Cell Transport Review
advertisement

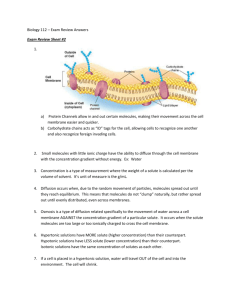
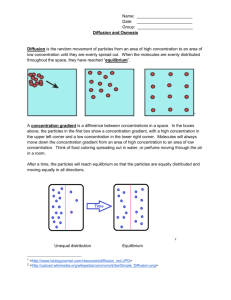
CELLULAR TRANSPORT REVIEW Name: ______________________________ Biology Date: _______________ Period: _____ Label the following: A. B. C. B. G. D. E. F. Fill in the blank 1. The process of diffusion causes molecules to move from (low to high or high to low) concentrations until a state of ____________________ is reached. 2. The diffusion of water is known as __________________. 3. ________________ diffusion uses proteins to bring materials into the cell from high to low concentration, requiring no cell energy. 4. Diffusion, osmosis and facilitated diffusion are all examples of _____________ transport, in which the cell does not need to use any energy. 5. During active transport molecules move from an area of ___________ concentration to an area of ____________ concentration. 6. ________________ is a form of active transport in which the cell sends materials out of the cell using vesicles, small storage structures that fuse to the cell membrane. 7. _________________ is the reverse of the process named in # 6. The cell membrane wraps around a substance to be brought into the cell forming a vesicle around it. 8. There are two types of endocytosis: __________________ which involves bringing solids or large molecules into the cell, and _________________, which deals with bringing liquids or very small molecules into the cell. 1 9. In the pictures below each “X” represents a molecule of water. In each diagram indicate which direction water will be moving (mostly in, mostly out, or equally in and out). XXXXX A. XXXXX XXXXX XX B. XXXXX XXXXXX XXXX C. 10. Look at each of the pictures below. Identify whether the picture represents a plant cell in fresh water or salt water. A. B. Multiple Choice: 1. The substance that dissolves to make a solution is called the ___________________ A. diffuser C. solute B. solvent D. concentrate 2. During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration 3. When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system has reached ____________. A. maximum concentration C. osmotic pressure B. homeostasis D. equilibrium 4. The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called ________________. A. active transport C. osmosis B. facilitated diffusion D. phagocytosis 5. Phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and exocytosis are all kinds of _______________ transport. A. active B. passive 6. Glucose enters cells most rapidly by _________________ A. diffusion B. facilitated diffusion C. ion channels D. phagocytosis 2 7. ________________ transport requires energy from ATP to move substances across membranes. A. Active B. Passive 8. A cell must expend energy to transport substances using ________________. A. diffusion D. osmosis B. facilitated diffusion E. endocytosis C. ion channels 9. White blood cells engulf, digest, and destroy invading bacteria using __________________. A. Facilitated diffusion C. phagocytosis B. pinocytosis D. osmosis 10. All of the following are kinds of passive transport EXCEPT ________________________ A. diffusion C. osmosis B. facilitated diffusion D. phagocytosis 11. Endocytosis that brings in small dissolved molecules (solutes) and fluids is called ___________________. A. pinocytosis C. facilitated diffusion B. phagocytosis D. osmosis 12. Placing an animal cell in a hypotonic solution will cause water to ______________________. A. move into the cell B. move out of the cell 13. When molecules move DOWN the concentration gradient it means they are moving from ______________ A. an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration B. an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration 14. Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide move across cell membranes using _____________________ A. endocytosis C. diffusion B. ion channels D. facilitated diffusion LOOK AT THE DIAGRAMS. The black dots represent solute molecules dissolved in water. A B 15. In which beaker is the concentration of solute the greatest? A or B 16. If the solute (dots) in this diagram is unable to pass through the dividing membrane, what will happen? A. the water level will rise on the right side of the tube B. the water level will rise on the left side of the tube C. the water level will stay equal on the two sides 3 17. Label the pictures below (isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic) A. _________________ B. __________________ C. _________________ 18. __________tonic means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. 19. __________ tonic means there is a LOWER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. 20. __________tonic means there is the SAME concentration of solute molecules outside the cell as inside. COMPARE/CONTRAST the kinds of transport Active or Passive What does it use to help? Carrier proteins? Vesicles? Needs no help? Example of substance(s) that use this kind of transport in cells DIFFUSION FACILITATED DIFFUSION OSMOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS (phagocytosis) ENDOCYTOSIS (pinocytosis) EXOCYTOSIS Any substance leaving cells 4 A Look at Cell Transport Examine the diagram below. The letters represent molecules. The relative size of the molecules is represented by the size of the letter. The concentrations of molecules on each side of the membrane can be determined by the numbers of each letter on each side of the membrane. Arrows show the direction the molecules travel as they cross the membrane. 1. What type of transport is demonstrated by molecule a? Explain how you know. Include anything else that you know about this process. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What type of transport is demonstrated by molecule B? Explain how you know. Include anything else that you know about this process. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What type of transport is demonstrated by molecule C? Explain in detail how molecule C could cross the membrane. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5 The diagram below shows molecules represented by X both outside and inside of a cell. 1. A process that would result in the movement of these molecules out of a cell requires the use of A. DNA B. ATP C. antigens D. antibodies Use the diagram on the right to answer questions 2 and 3. Starch turns blue black in the presence of a starch indicator such as iodine. Dialysis tubing tied at both ends and containing starch solution is placed in a beaker of water. The yellowish brown starch indicator (iodine) is then added to the water. 2. What will the solutions in the beaker and the tubing look like after 20 minutes? A. The indicator solution in the beaker will be blue black and the starch solution in the tubing will not change color. B. The starch solution in the tubing will be blue black and the indicator solution in the beaker will not change color. C. Neither the indicator solution nor the starch solution will be blue black. D. Both the indicator solution and the starch solution will be blue black. 3. This laboratory setup would most likely be used to demonstrate the process of A. diffusion C. replication B. active transport D. cellular respiration 4. Two molecules, A and B and their distribution inside and outside of a cell are represented in the diagram to the right. State one possible reason why molecule A could diffuse across the membrane of the cell but molecule B could not. 5. Some animals can produce a potassium ion concentration inside their cells that is 20 times greater than that of their environment. The ion concentration gradient is maintained by the plasma membrane. Explain the process that occurs as the cell produces the ion concentration gradient. 6