File
advertisement

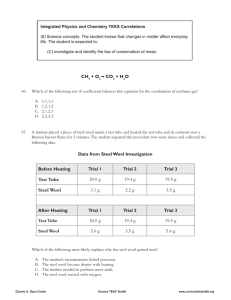
Print First and Last Name: Date: Class: A chemical reaction is indicated by any of the following: color change, energy change, odor change, bubbles formed or precipitate formed. Define “chemical properties.” Chemical properties describe the chemical reactions a substance undergoes. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS The reactions you will predict based on your knowledge of the organization of the periodic table in order are: 1. sodium + water 2. magnesium + water 3. potassium + water 4. calcium + water Groups or families are in vertical columns on the periodic table. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties, that is, they undergo similar reactions. This allows us to use the periodic table to make predictions. Example Will lithium react with water? Lithium, sodium and potassium are found in the same group on the periodic table. We can predict lithium will react with water, just as sodium and potassium. Metallic elements increase in reactivity as we go down the table. Sodium is less reactive than potassium. Based on its position, we can predict that lithium will be even less reactive than sodium. Check your understanding of this segment by completing the following. In which of these reactions are you more likely to observe flames? Why? cesium + water or beryllium + water Why do sodium and potassium metal need to be stored in oil? Hydrogen is one product of the reaction of potassium with water. What two pieces of evidence would you observe for the presence of hydrogen? CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF NON-METALS The four reactions for non-metals are: 1. 2. 3. 4. chlorine + steel wool helium + steel wool neon + steel wool iodine + steel wool Chlorine and iodine belong to the family known as the halogens. This family also includes fluorine, bromine and astatine. The halogens tend to be very reactive, and their reactivity increases as we move up the group from astatine to iodine, etc. The most reactive halogen is fluorine. Helium and neon belong to the noble gases. This family was unknown until the late 1800s because they do not participate in chemical reactions under most laboratory conditions. Check your understanding of this segment by completing the following. Name two gases from the list above that are not likely to react with hot steel wool. Which halogen would be more reactive with hot steel wool, iodine or chlorine? Why? Predict what you would observe if hot steel wool was added to fluorine.