Deposition
advertisement
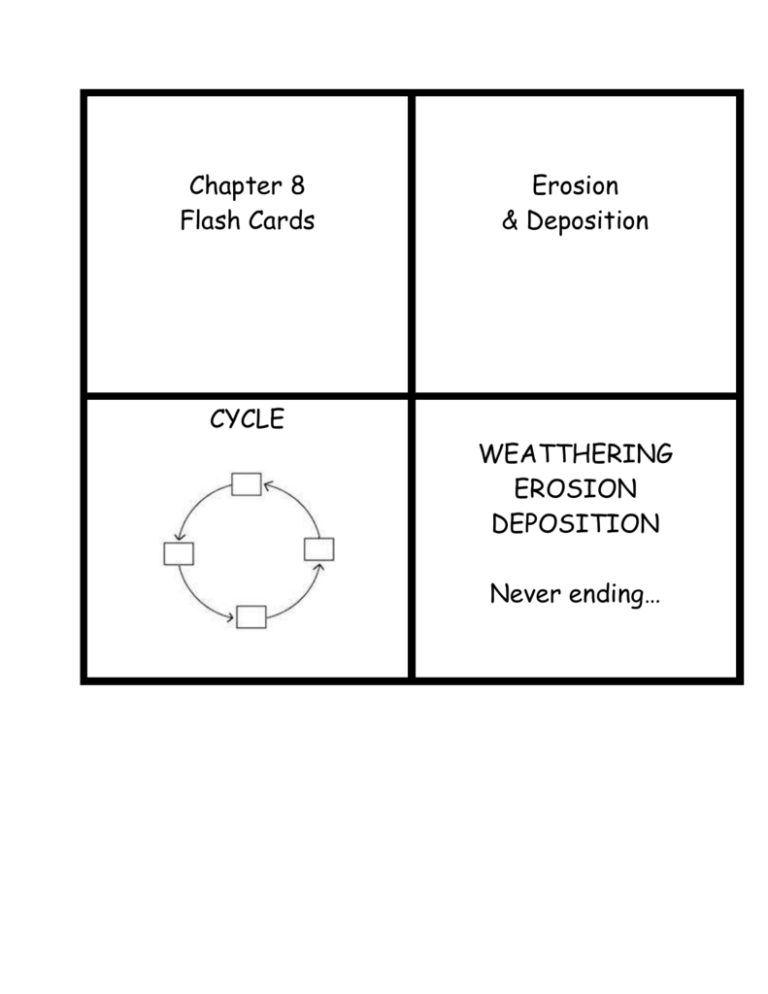
Chapter 8 Flash Cards CYCLE Erosion & Deposition WEATTHERING EROSION DEPOSITION Never ending… 5 AGENTS OF EROSION Water running Wind Waves Gravity Glaciers 3w’s +2G’s Sediment Material moved by erosion (mud;stuff) Deposition When sediment get DEPOSITED or dropped/placed down by Wind,waves, running water, gravity or glaciers Gravity Whatever goes UP will COME DOWN! A FORCE that moves stuff downhill 4 kinds of “mass movement” Creep The process when stuff moves downhill 1. landslide 2. mudflow 3. slump 4. creep VERY slow movement of soil downhill over time Slump ONE large rock chunk that falls QUICKLY mudflow landslide Dry rock, soil goes downhill FAST ?? Moving water !!! Major erosion agent ?? WHERE can RAIN Go? runoff 1. 2. 3. 4. sink into ground evaporate plants drink it move over land Water that moves over the Earth’s surface (doesn’t sink in) runoff Rill Water path sizes , r, r, G S R Gully Stream River rills Tiny grooves in the land made by running water gullies Large grooves, or channels, in the soil Formed by running water ?? What affects RUNOFF Tributary 1. how much rain 2. how much vegetation 3. type of soil 4. steepness of land 5. human use of land A littler stream that flows into a larger stream of water drainage basin LAND area (bowl) From which a river & its tributaries get their water A divide High ground Between drainage basins Rivers form V-SHAPED valleys ? HOW ? Near source (up in mountains) steep; runs fast; digs a “V” Waterfall Formation Flood plain FLAT, wide land area along a river; where the river overflows onto the banks A bend in a river A meander Oxbow lake Word comes from ox’s harness WHEN do rivers deposit sediment? When the flow SLOWS down; the sediment settles on bottom Alluvial fan At bottom of mountain delta Fan shaped, BUT at mouth of river; flat plain area – not mountain Flood plains Are fertile b/c of all the rich sediment that becomes soil WHY?? groundwater EASY ! Water IN THE GROUND Stala tite Vs. Stala mite stalactite = ceiling (also ‘tite –top) ttttt Stalagmite KARST topography Sinkhole; caverns Because of limestone The ABILITY to do WORK energy POTENTIAL ENERGY STORED UP energy KINETIC ENERGY An object’s energy because of its MOTION Water moving down A slope ENERGY INCREASES ! ?? Load is the AMOUNT of sediment that a river carries Abrasion The wearing away of rock By a grinding action A river’s LOAD Rocks bump & grind on bottom as river flows HOW does most SEDIMENT enter a river? #1 WAY = mass movement and runoff Erodes from bottom & sides of river Wind drops sediment into river abrasion How is sediment transported in a river? What FACTORS determine show fast a river flows? 1. BIG particles roll & slide 2. smaller sediment carried by the river 3. dissolved sediment carried in solution 1. river’s slope – how STEEP 2. VOLUME of water S , V , SH 3. SHAPE of streambed Shallow = slow Deep = fast Its STEEPness What is a river’s SLOPE Steep Fast or little slope slow River VOLUME During Flooding Volume = how MUCH ?? MUCH MUCH MORE increases