PolarityEN = 2.23 (3.16 - 0.93) is too big for a covalent bond. As the chlorine atom has a much larger electronegativity (EN), it snatches the valence electron away from the sodium atom. In general: With EN values greater than 1.5 one no longer speaks of a covalent bond, but of an ionic bond. (Actually, the transition is fluent) Non-metal atoms snatch valence electrons away from metal atoms. As a result positively charged metal ions and negatively charged non-metal ions are being formed. Actually the following reaction occurs: Na + Cl Na+ + Cl- (Na+-ions Cl—ions) Na+ has also reached the noble gas state, because its valence electron (outermost electron) was taken away. Thus its next closest inner shell contains 8 electrons and is therefore a fully occupied valence shell. Homework: draw a Na-atom, a Na+-ion, a Cl-atom and a Cl-ion Experiment Observations (Pay attention to the colours of the substances and the energytransfer!) Silvery, shining, soft sodium metal is being melted (heated up to the orange glow) and is reacting with green chlorine gas to white cooking salt. The orange-yellow light remained even after the burner had been removed. It must be an exothermic reaction. General energy diagrams of an endothermic and an exothermic reaction Arrow pointing upwards: energy which is invested Arrow pointing downwards: energy which is realeased (set free) Detailed energy diagram of the cooking salt synthesis an exothermic reaction: reactants: Na, Cl2 product: NaCl Energy is required: 109 kJ: to melt sodium-metal and to evaporate it 121 kJ: to separate Cl2 molecules into single Cl-atoms 502 kJ: to snatch an electron away from the sodium-atoms This costs less energy than with other atoms, but it costs energy Energy is released: 363 kJ: when chlorine atoms take up an electron 780 kJ: when gaseous Na+ and Cl- ions assemble to form a lattice.