211-12Acid-Base
advertisement
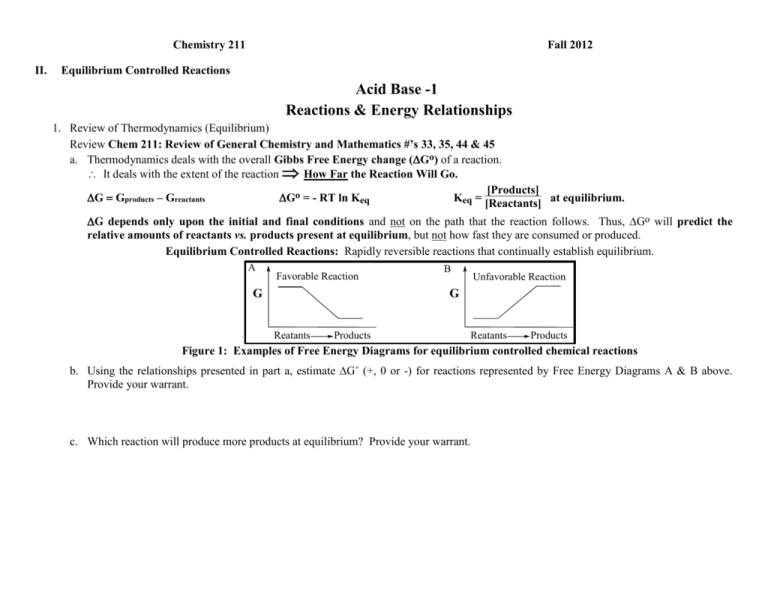
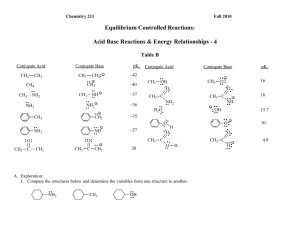
Chemistry 211 II. Fall 2012 Equilibrium Controlled Reactions Acid Base -1 Reactions & Energy Relationships 1. Review of Thermodynamics (Equilibrium) Review Chem 211: Review of General Chemistry and Mathematics #’s 33, 35, 44 & 45 a. Thermodynamics deals with the overall Gibbs Free Energy change (Go) of a reaction. It deals with the extent of the reaction How Far the Reaction Will Go. [Products] GGproducts – Greactants Go = - RT ln Keq Keq = at equilibrium. [Reactants] G depends only upon the initial and final conditions and not on the path that the reaction follows. Thus, Go will predict the relative amounts of reactants vs. products present at equilibrium, but not how fast they are consumed or produced. Equilibrium Controlled Reactions: Rapidly reversible reactions that continually establish equilibrium. A Favorable Reaction G B Unfavorable Reaction G Reatants Products Reatants Products Figure 1: Examples of Free Energy Diagrams for equilibrium controlled chemical reactions b. Using the relationships presented in part a, estimate G˚ (+, 0 or -) for reactions represented by Free Energy Diagrams A & B above. Provide your warrant. c. Which reaction will produce more products at equilibrium? Provide your warrant. Acid-Base Rxns & Energy Relationships-1 2 2. Acid-Base Reactions (Equilibrium Controlled): a. REVIEW of the Brønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and Bases See Chem 211: Review of General Chemistry and Mathematics #’s 39 & 40. Equilibrium Constants We will use only acid dissociation constants (Ka and pKa) in aqueous solutions. .. A . + H3O.. .. H + H2O [H3O+][A-] Ka = [HA] A pKa = - log Ka b. Ka and pKa as measures of the strengths of acids. (1.) Ka is an experimentally determined equilibrium constant as defined above. Consider the following experimental data on three acids, H-A, H-B & H-C: H-A H-B H-C Ka 2.51 x 10-9 1.58 x 10-5 3.16 x 10-3 pKa 8.6 4.8 2.5 Table 1: Experimentally Determined Equilibrium Constants of Selected Acids. (a.) Based on the data in Table 1, how does pKa change as Ka increases? Cite the specific data in Table 1 you used and provide your warrant. (b.) Based on the data in Table 1, which acid, H-A, H-B or H-C is the strongest acid. Cite the specific data in Table 1 you used and provide your warrant Acid-Base Rxns & Energy Relationships-1 3 (c.) Based on the data in Table 1, which acid is the weakest acid? Cite the specific data in Table 1 you used and provide your warrant. (d.) Based on your conclusions above, how is acid strength related to pKa? Cite the specific data you used and provide your warrant. (e.) What is the trend in G˚ from acid-base reactions of H-A to H-B to H-C? Cite the specific data you used and provide your warrant. (f.) How does the direction of change in G˚ compare with the direction of change in pKa from reactions of H-A to H-B to H-C? Provide your warrant. Acid-Base Rxns & Energy Relationships-1 4 B. Exploration of Energy Changes in Acid-Base Reactions: Answer the following on the basis of the data in Table 2: 1. On Table 2 below, indicate whether there is an increase or decrease in Gibbs Free Energy for each reaction. Cite the specific data you used and provide your warrant. General pKa Reaction .. A. H2O + H + .. A Conjugate Acid H3O.. Conjugate Base pKa (pKaH) Conjugate Acid Conjugate Base -7 H-Cl Cl O O CH3 C 4.8 O O CH3 C H O O O O CH3 C CH2 C CH3 9 CH3 C CH C CH3 H2 O 15.7 OH O O CH3 C CH3 CH3 CH3 20 ~42 CH3 C CH2 CH3 CH2 Table 2: pKa Values of Selected Acids 2. Which of the acids in Table 2 is the strongest acid? Cite the specific data in Table 2 you used and provide your warrant. (Refer to acids in Table 2 using their pKas) Acid-Base Rxns & Energy Relationships-1 5 3. Which reaction in Table 2 has the largest increase in Gibbs Free Energy? Cite the specific data in Table 2 you used and provide your warrant. (Refer to reactions in Table 2 using their pKas) 4. Use the data in Table 2 and your experience with this activity to help you place the structures of each acid and its conjugate base (H-D -> Dand H-E -> E-) on the lines in the Free Energy Diagram below that best illustrates the relative G˚ between the acid and its conjugate base. Cite the specific data in Table 2 you used and provide your warrant. O O CH3 CH3 C O C O H DH-D G O CH3 C H-E O CH3 CH3 C CH2 E- HD & H-E D- & E - Figure 1: Energy Relationships in Acid-Base Reactions 5. In the diagram above draw an arrow that represents the G˚ of each acid-base reaction. How do the lengths of these arrows compare with the relative magnitudes of the pKas of the reactions? 6. What information do the pKa values of acid-base reactions provide for judging the relative G˚s of the reactions? Cite the specific data you used and provide your warrant. 7. What information do the pKa values provide for judging the relative energies of two acid molecules such as H-D vs. H-E? Cite the specific data you used and provide your warrant. Acid-Base Rxns & Energy Relationships-1 6